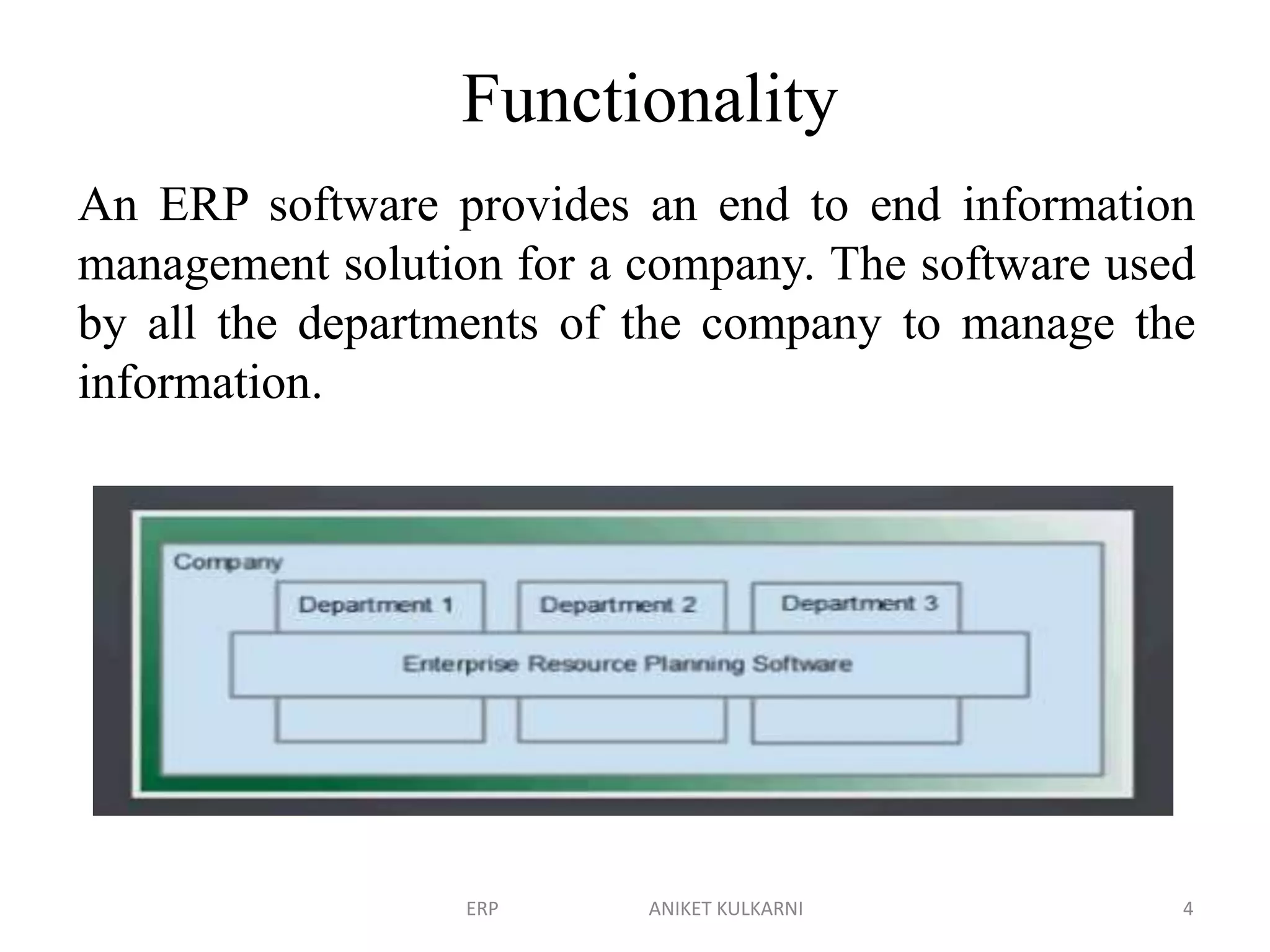
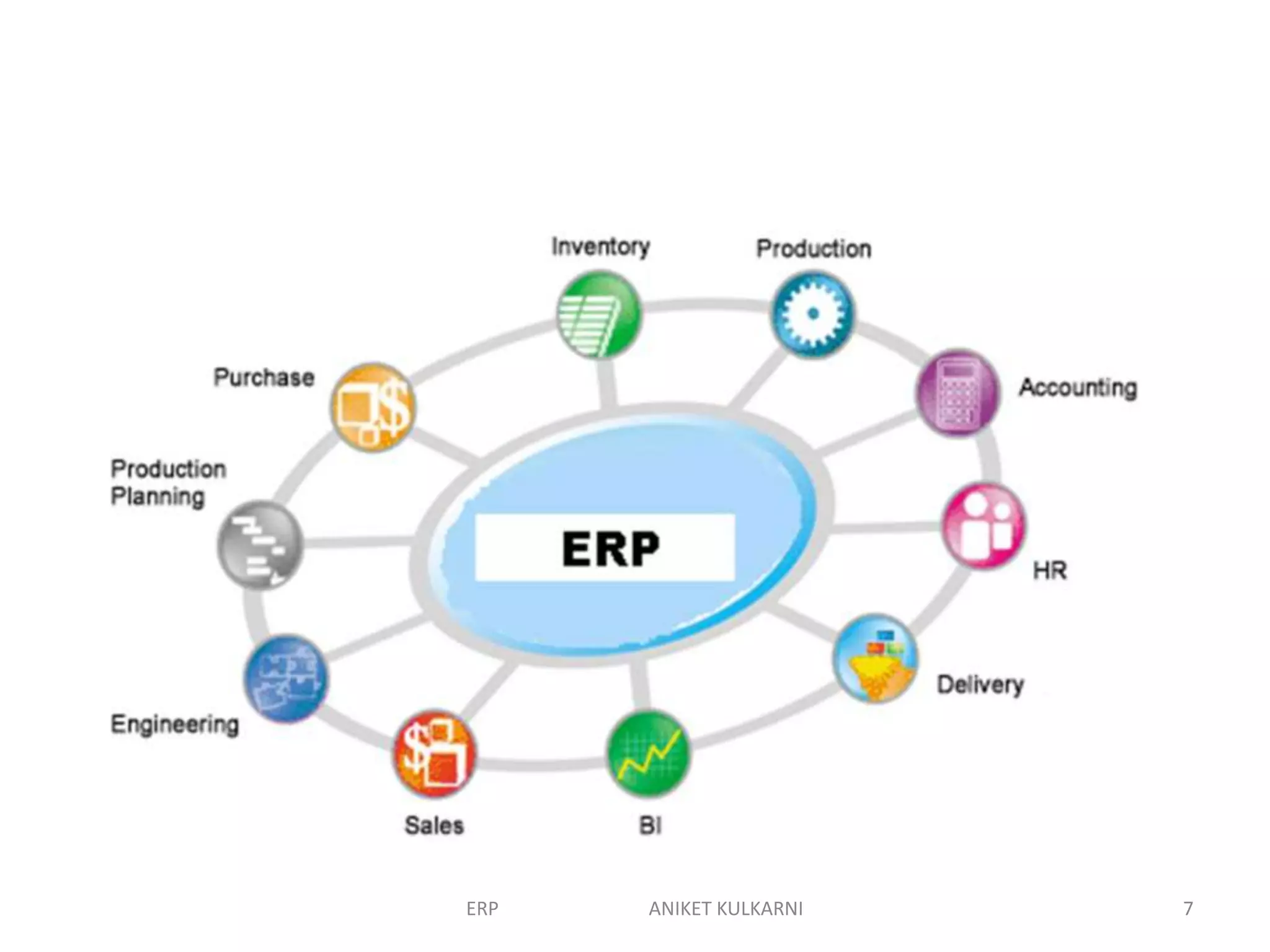
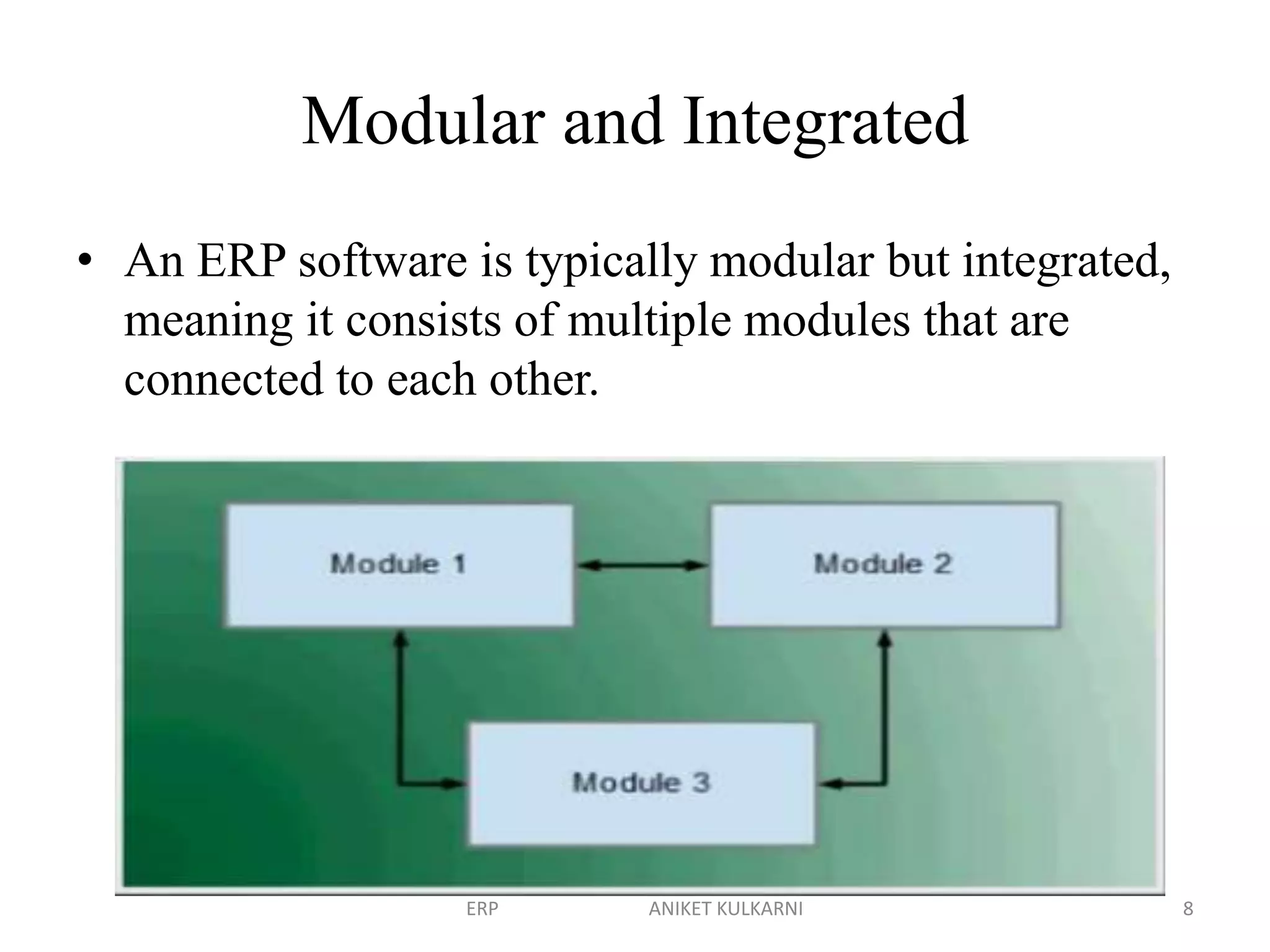
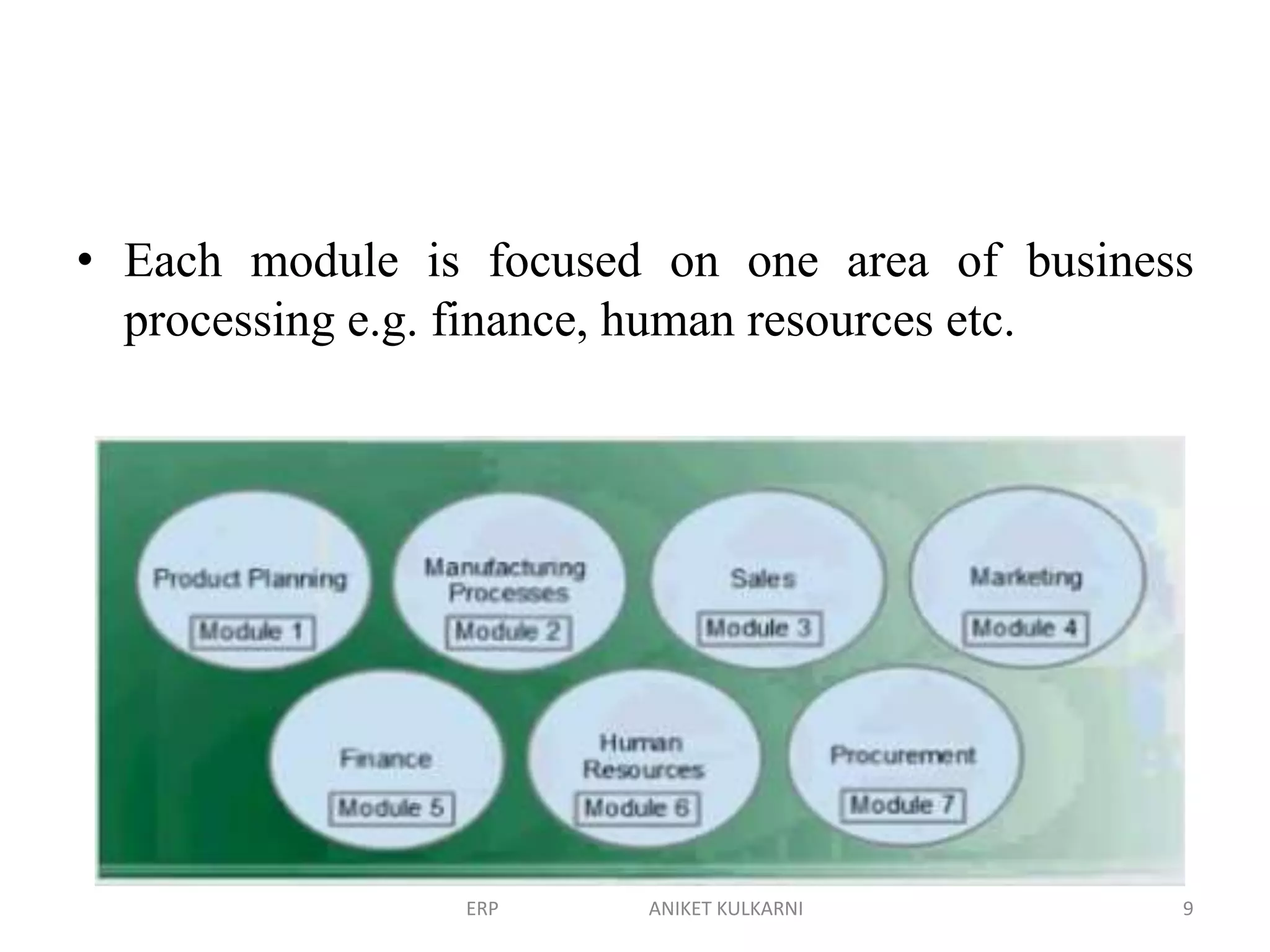
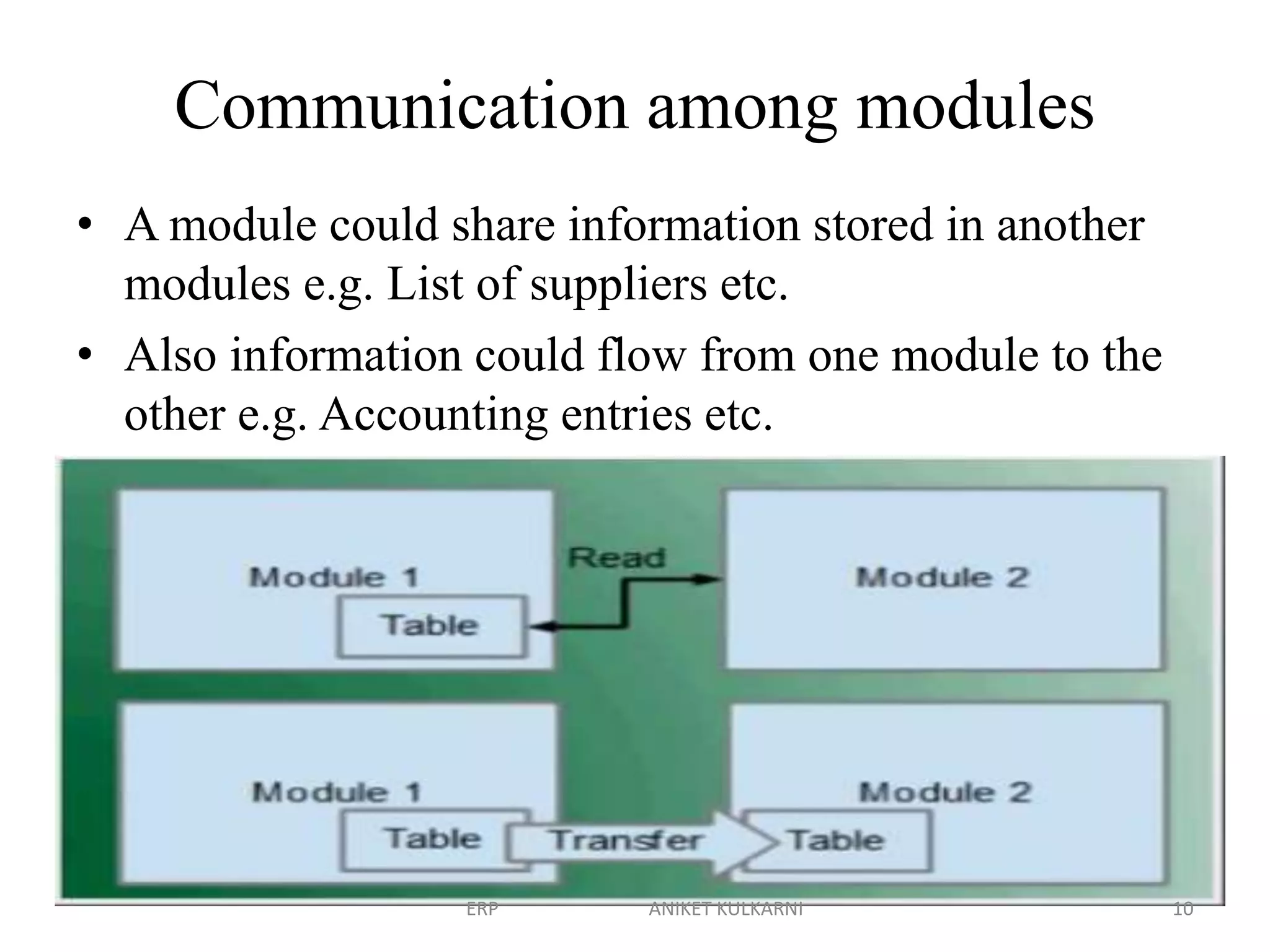
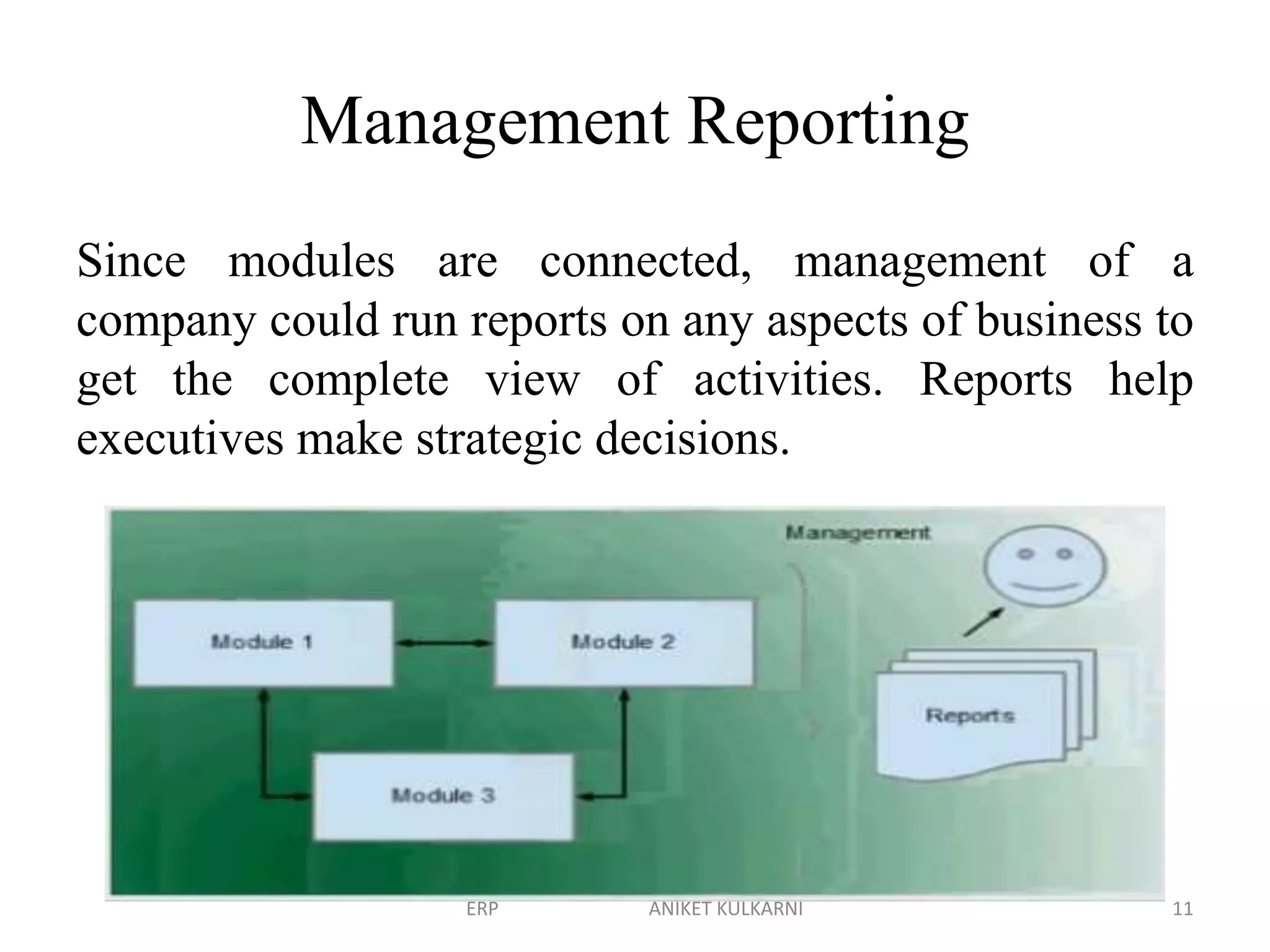
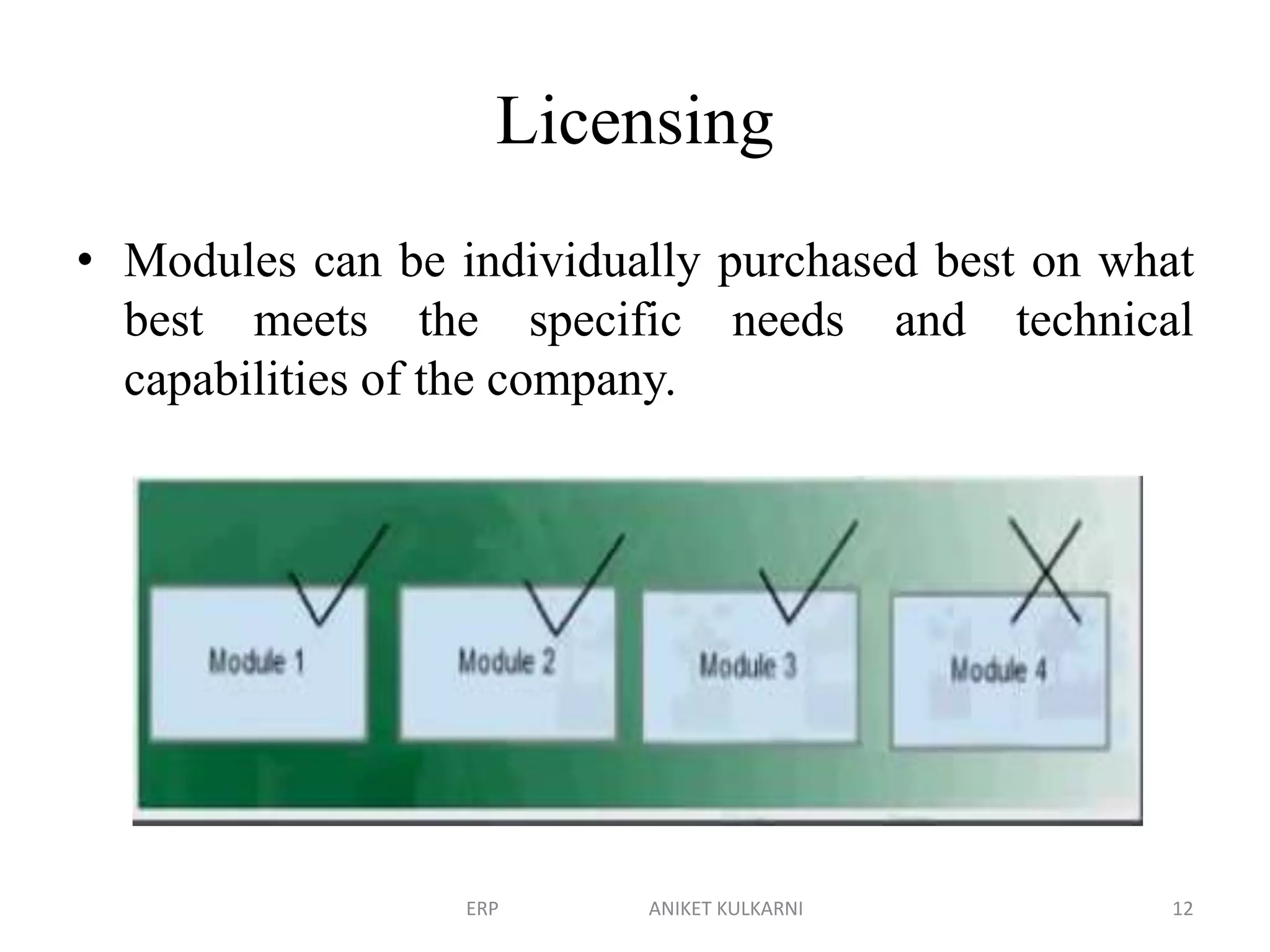
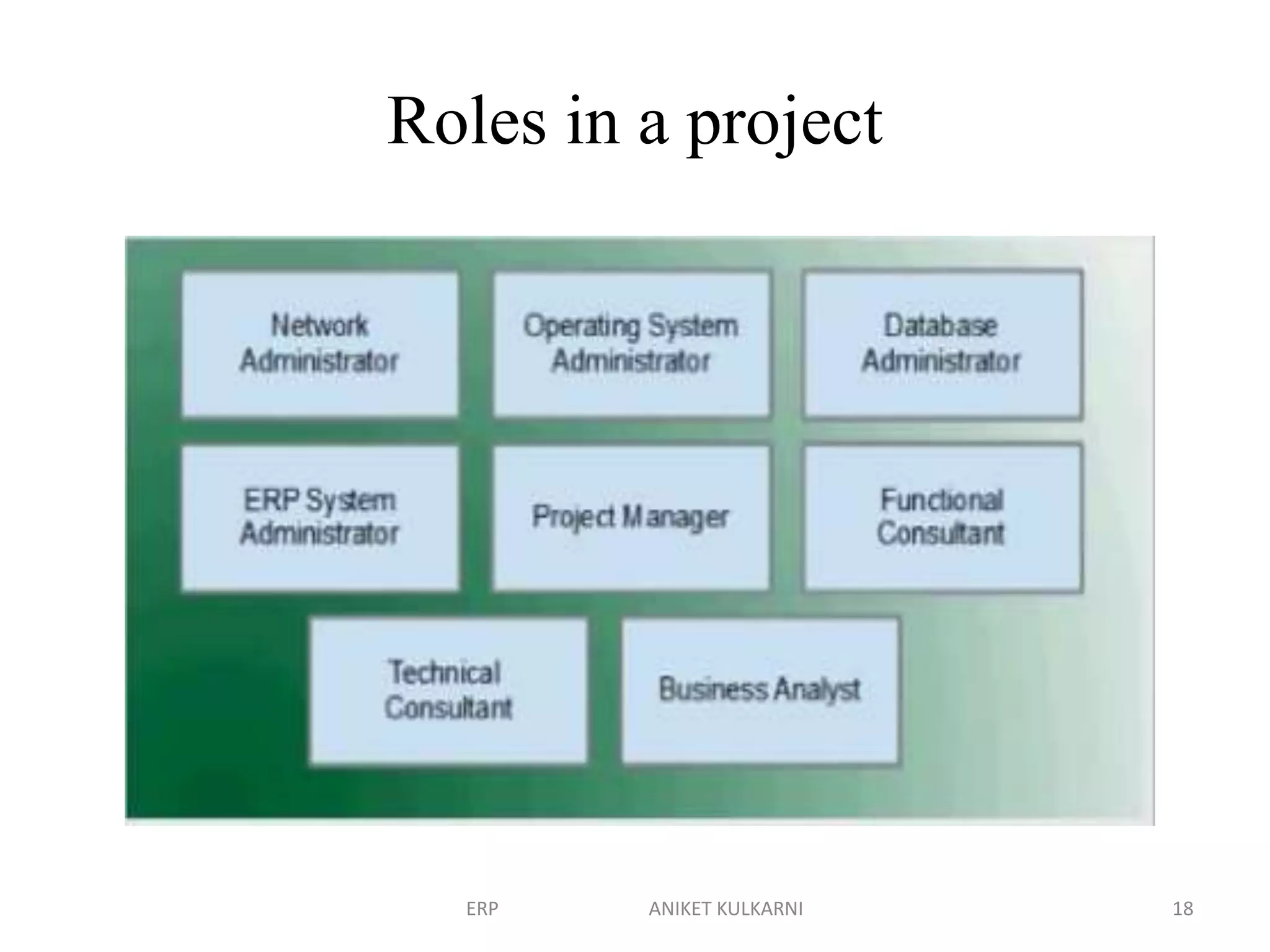
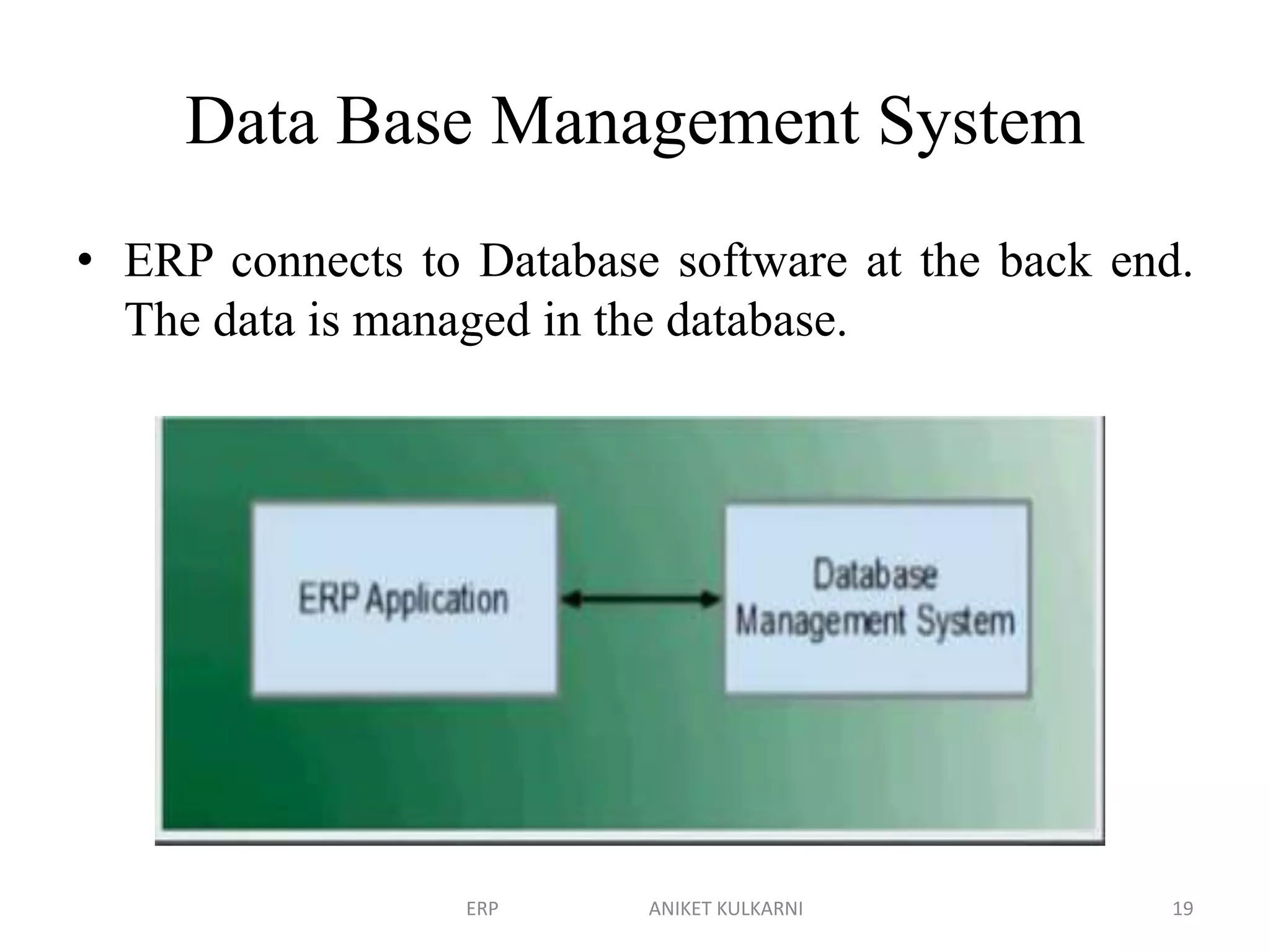
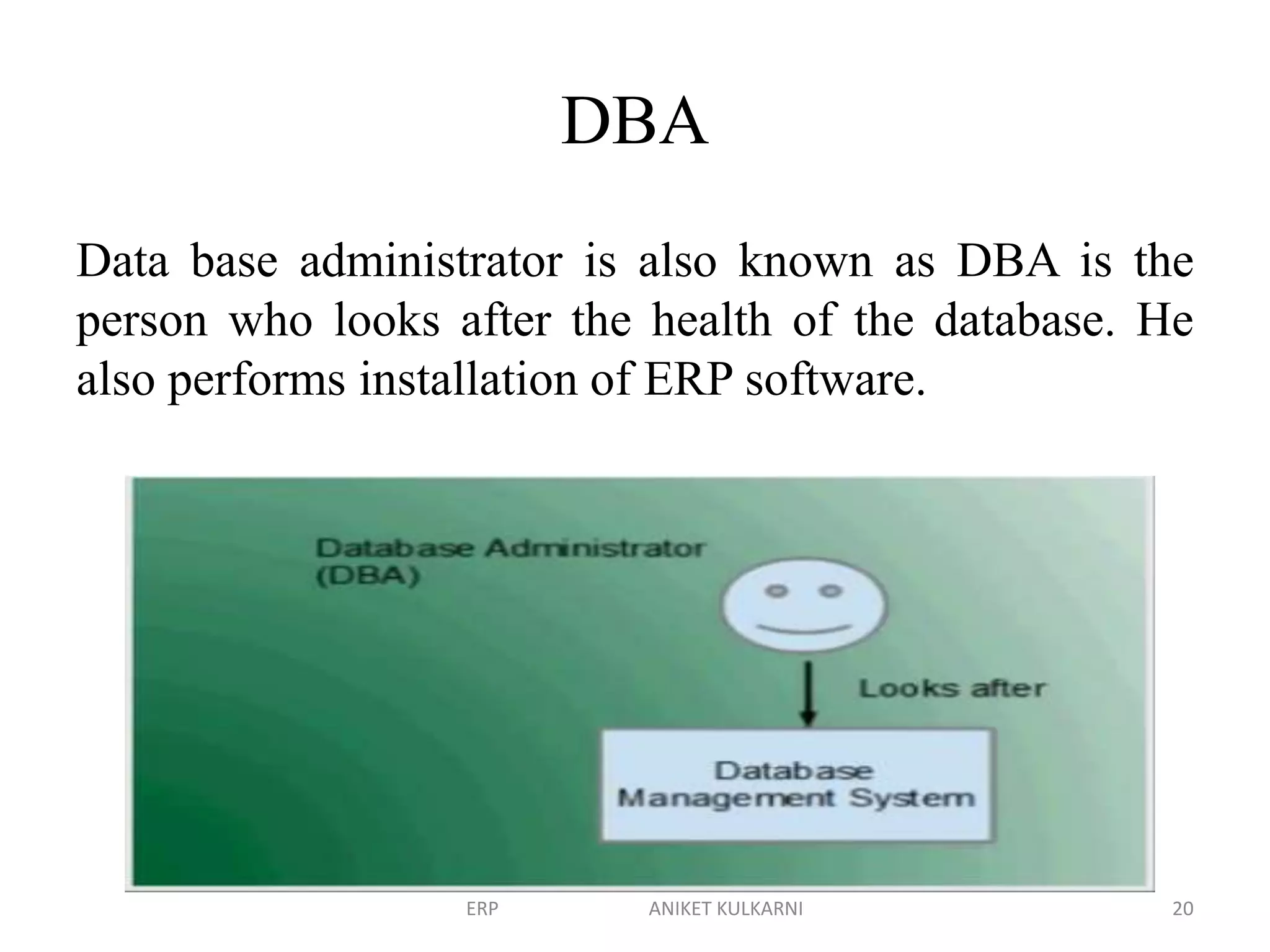
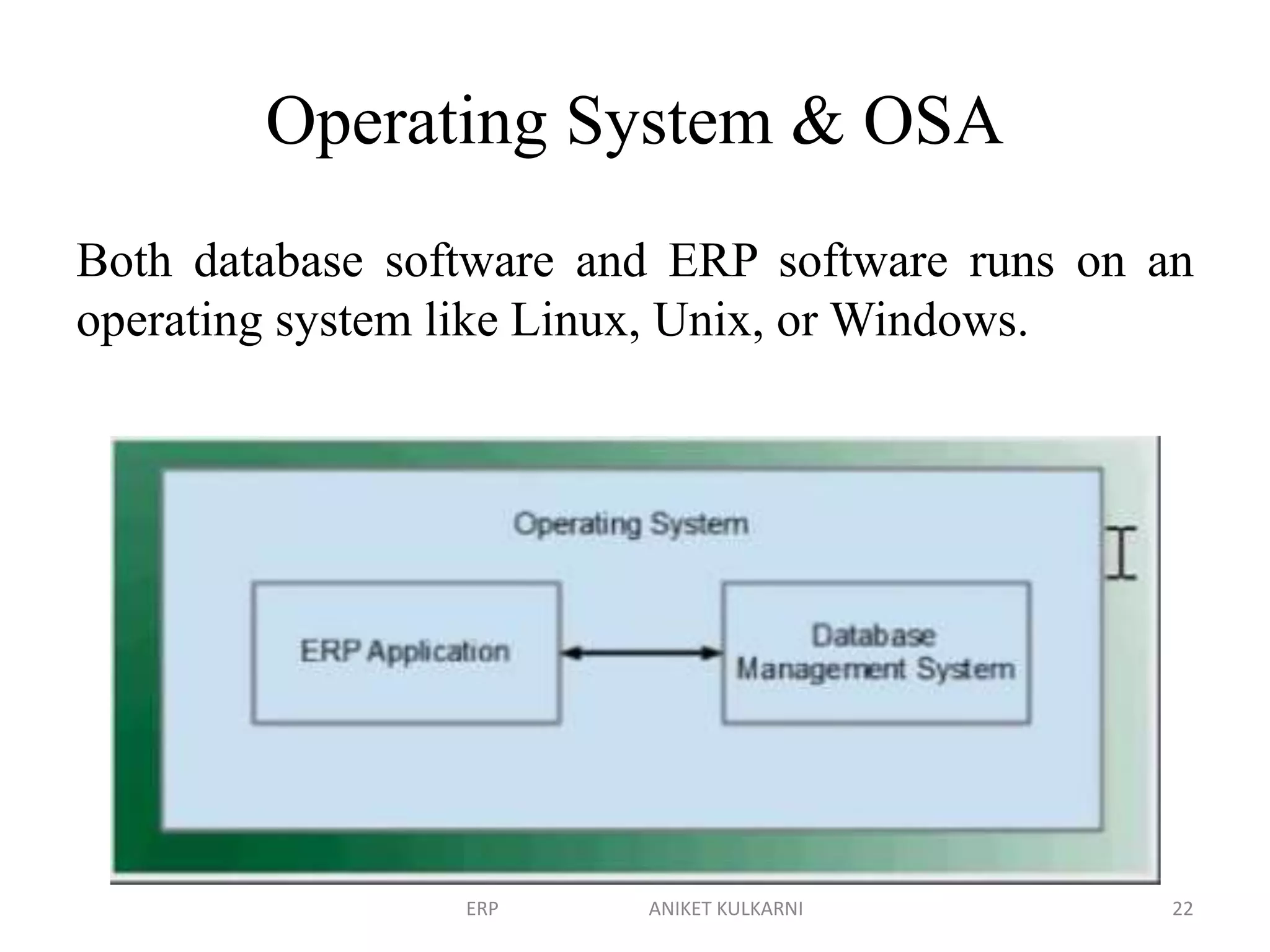
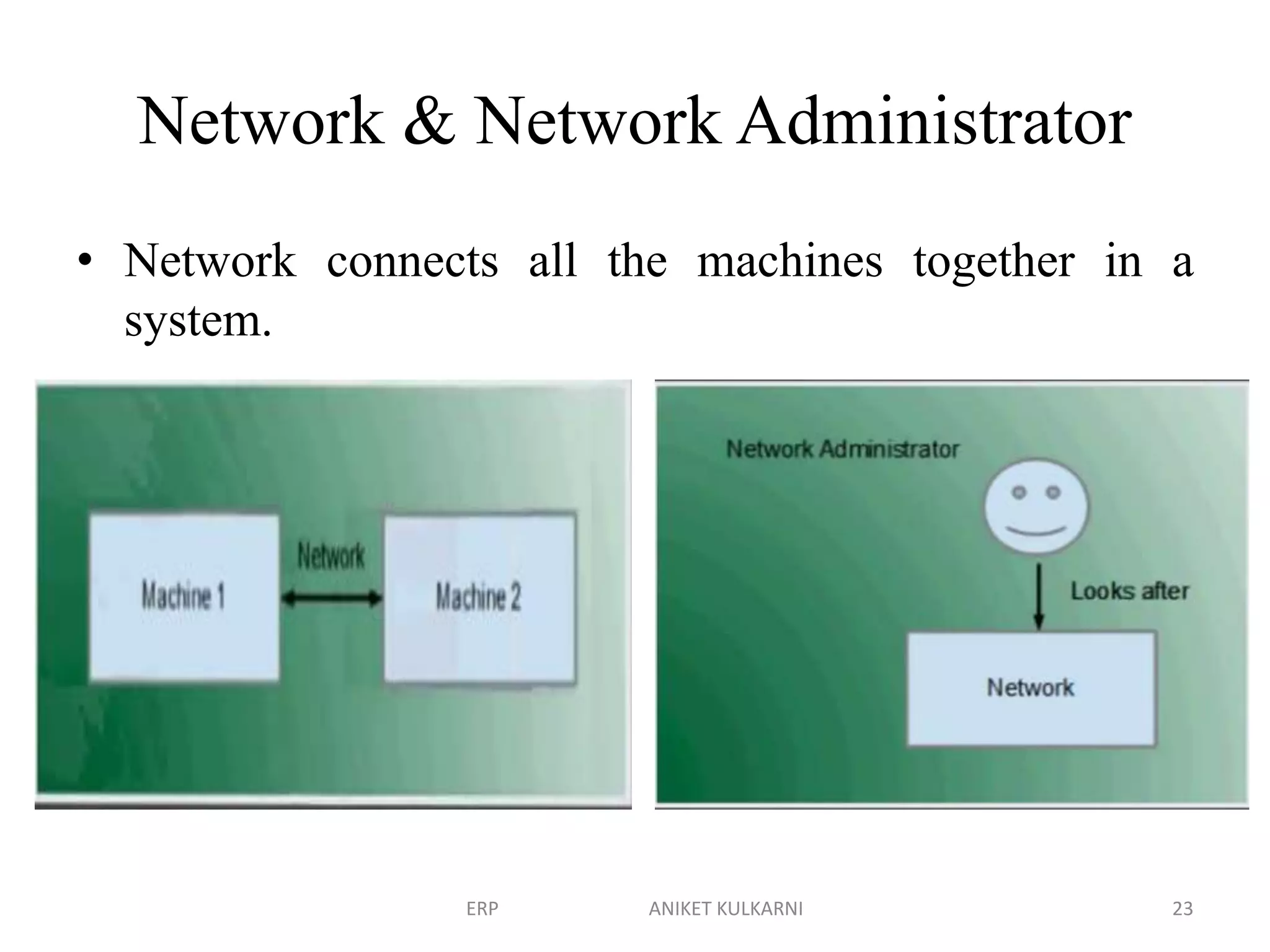
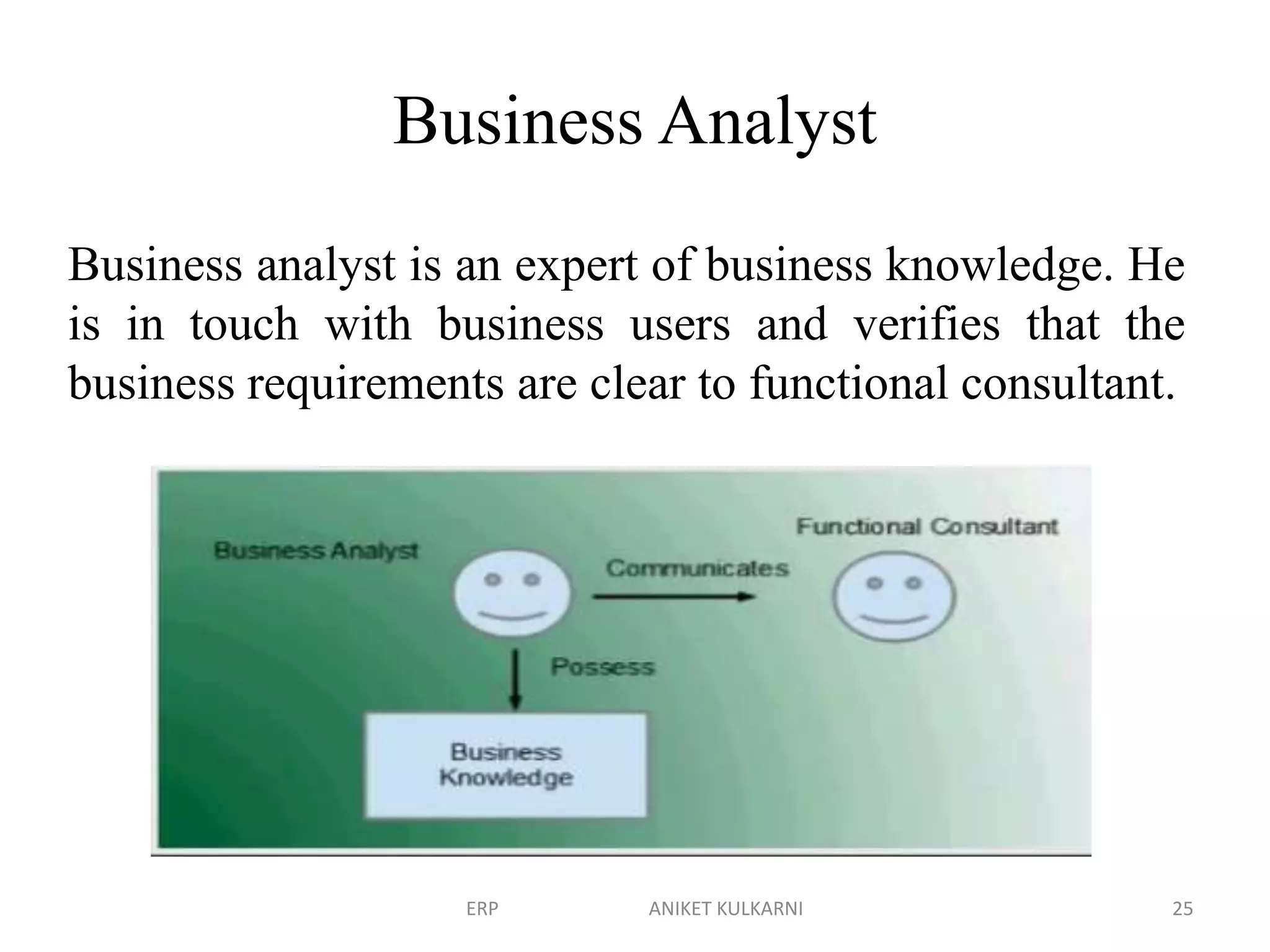
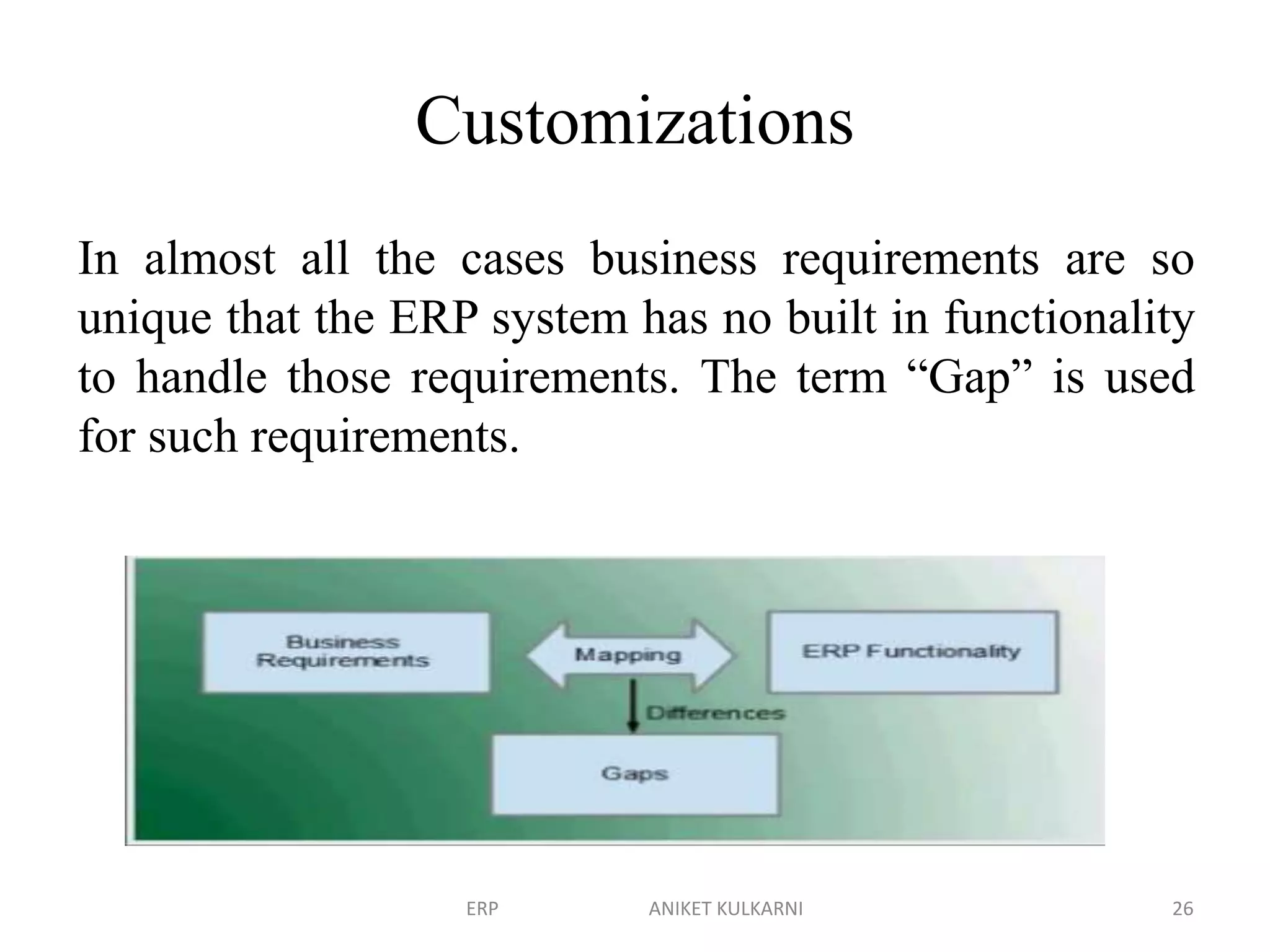
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software allows organizations to integrate business functions across departments onto a single computer system. ERP has evolved from systems focused only on inventory control in the 1960s to modern ERP packages that integrate functions like manufacturing, sales, marketing, procurement and finance. ERP implementations require configuring software modules to match business needs, filling gaps between requirements and functionality, and customizing the system. Key roles in ERP projects include functional consultants, business analysts, technical consultants and a project manager.