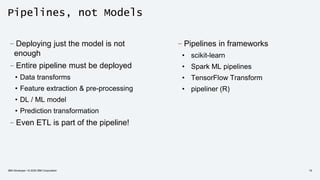
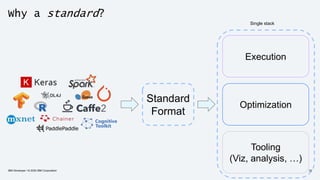
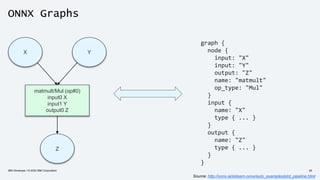
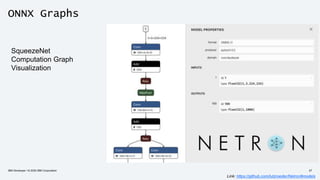
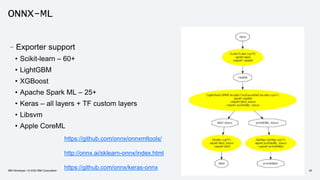
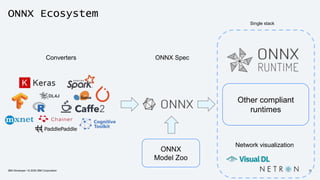
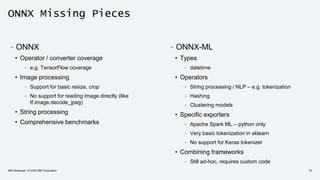
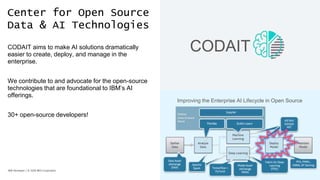
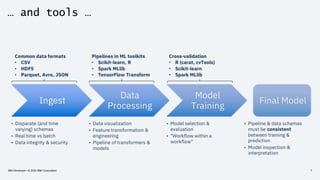
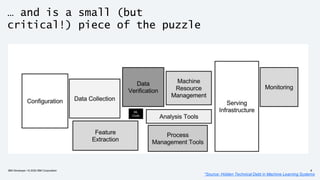
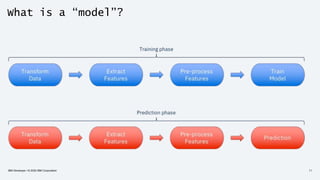
The document discusses the end-to-end deployment of deep learning models using the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format, highlighting its advantages for model serialization and interoperability across various frameworks. It emphasizes the importance of deploying entire machine learning pipelines, not just models, and addresses challenges in deployment, standardization, and team collaboration. ONNX aims to provide a performance-oriented, open standard that allows true portability and simplifies the deployment process of deep learning applications.






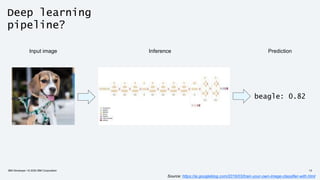
![Deep learning
pipeline!
IBM Developer / © 2020 IBM Corporation 14
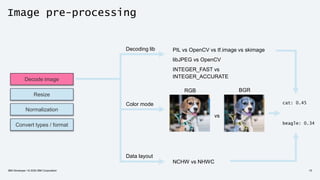
beagle: 0.82
basset: 0.09
bluetick: 0.07
...
Input image Image pre-processing Prediction
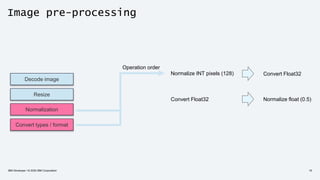
Decode image
Resize
Normalization
Convert types / format
Inference Post-processing
[0.2, 0.3, … ]
(label, prob)
Sort
Label map
PIL, OpenCV, tf.image,
…
Custom
Python
* Logos trademarks of their respective projects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onnxpipelines-deployai-mar2020-np-200601125812/85/End-to-End-Deep-Learning-Deployment-with-ONNX-14-320.jpg)
![Inference post-
processing
IBM Developer / © 2020 IBM Corporation 17
Convert to numpy array
[0.2, 0.3, … ]
(label, prob)
Sort
Label map
Custom loading label mapping / vocab / …
TF SavedModel (assets)
Keras decode_predictions
Custom code
Custom code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onnxpipelines-deployai-mar2020-np-200601125812/85/End-to-End-Deep-Learning-Deployment-with-ONNX-17-320.jpg)