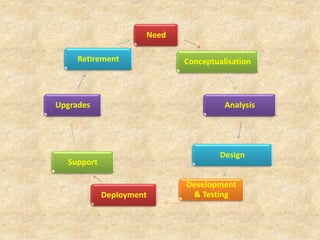
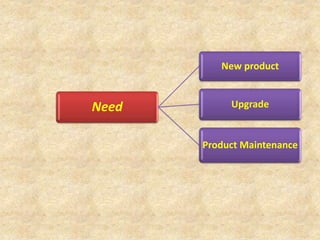
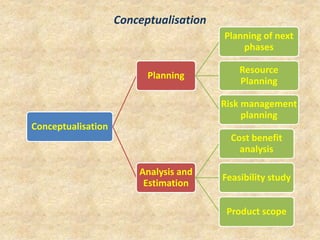
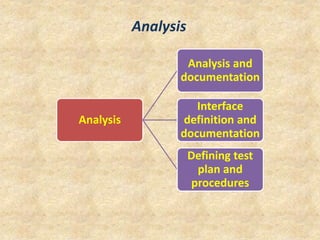
The document describes the embedded product development life cycle (EDLC) which involves multiple phases from conceptualization to retirement. It begins with identifying a need for a new or upgraded product. This is followed by conceptualization, analysis, design, development and testing, deployment, support, and upgrades. Each phase is described in detail along with its key activities such as feasibility studies, requirements analysis, interface definition, testing plans, product installation, and providing support. The life cycle concludes with retiring the product when a new technology becomes available.