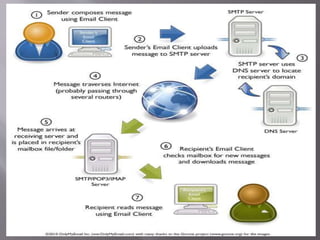
Electronic mail works by a user connecting to an SMTP server when sending a message. The SMTP server looks up the recipient's domain name using DNS to determine the destination Mail eXchanger server. It then sends the message to that server via SMTP. The receiving server stores the message and makes it available for the recipient to access via web, POP, or IMAP. Over 204 million emails are sent per minute, demonstrating how email has become indispensable in modern society for maintaining social and professional networks through asynchronous communication that is faster than regular mail but not as immediate as a phone call.