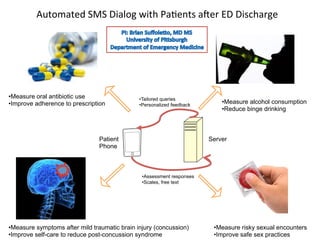
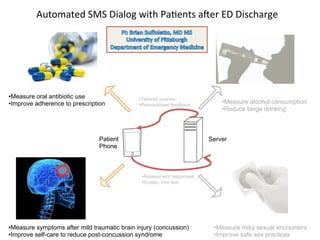
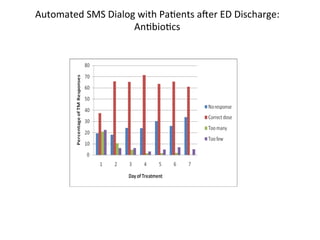
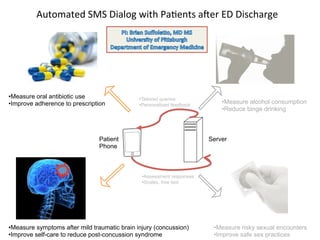
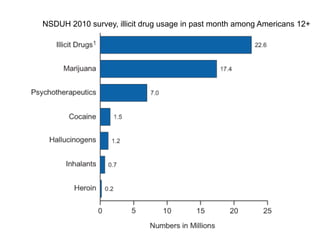
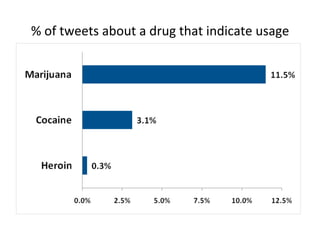
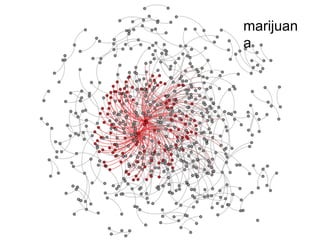
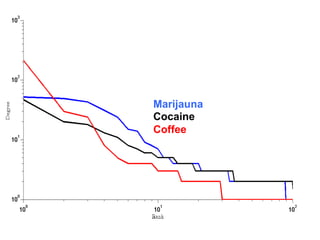
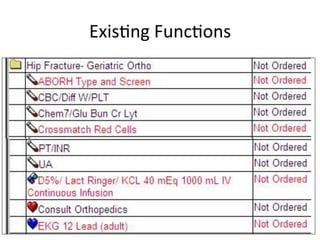
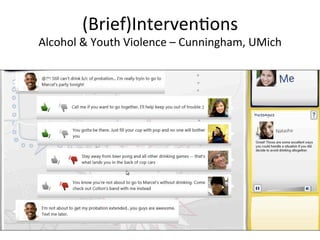
The document discusses innovations in emergency departments (EDs) and public health, highlighting the increasing use of technology, such as computers and mobile phones, to improve patient care and communication. It explores the unique challenges and patient demographics in ED settings, emphasizing the need for effective interventions and the potential of emerging technologies. Additionally, it addresses the role of social networks in enhancing emergency preparedness and response, while presenting future directions for integrating technology into emergency medicine.

























![Future
DirecKons?
[Need graphic]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emtechsessionatmed2-0-120918154900-phpapp01/85/Medicine-2-0-for-the-Emergency-Department-Public-Health-Beyond-the-Basics-30-320.jpg)