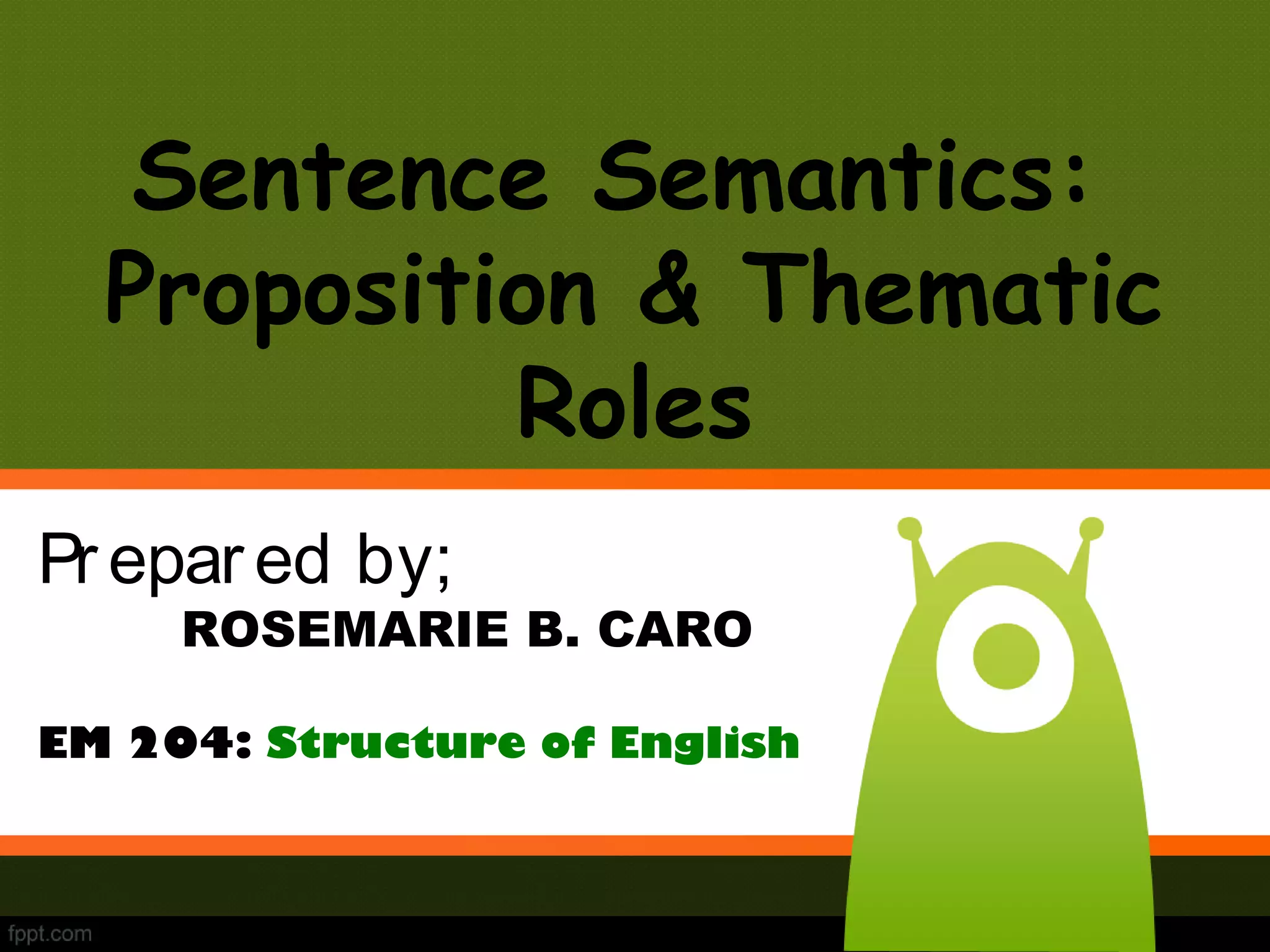
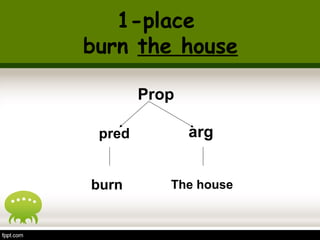
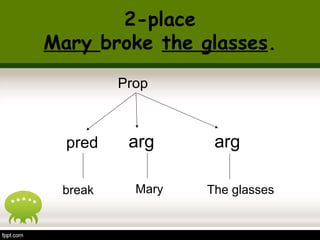
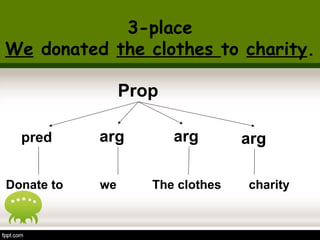
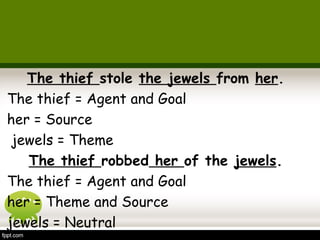
This document discusses semantics and thematic roles in sentences. It defines propositions as the semantic content of a clause without syntax or force. Propositions have predicates and arguments. Thematic roles describe the semantic relations between predicates and arguments, such as agent, experiencer, goal, and patient. Certain verbs can assign dual thematic roles to arguments. The document provides examples to illustrate different thematic roles.