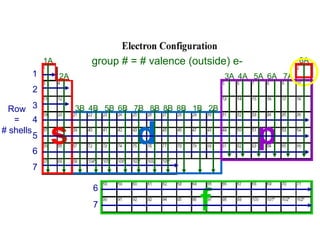
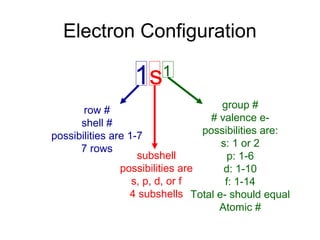
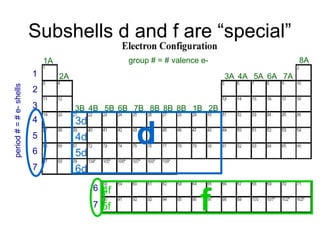
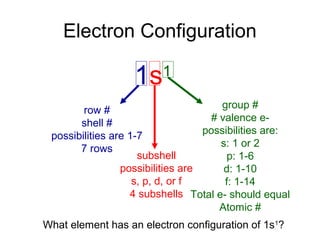
The document discusses electronic configuration, which is the distribution of electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals. It explains that electrons are arranged in shells and subshells around the nucleus, with the subshells labeled s, p, d, and f. The order that electron subshells are filled is provided, with exceptions to a simple ordering. Examples of writing the electronic configuration of different elements are given by asking a series of questions.