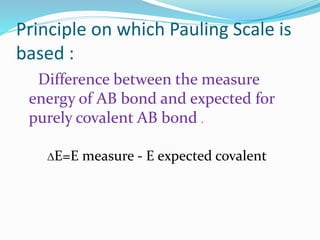
Pauling was the first to propose a scale of electronegativity in 1932 based on the difference in the measured energy of an AB bond and the expected energy of a purely covalent AB bond. Mulliken suggested an approach to electronegativity in 1934 based on ionization enthalpy and electron affinity, defining electronegativity as the arithmetic mean of ionization energy and electron affinity. Electronegativity is influenced by factors such as charge on the atom, hybridization state, ionization energy, electron affinity, and effective nuclear charge. It is used to determine bond polarity, percent ionic character, and enthalpy of formation.




![Conditions given by Pauling
If two atom A and B have same electro negativity value
than the molecules AB is bonded by purely covalent bond
.Then energy of AB covalent bond would be the mean of
energy of A2 and B2 molecules.
EA-B =(EA-A +EB-B)1/2
∆E=EA-B -[EA-A * EB-B]1/2
EA-B =[EA-A * EB-B]1/2
∆E= 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronegativity2-180412185954/85/ELECTRONEGATIVITY-6-320.jpg)
![Second Conditions
If two atoms A and B have different electro negativity .
The bond AB will no longer be purely covalent and
energy would be greater than mean of energy A2 and
B2 molecule.
EA-B>[EA-A * EB-B ]
∆E>0
This excess bond energy ∆E is known ionic covalent
resonance energy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronegativity2-180412185954/85/ELECTRONEGATIVITY-7-320.jpg)











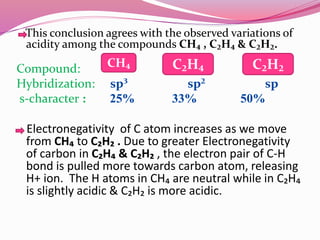
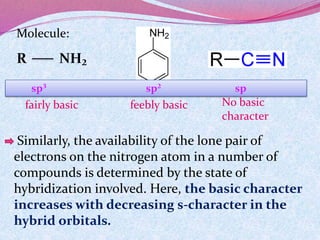


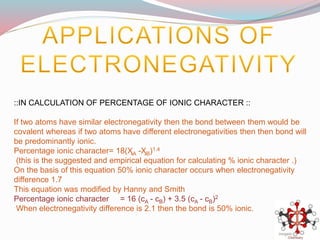
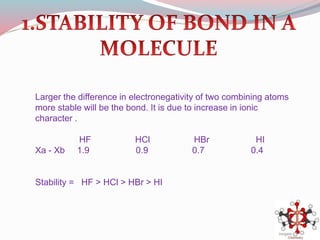


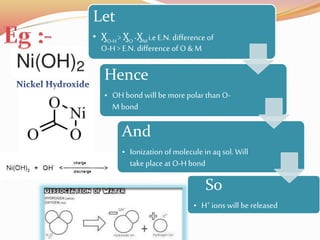

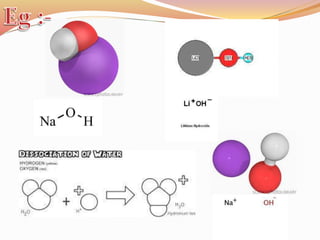
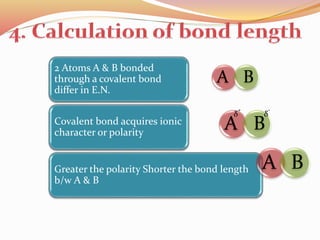
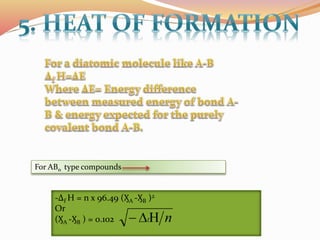
![Bond length of A & B [d(A-B) ] = rA + rB or r+ + r- or 2rA
[d(A-B) ] = rA + rB - 0.09(ӼA -ӼB)
Where rA & rB are atomic or molecular
covalent radii
rA + rB
Normal length of covalent bond b/w A & B = rA + rB
E.N.
Difference
Shortening
of bond
=0.09(ӼA -
ӼB)
A B
rA + rB - 0.09(ӼA -ӼB)
A B
Reduction in bond length leads to
more stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronegativity2-180412185954/85/ELECTRONEGATIVITY-33-320.jpg)