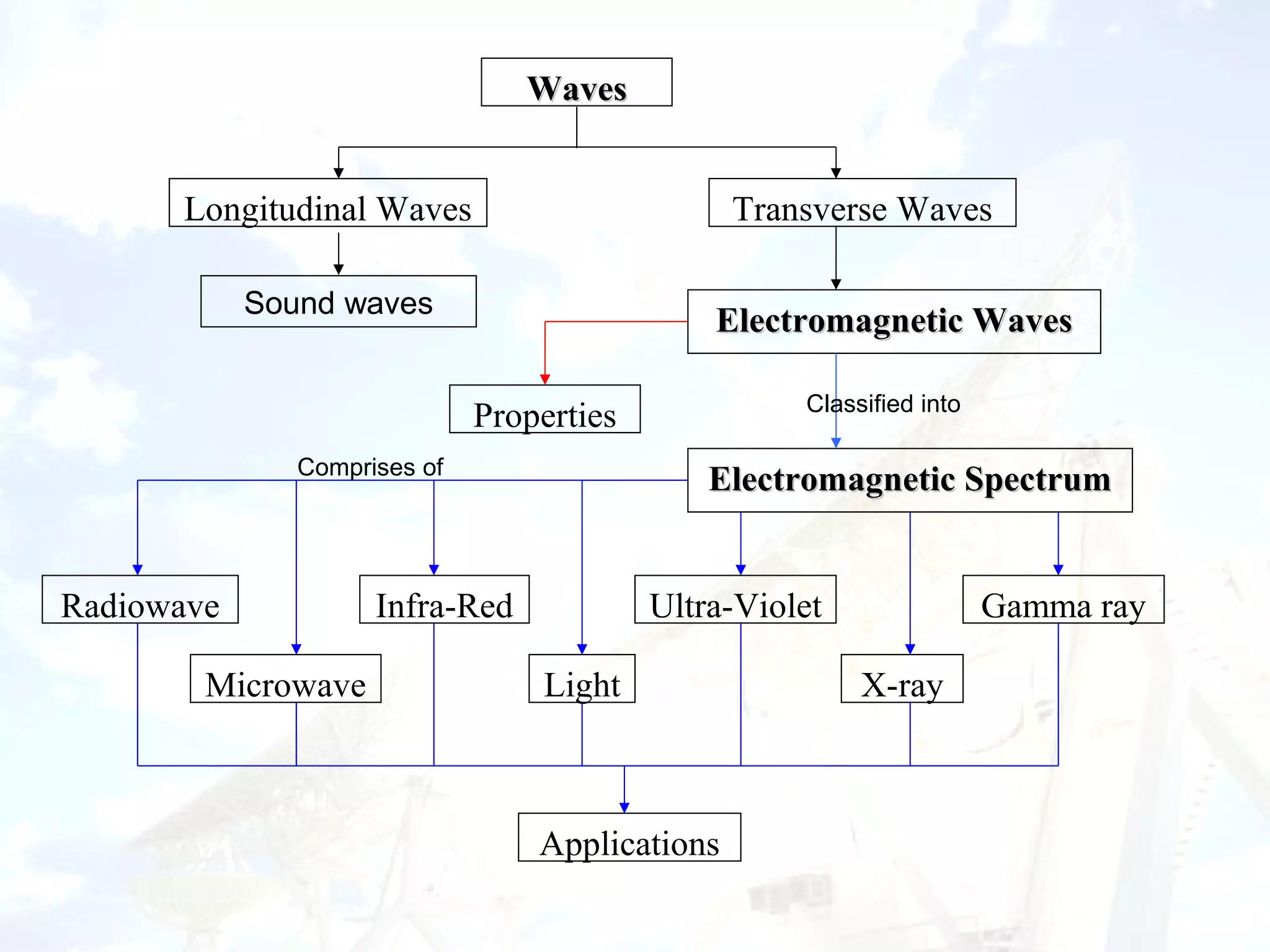
The document is a presentation about electromagnetic waves. It contains the following key points:
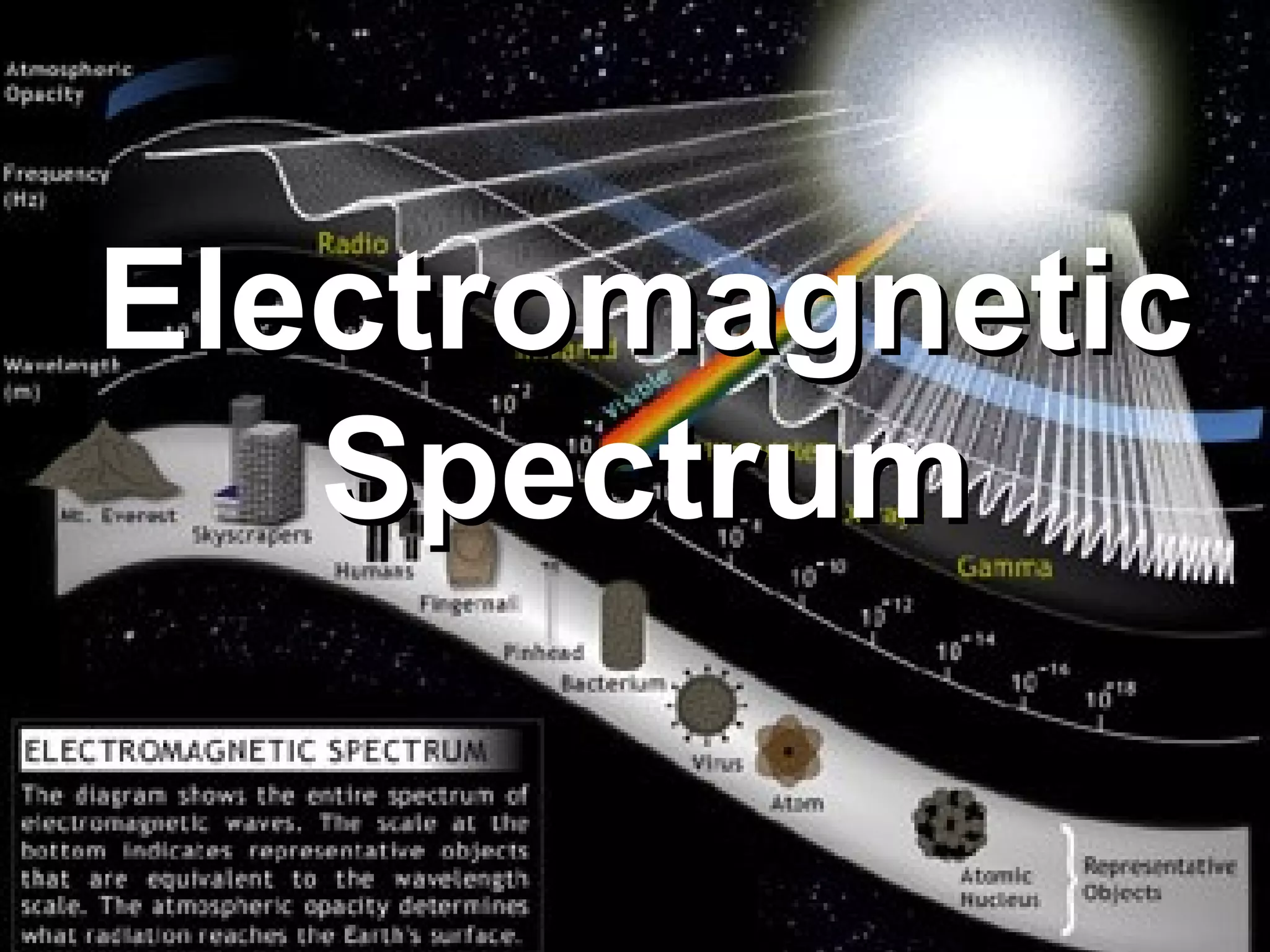
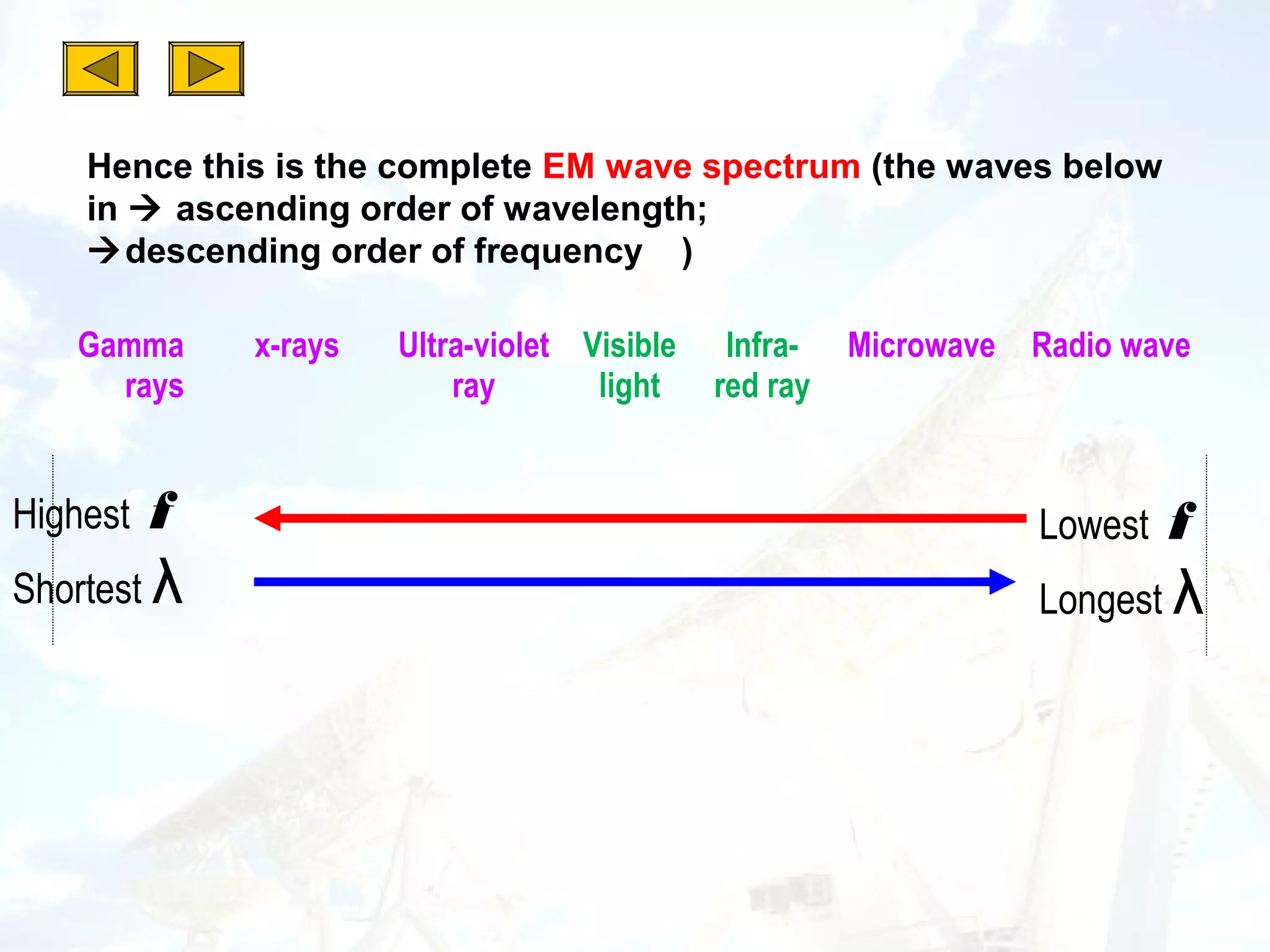
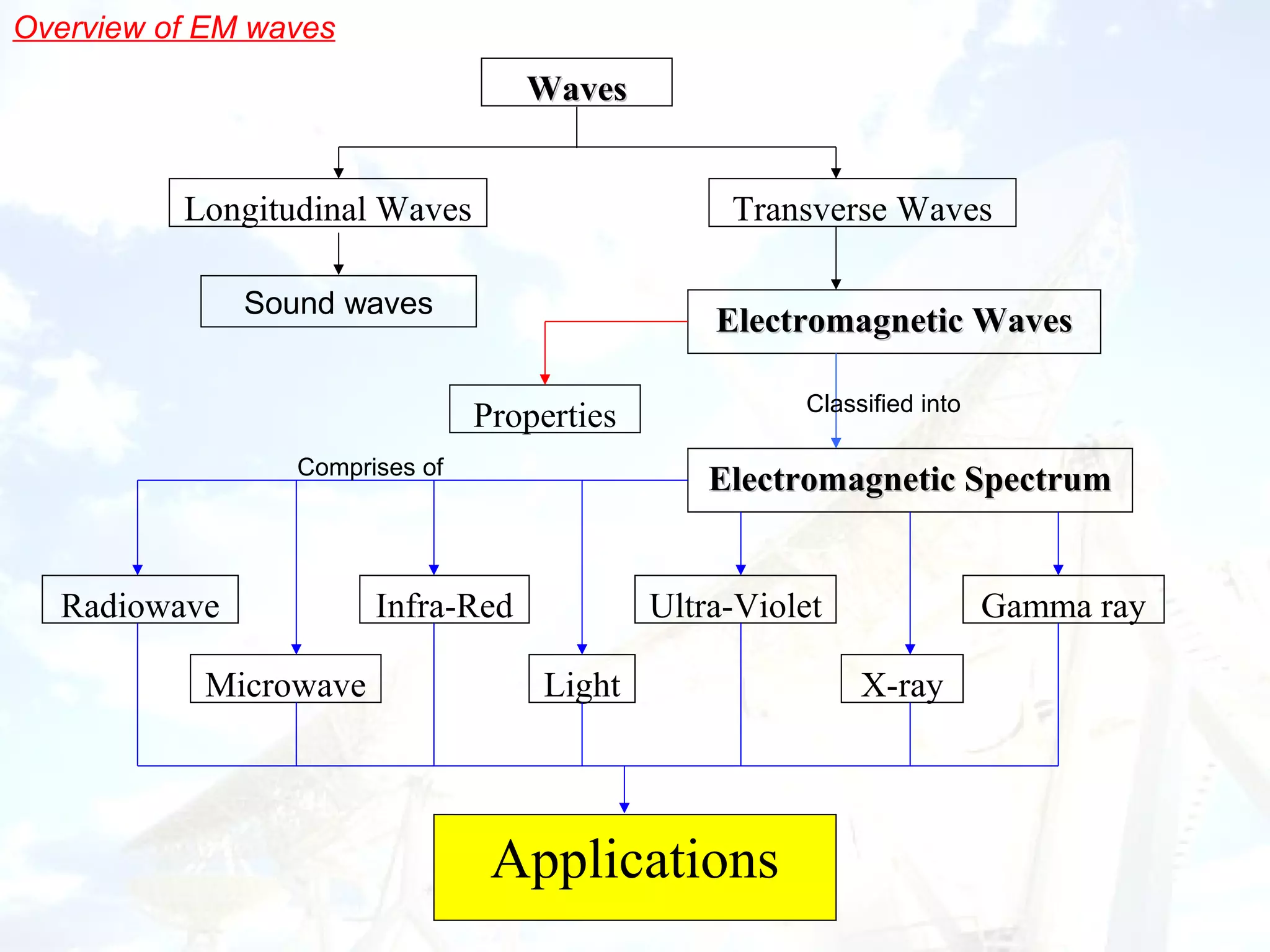
1. Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays. They are classified based on wavelength and frequency.
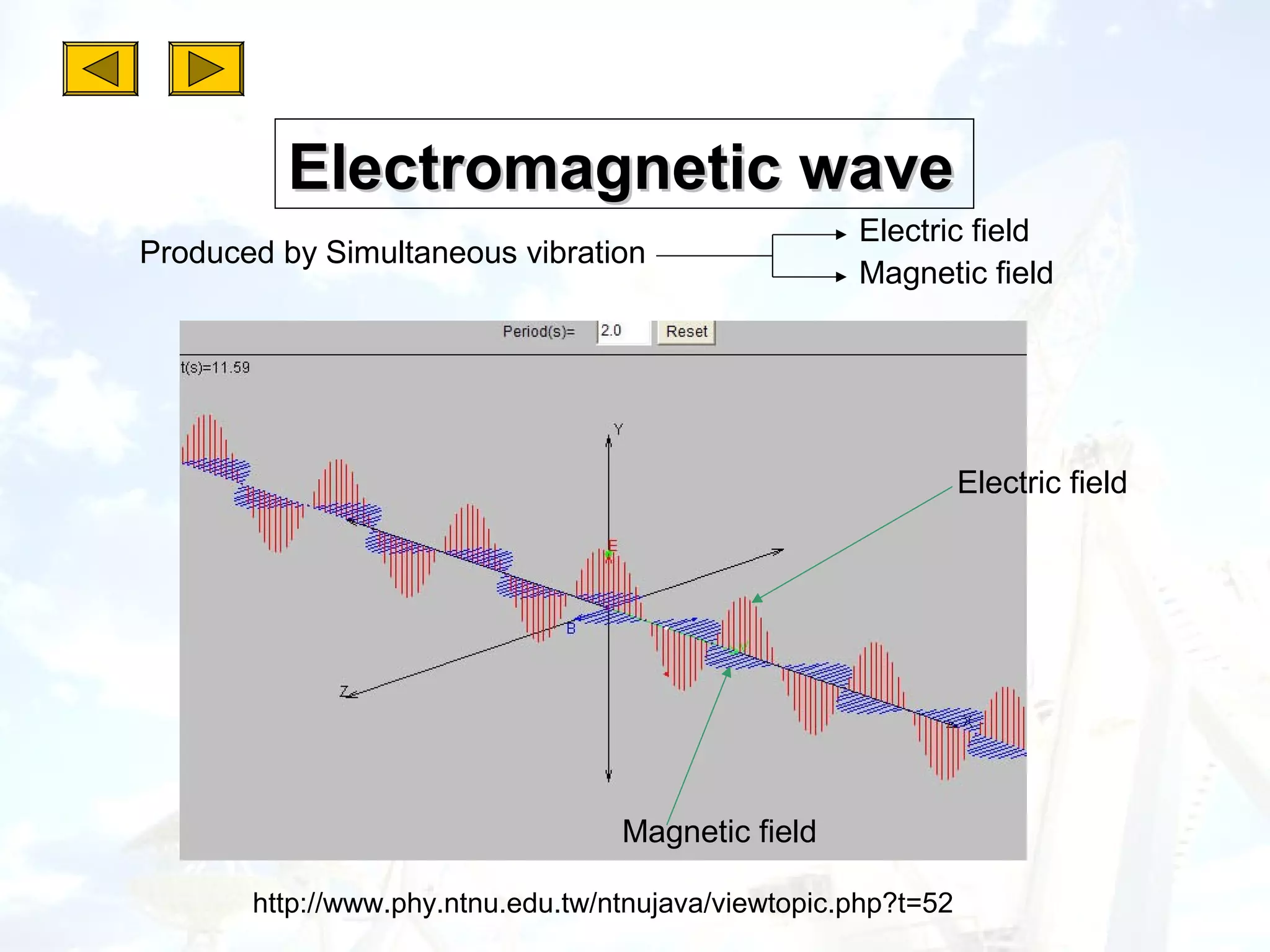
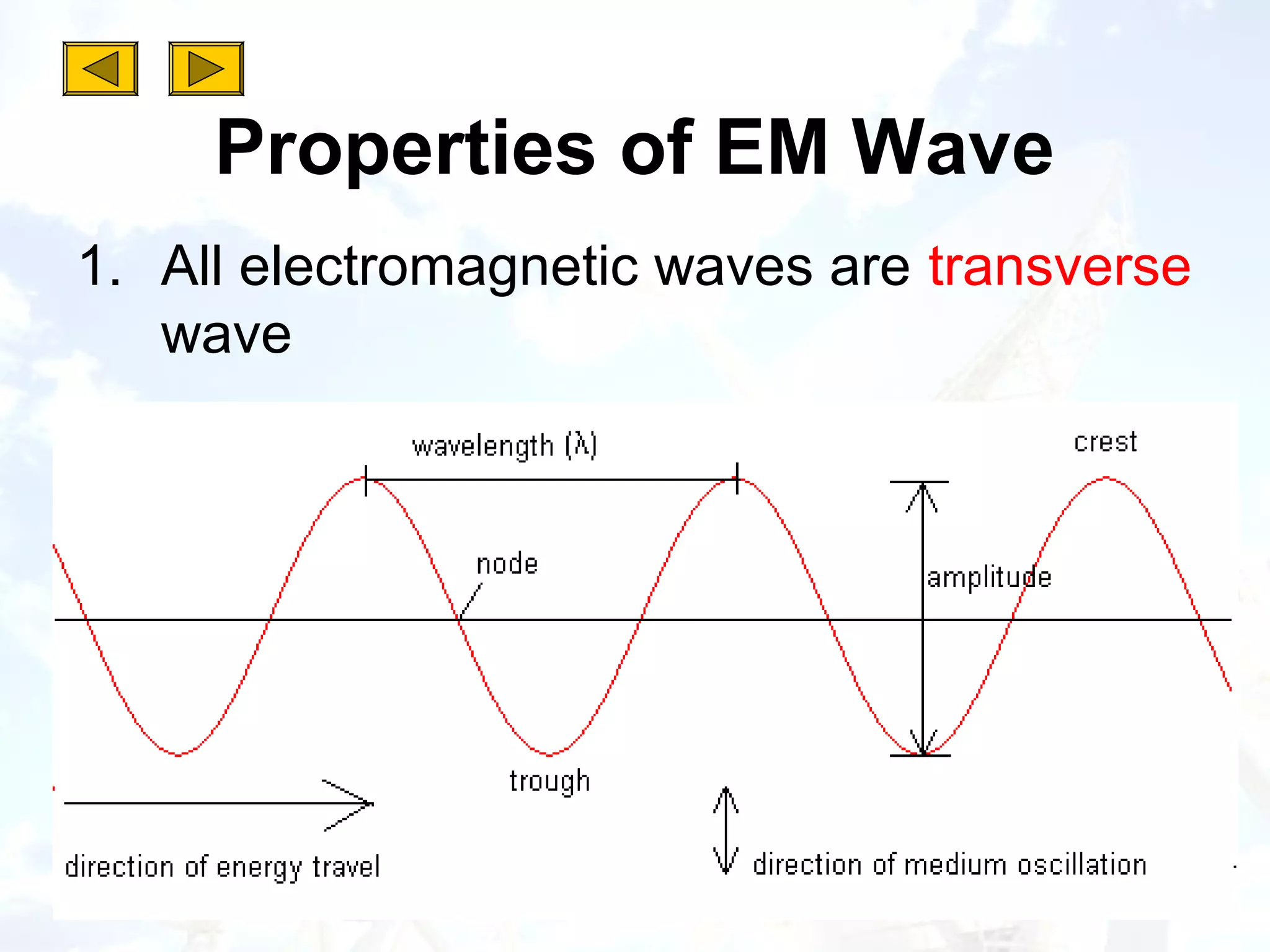
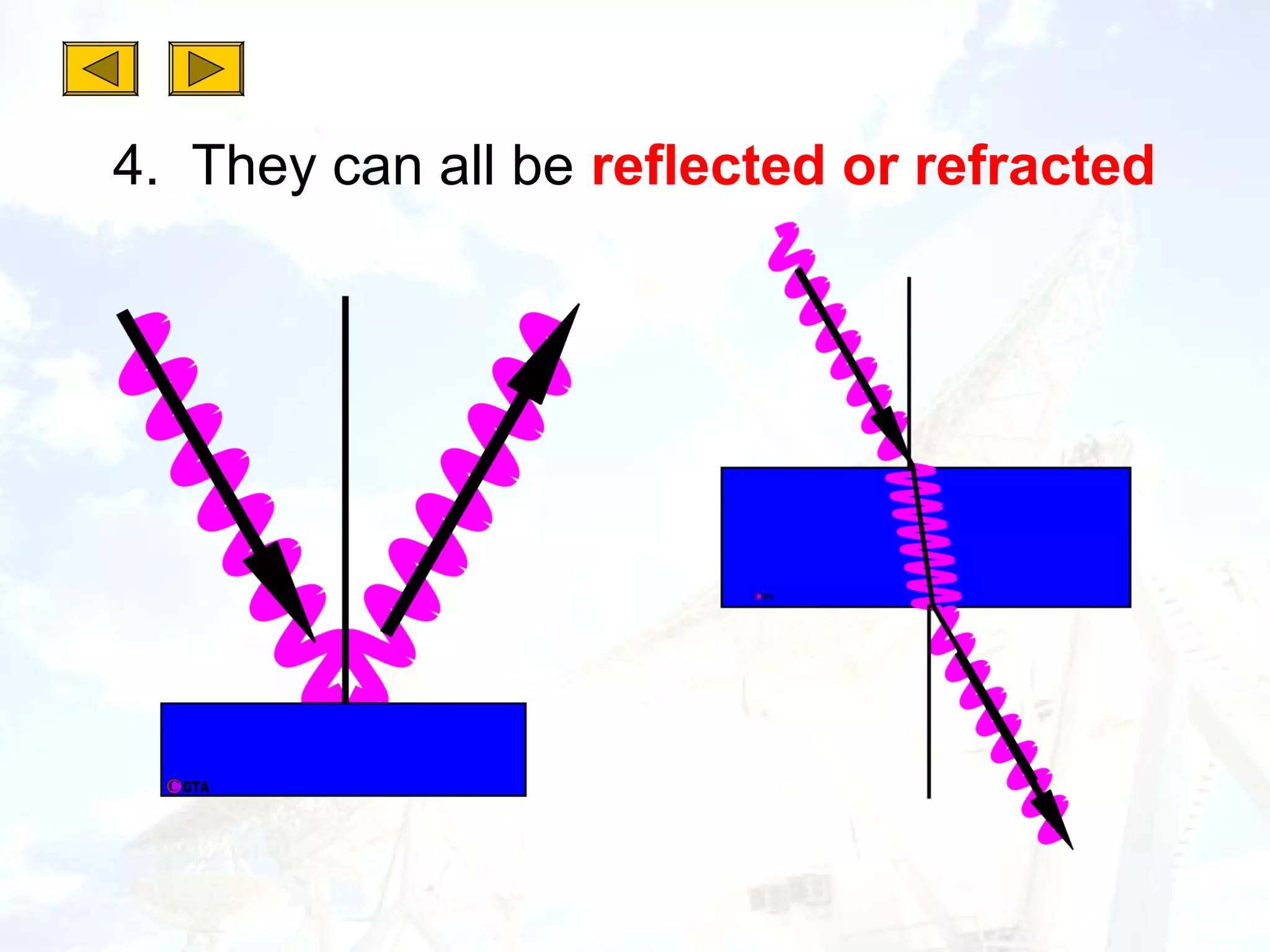
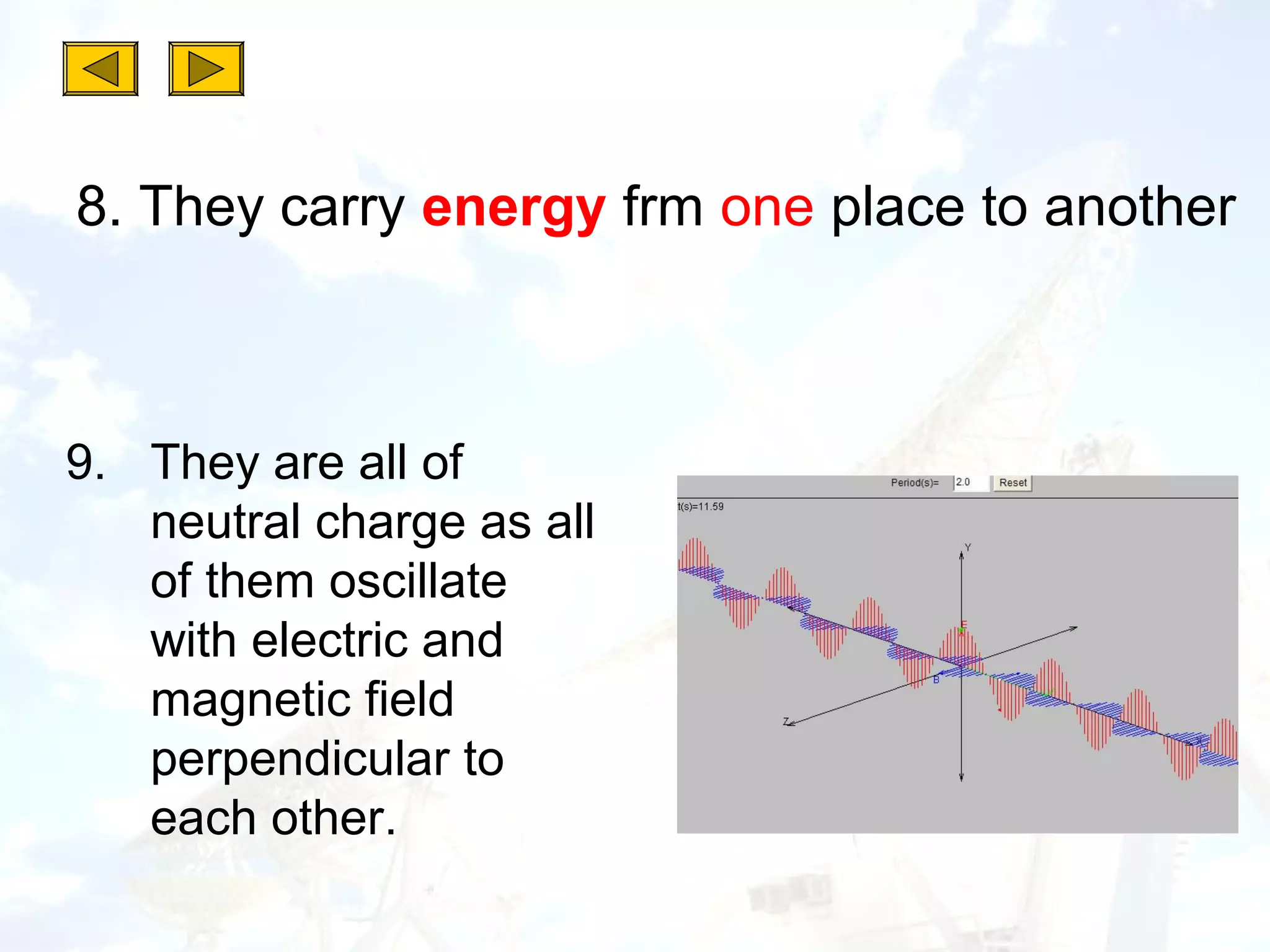
2. All electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that travel at the speed of light and can be reflected, refracted, emitted or absorbed.
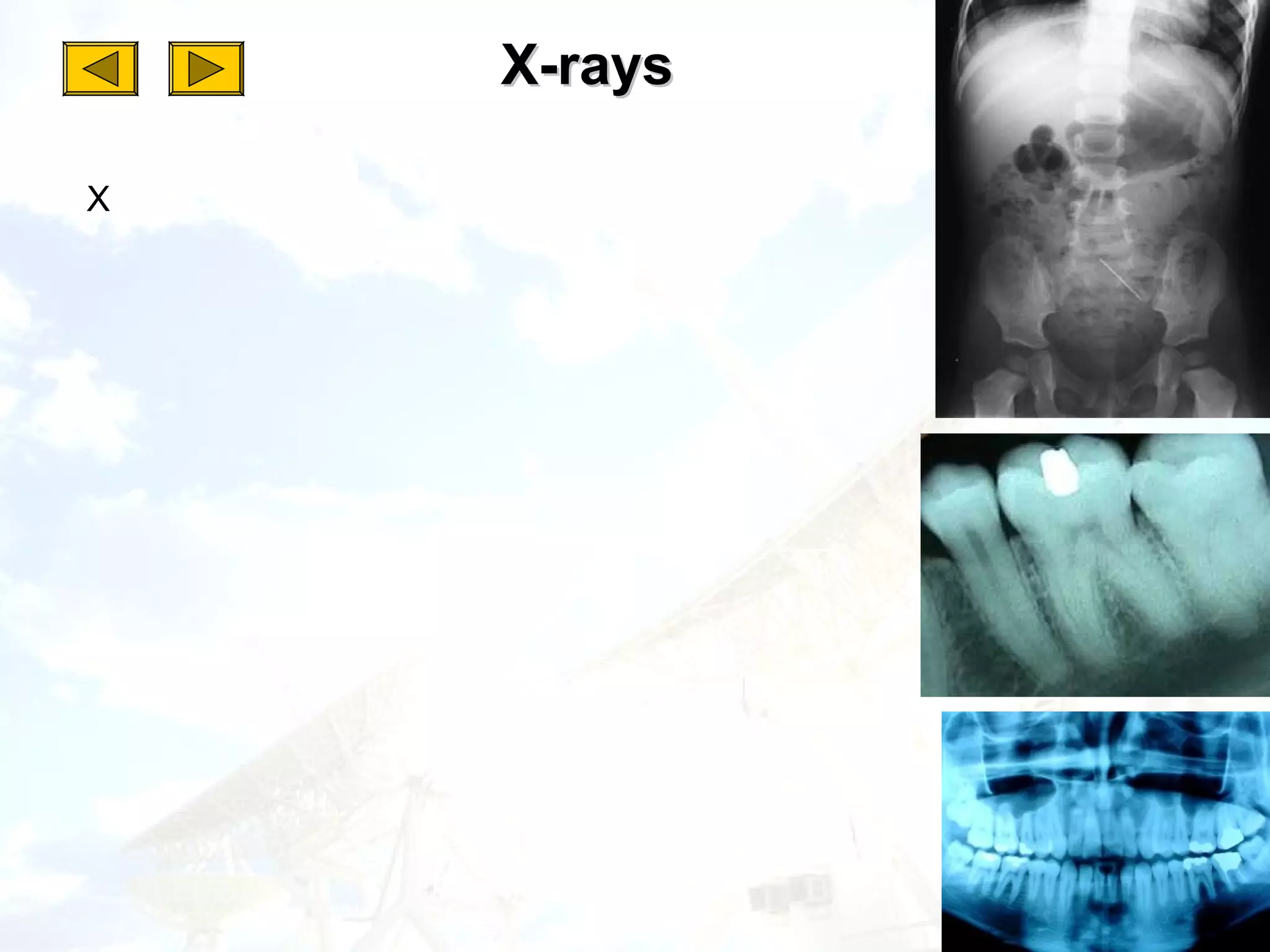
3. Different types of electromagnetic waves have various applications like radio for communication, infrared for night vision, visible light for sight, ultraviolet for sterilization, X-rays for medical imaging and gamma rays for cancer treatment.
4. Students are instructed to read the presentation, take an