Embed presentation
Downloaded 106 times
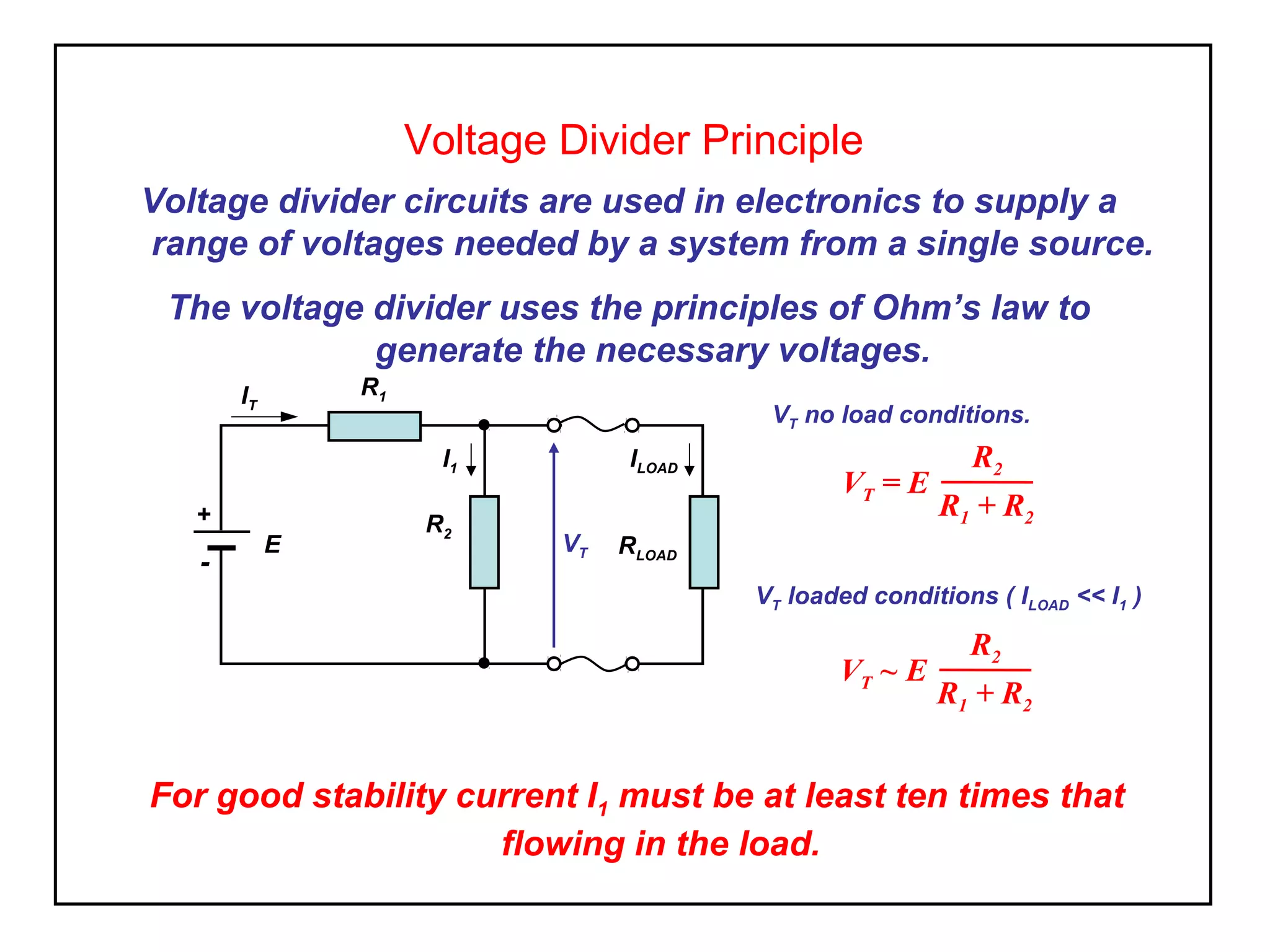
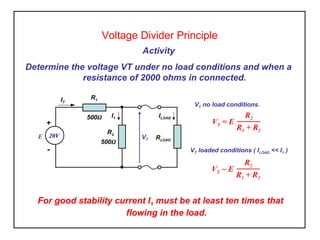
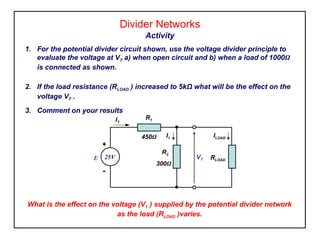
Voltage divider circuits use resistors connected in series to a power supply to generate a range of output voltages. The voltage at the output (VT) is calculated using Ohm's law and depends on the values of the two resistors (R1 and R2) and the supply voltage (E). Under no load conditions, VT equals E*(R2/(R1+R2)). When a load is connected, VT remains approximately the same as long as the load current is much less than the divider current.


