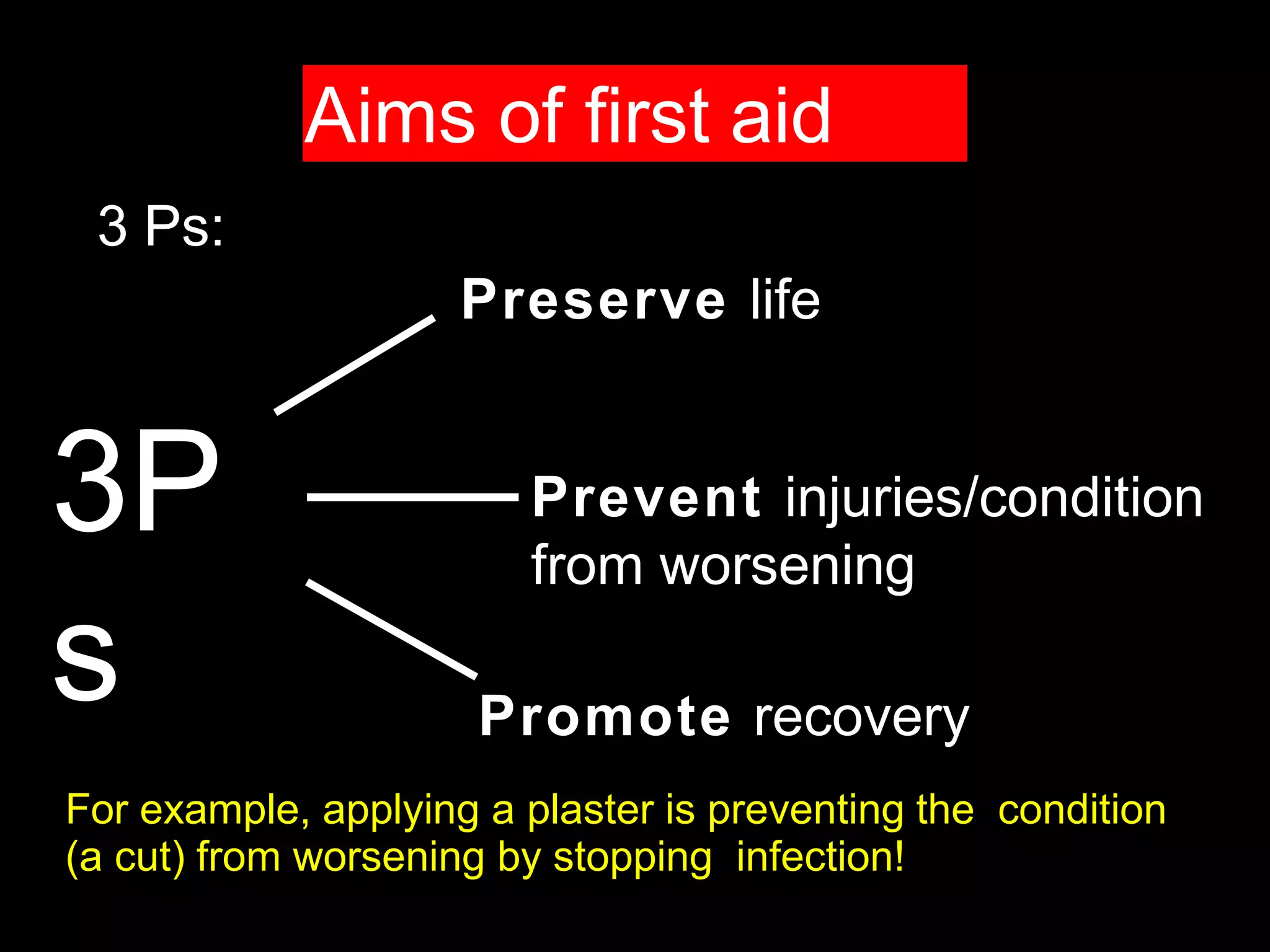
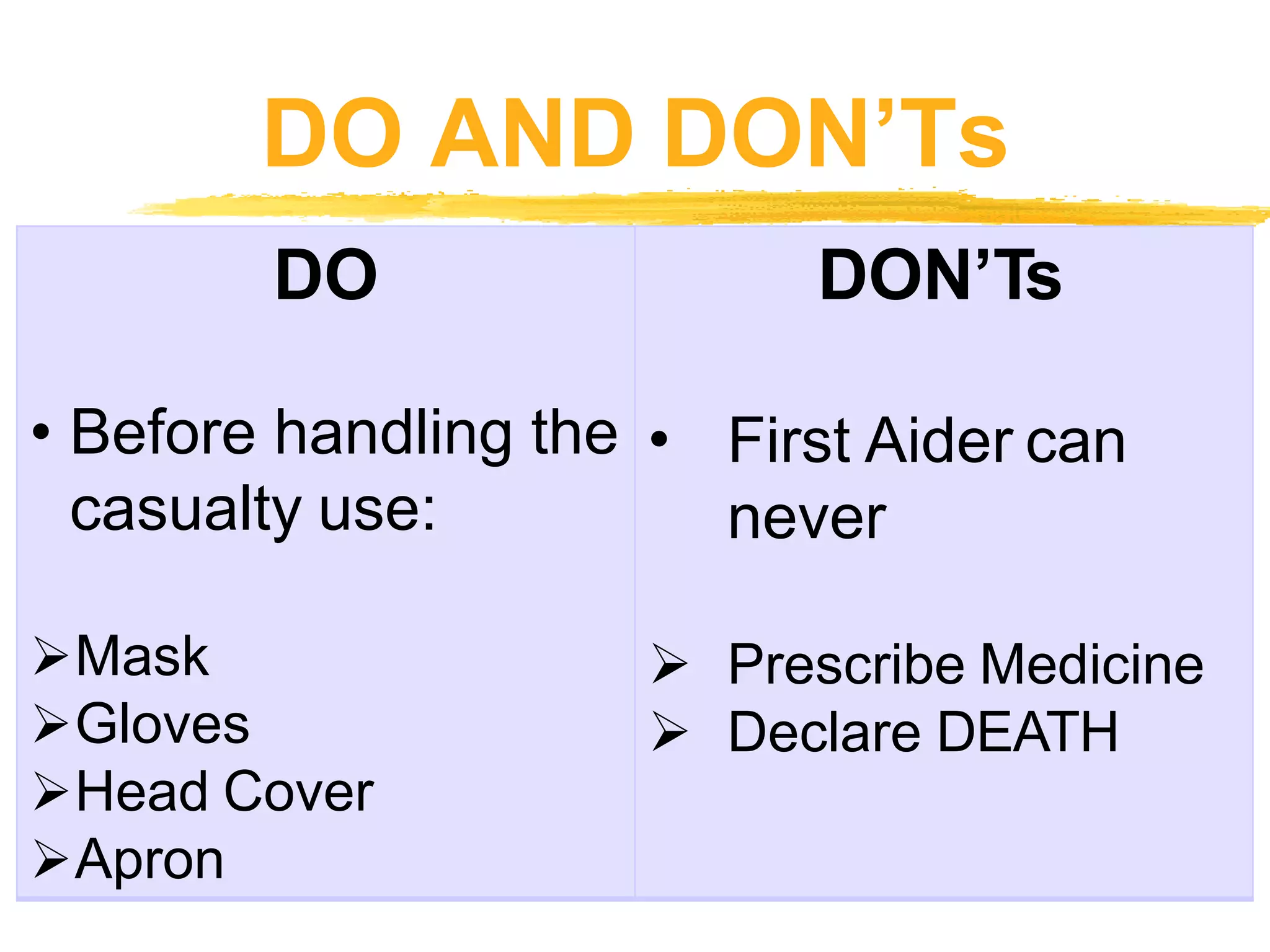
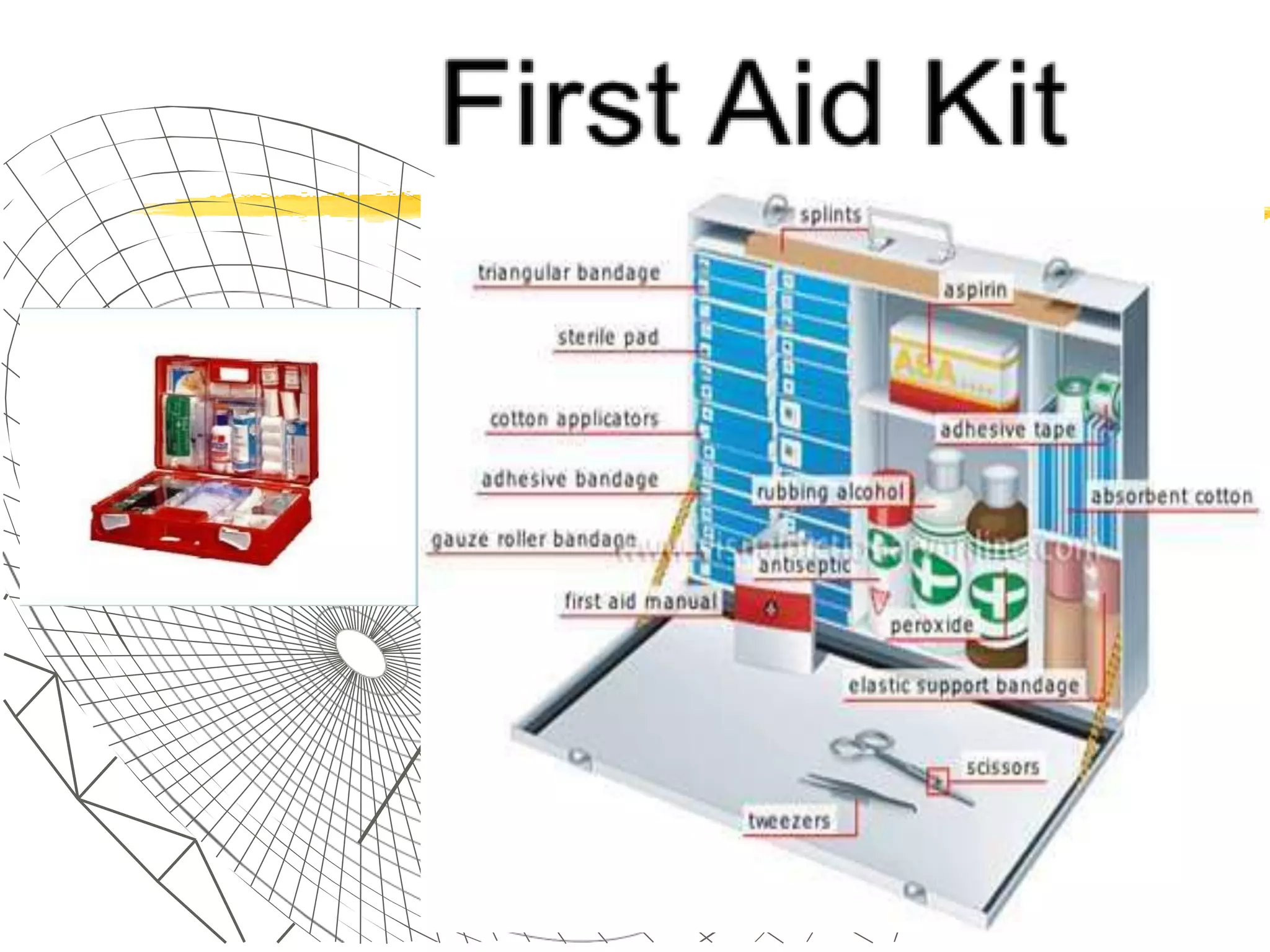
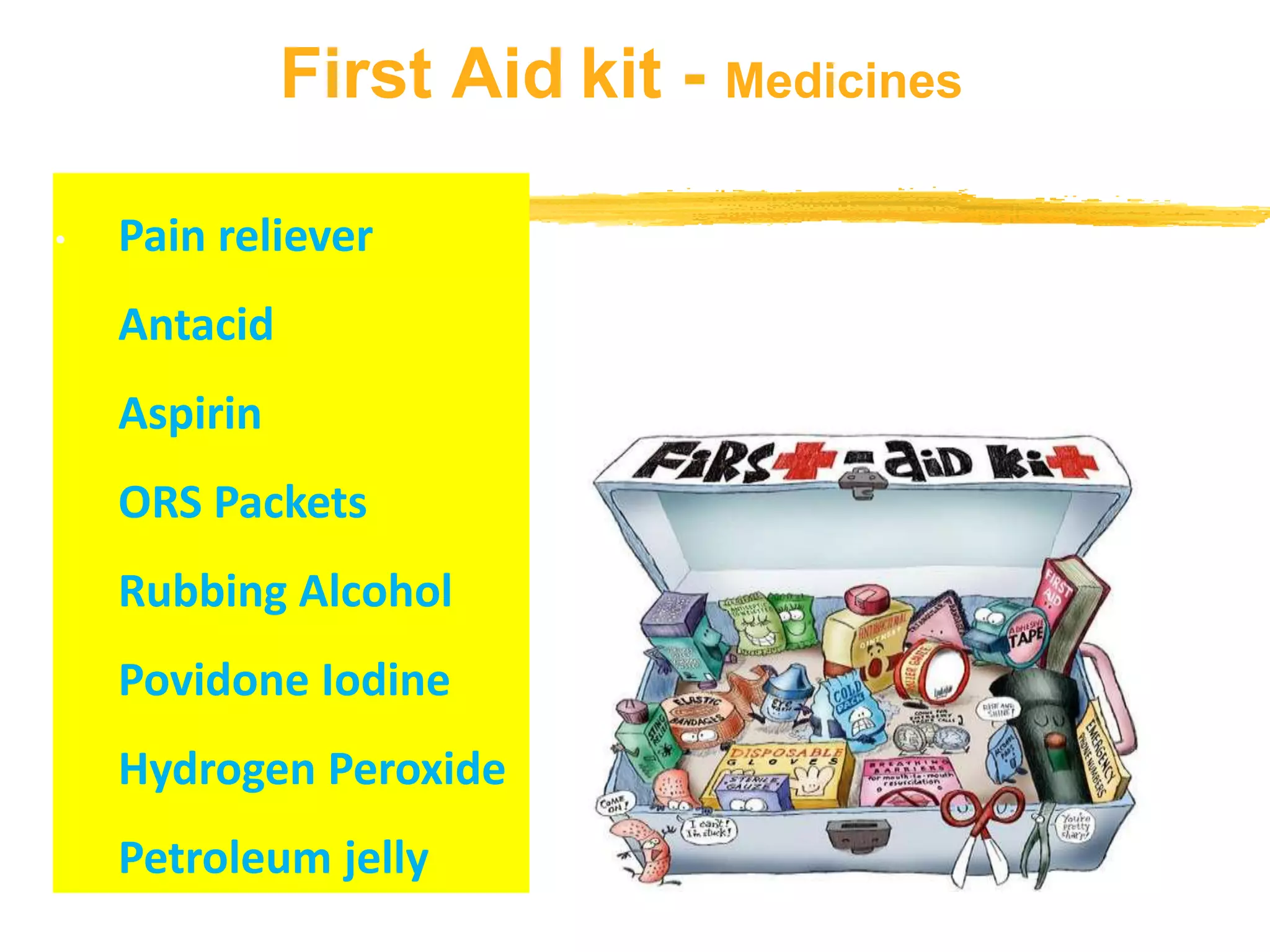
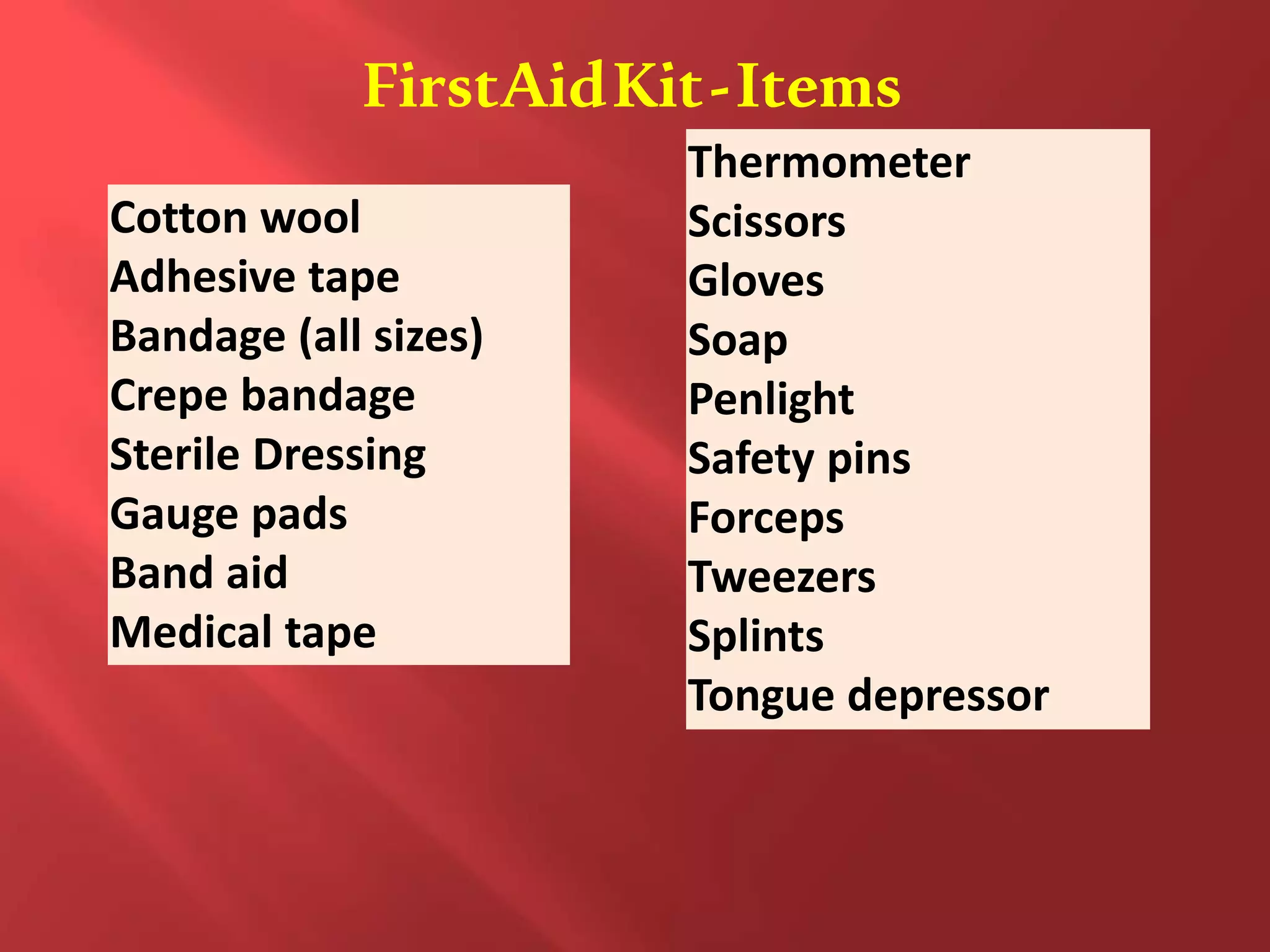
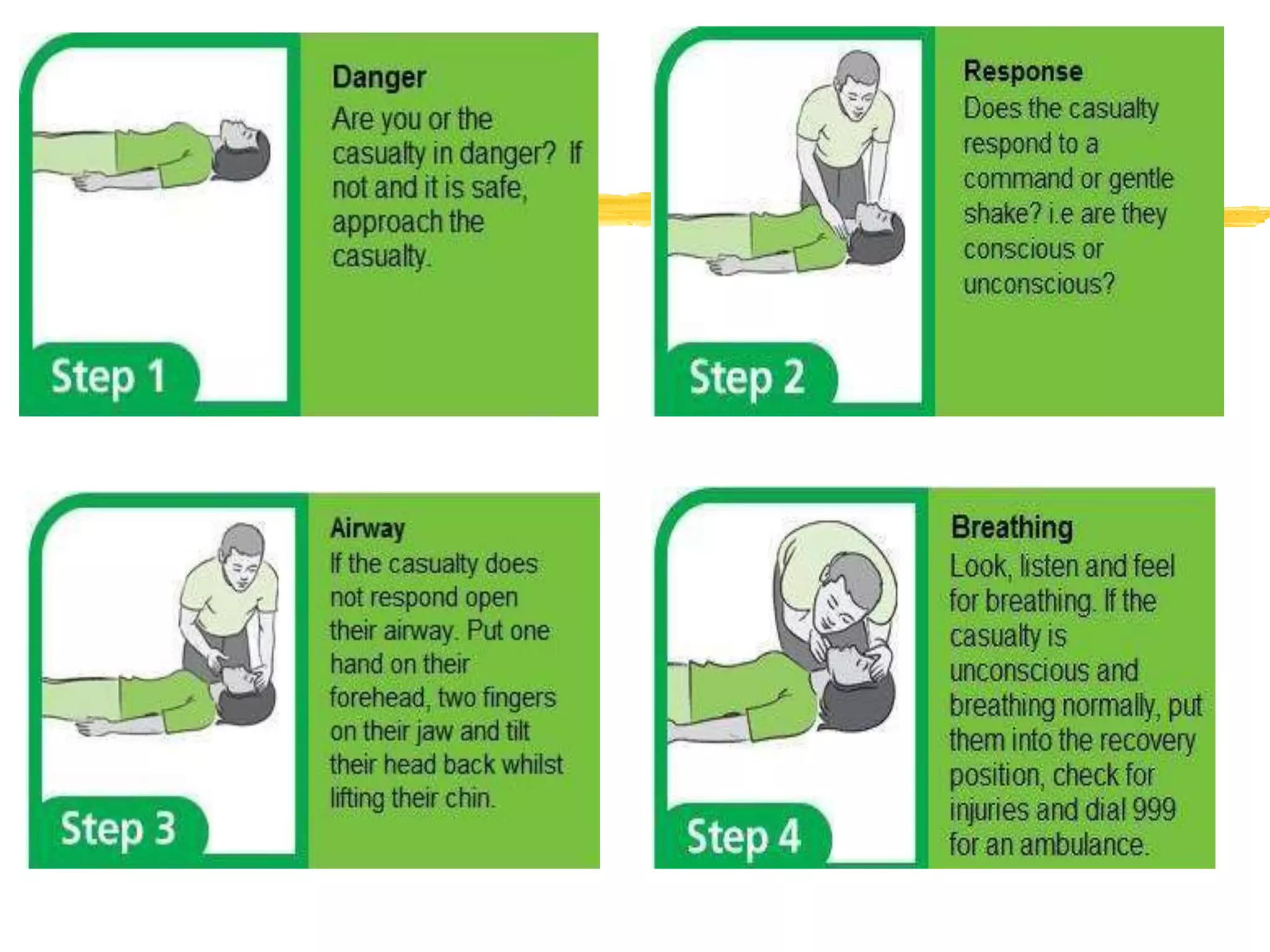
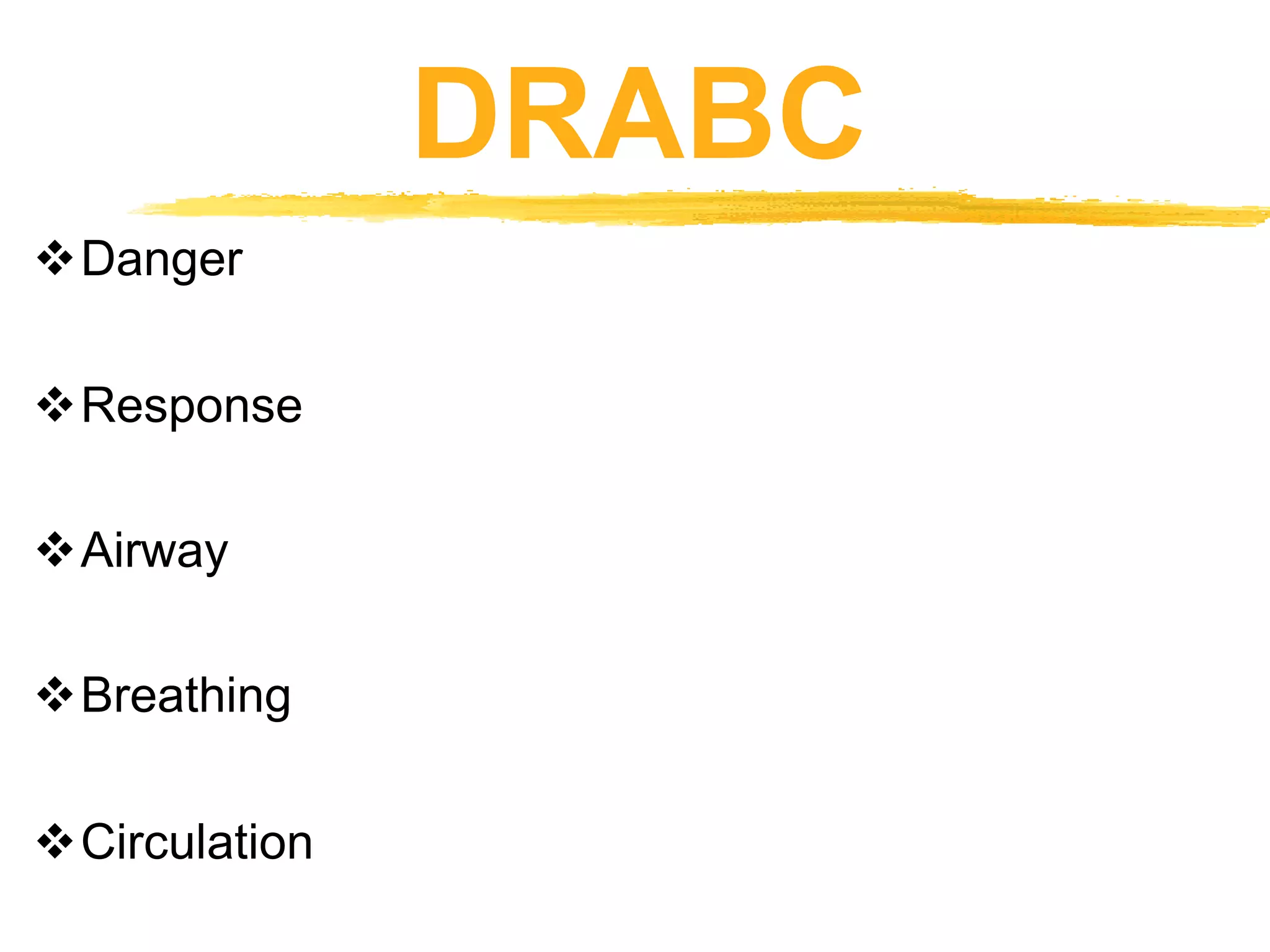
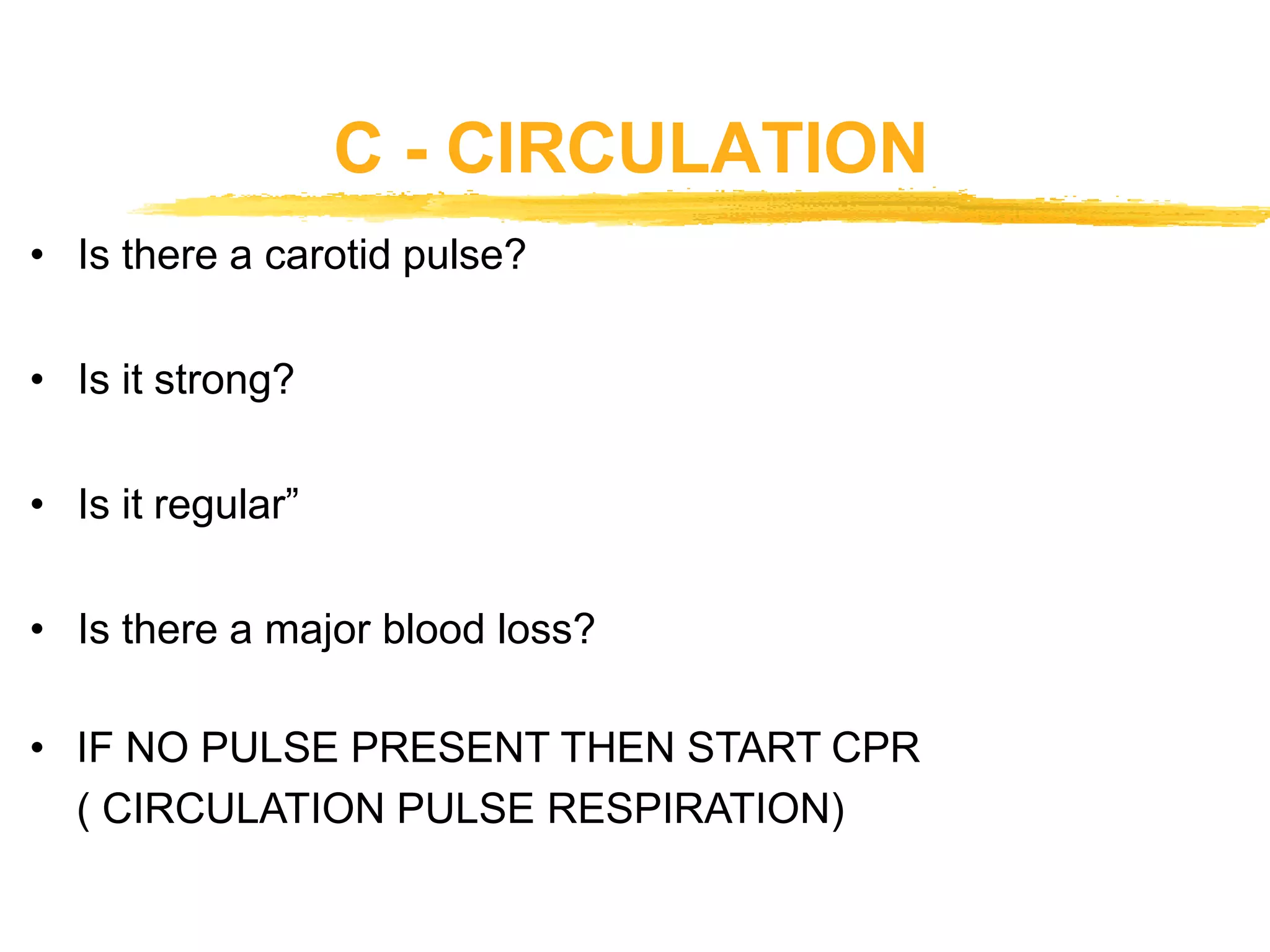
The document outlines the key principles and procedures of first aid. It discusses that first aid involves immediately assisting or treating someone before medical help arrives using available resources to preserve life, prevent worsening of conditions, and promote recovery. The key aims of first aid are to preserve life, prevent injuries from worsening, and promote recovery. It also describes the DRABC action plan that first aiders should follow to assess dangers, check response, open airways, check breathing, and check circulation of a casualty. Protecting oneself from infection as a first aider is also emphasized.