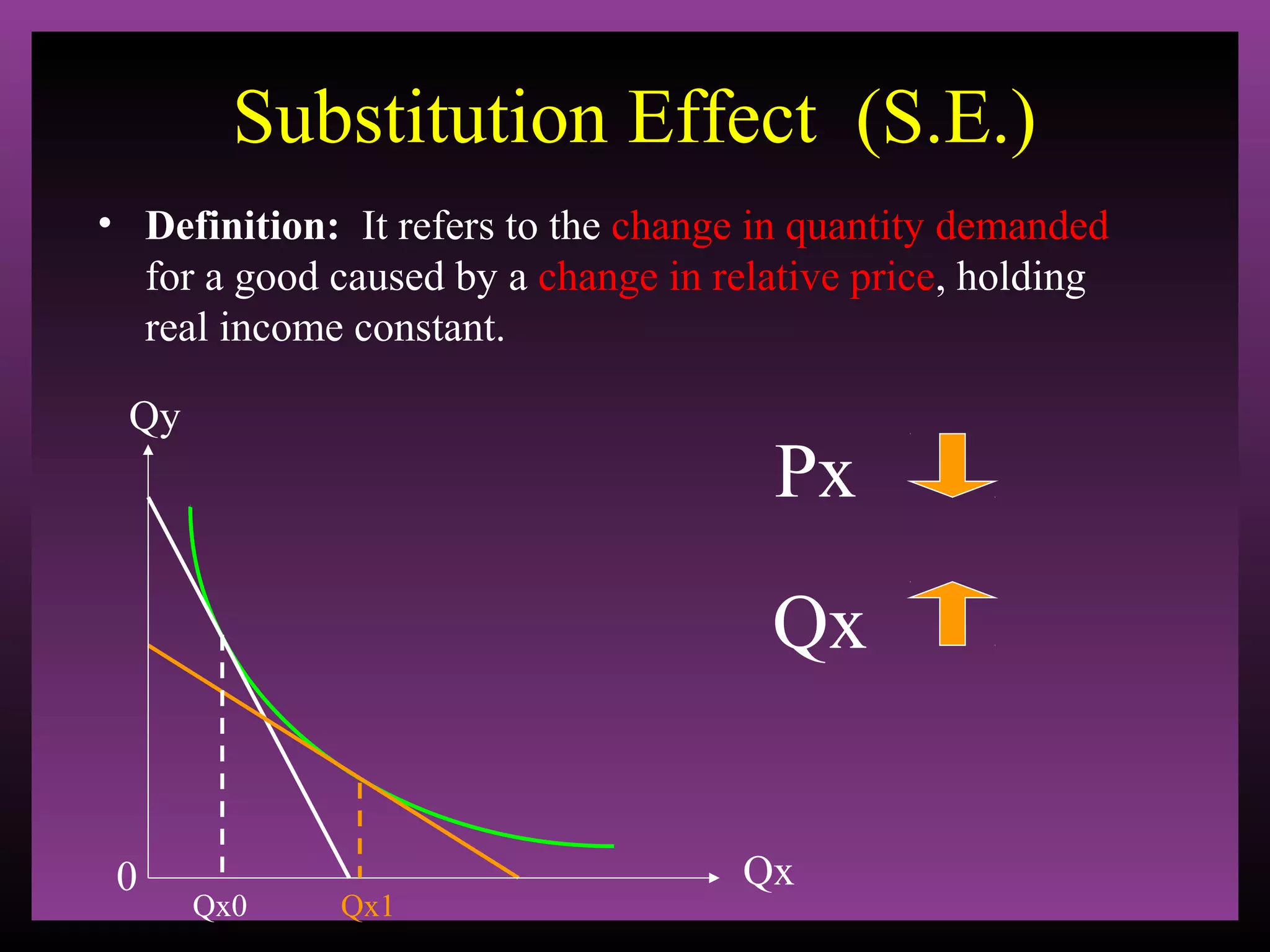
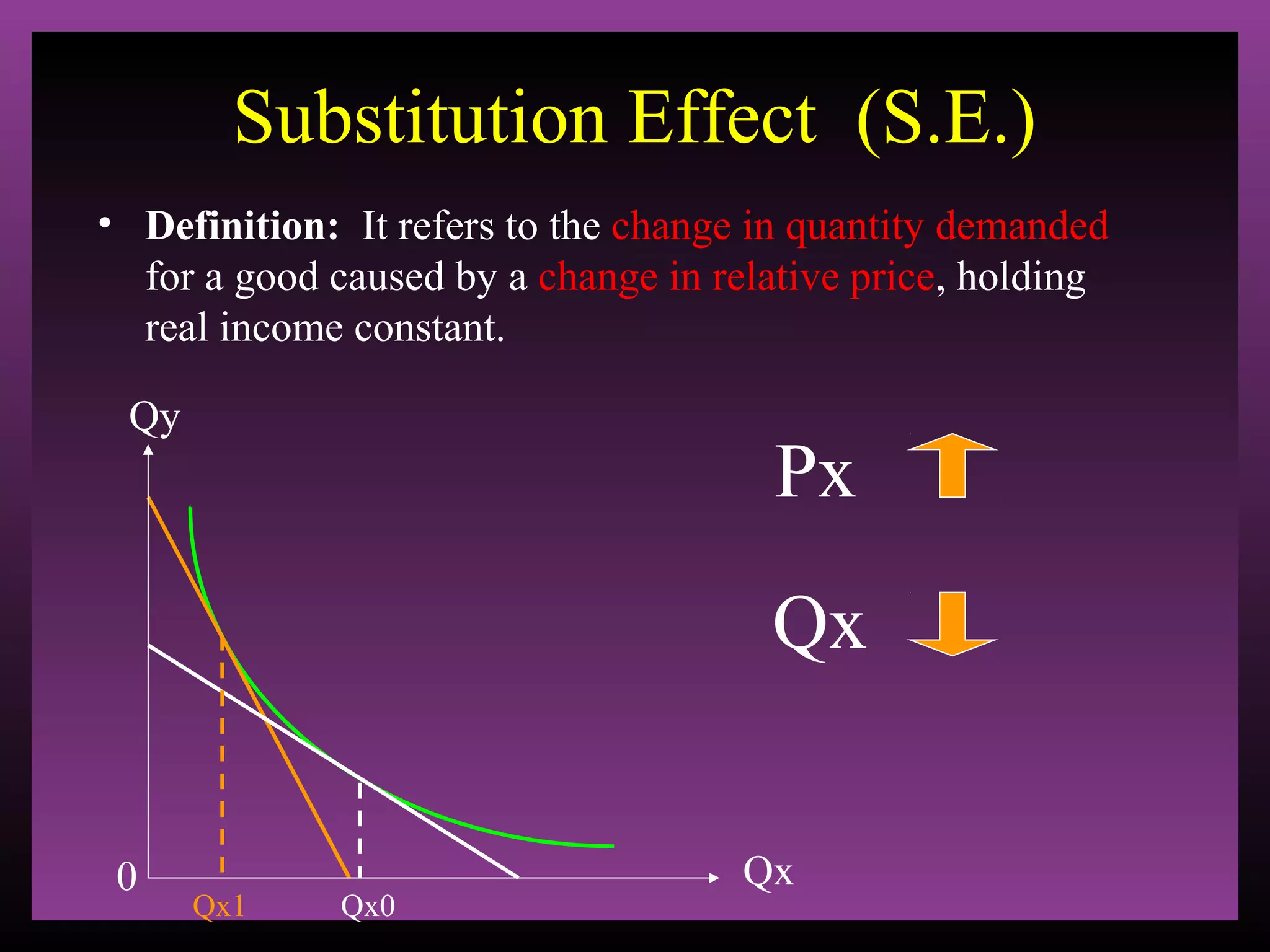
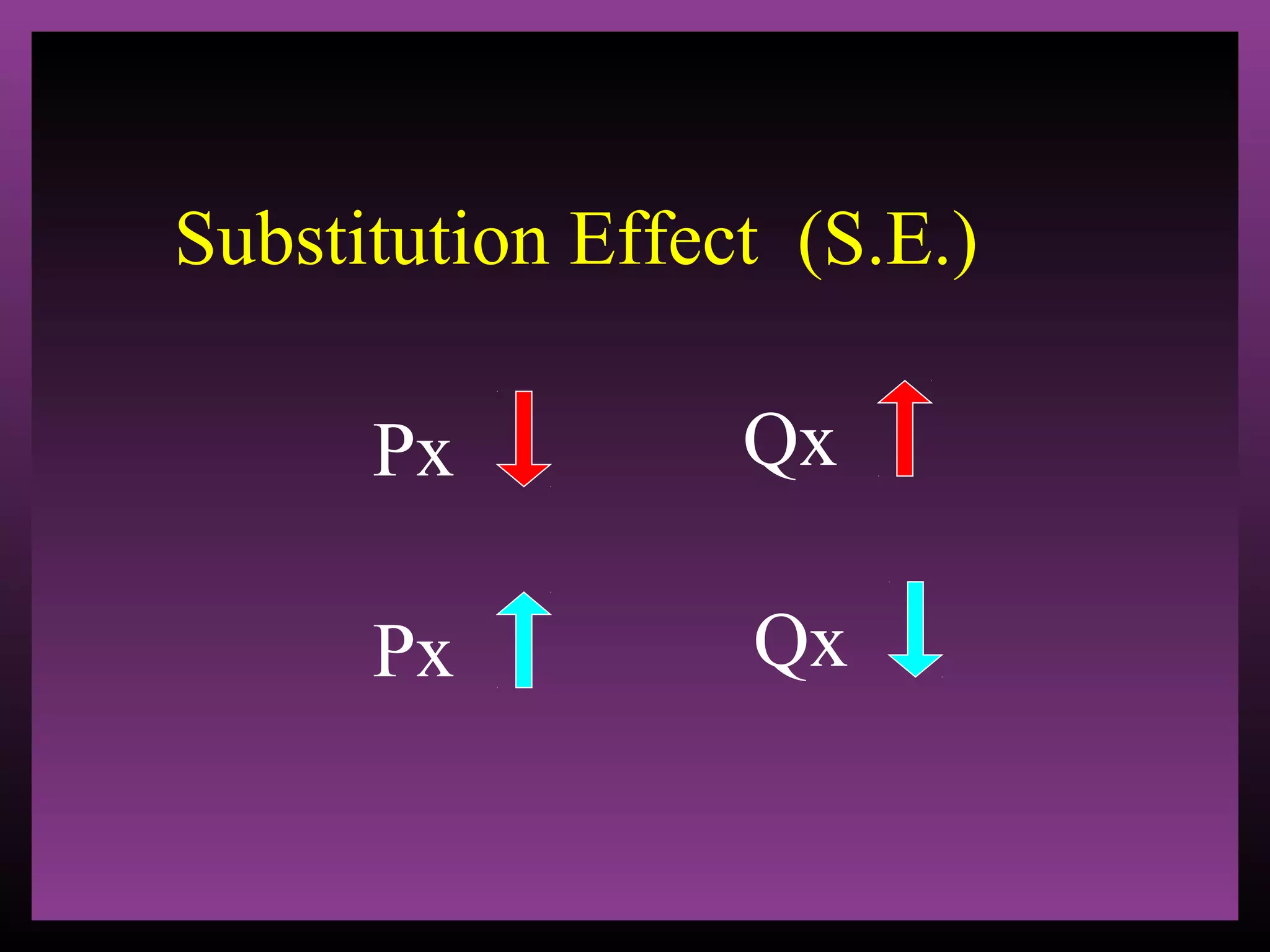
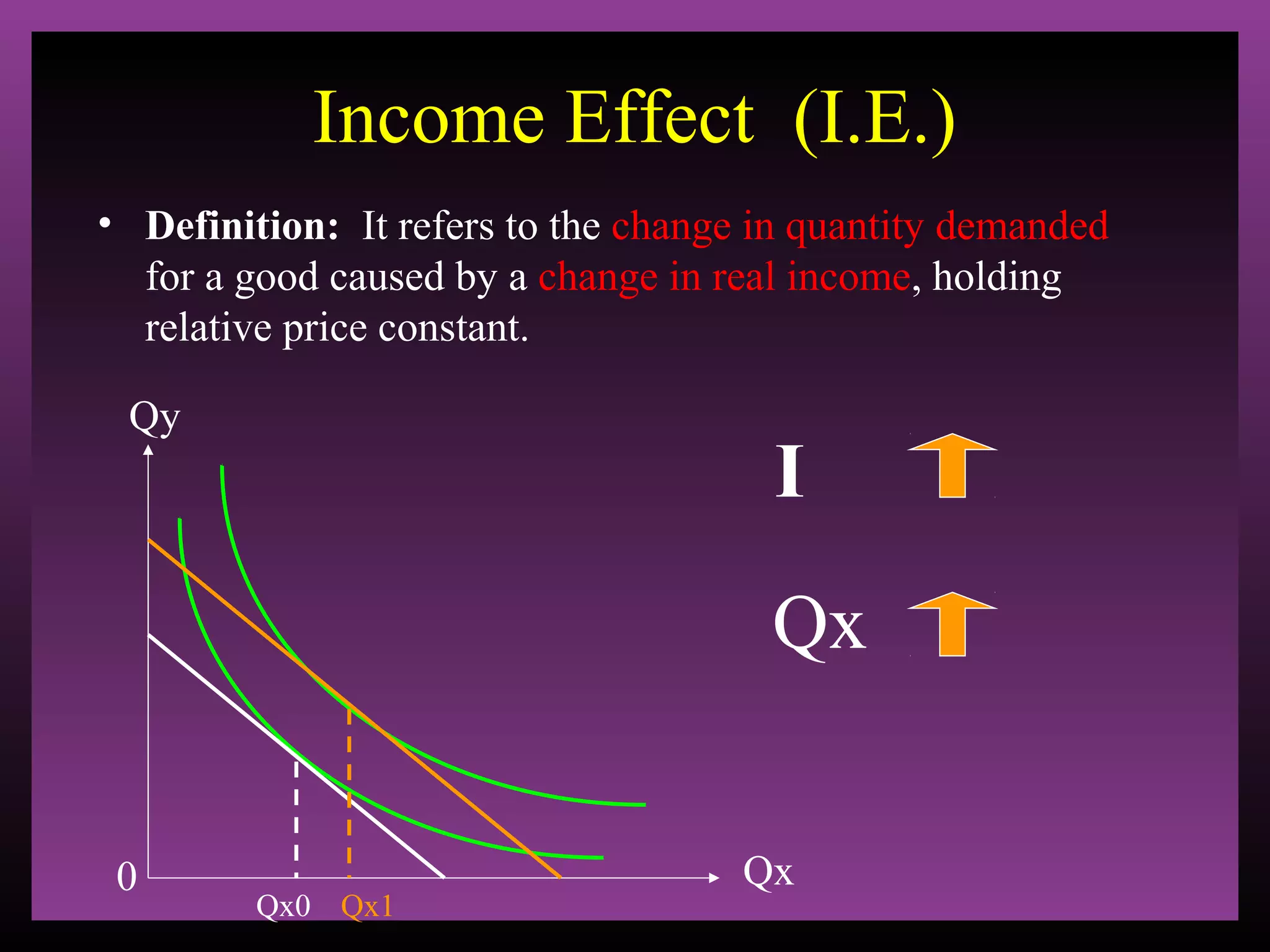
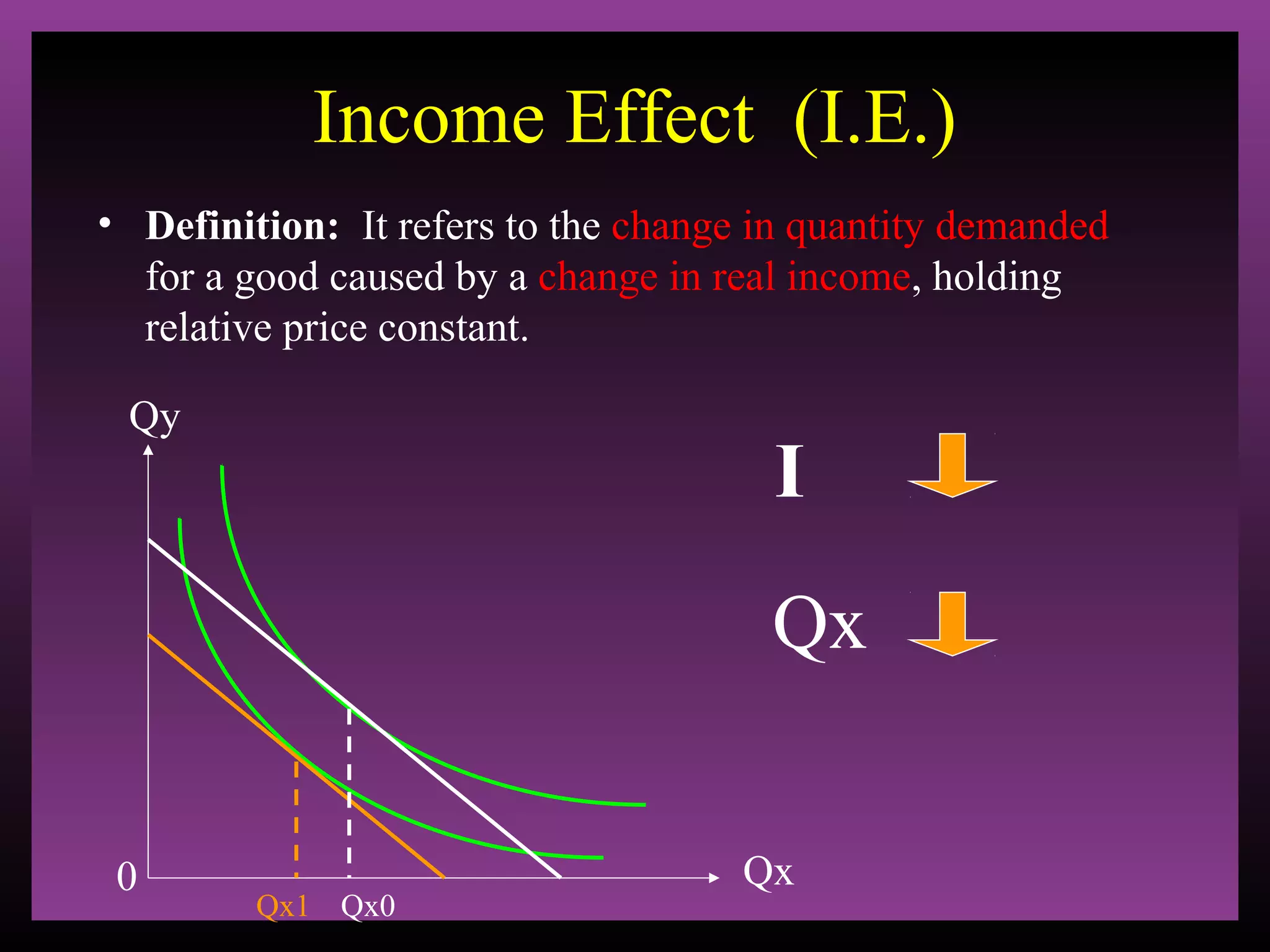
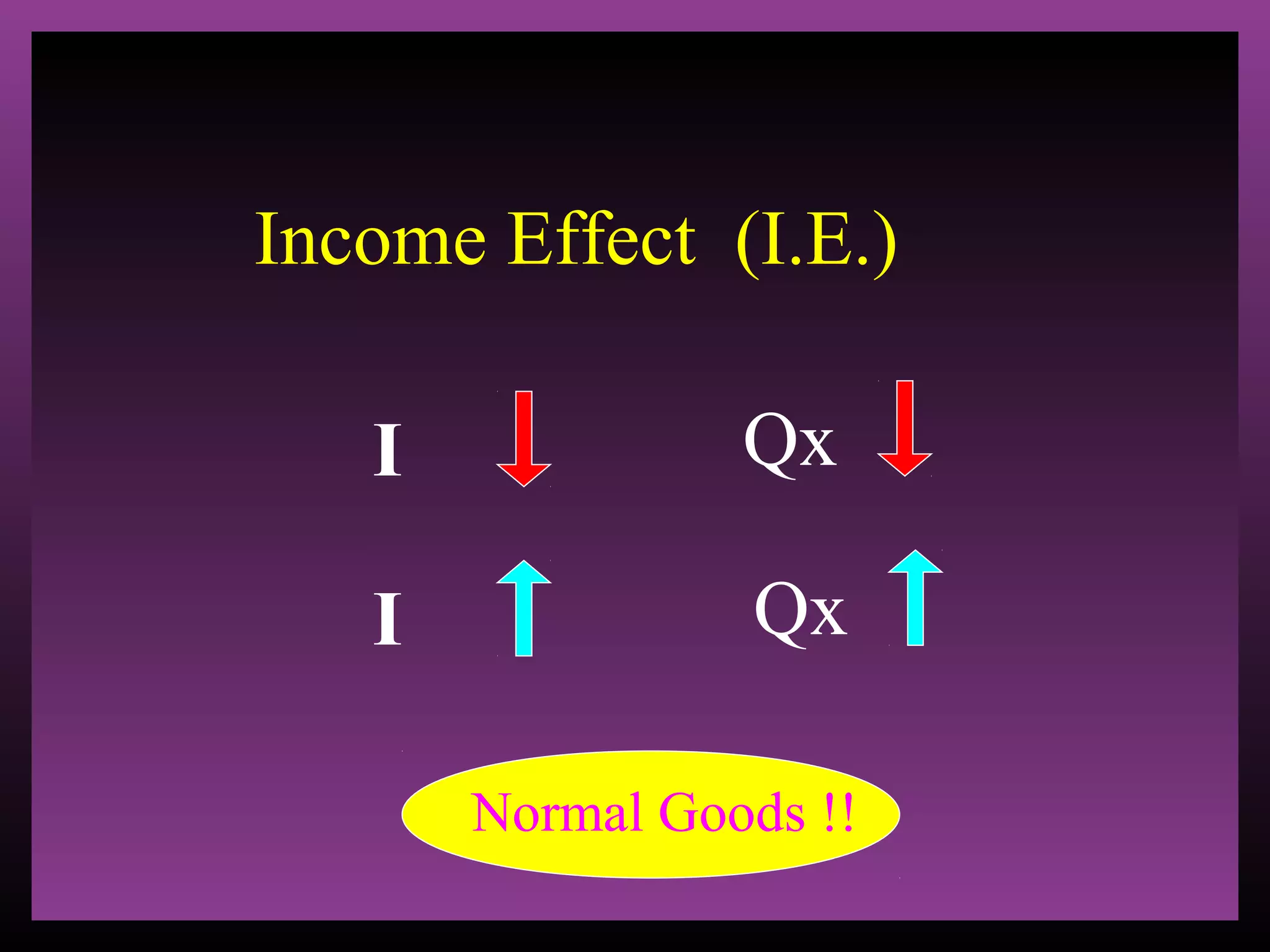
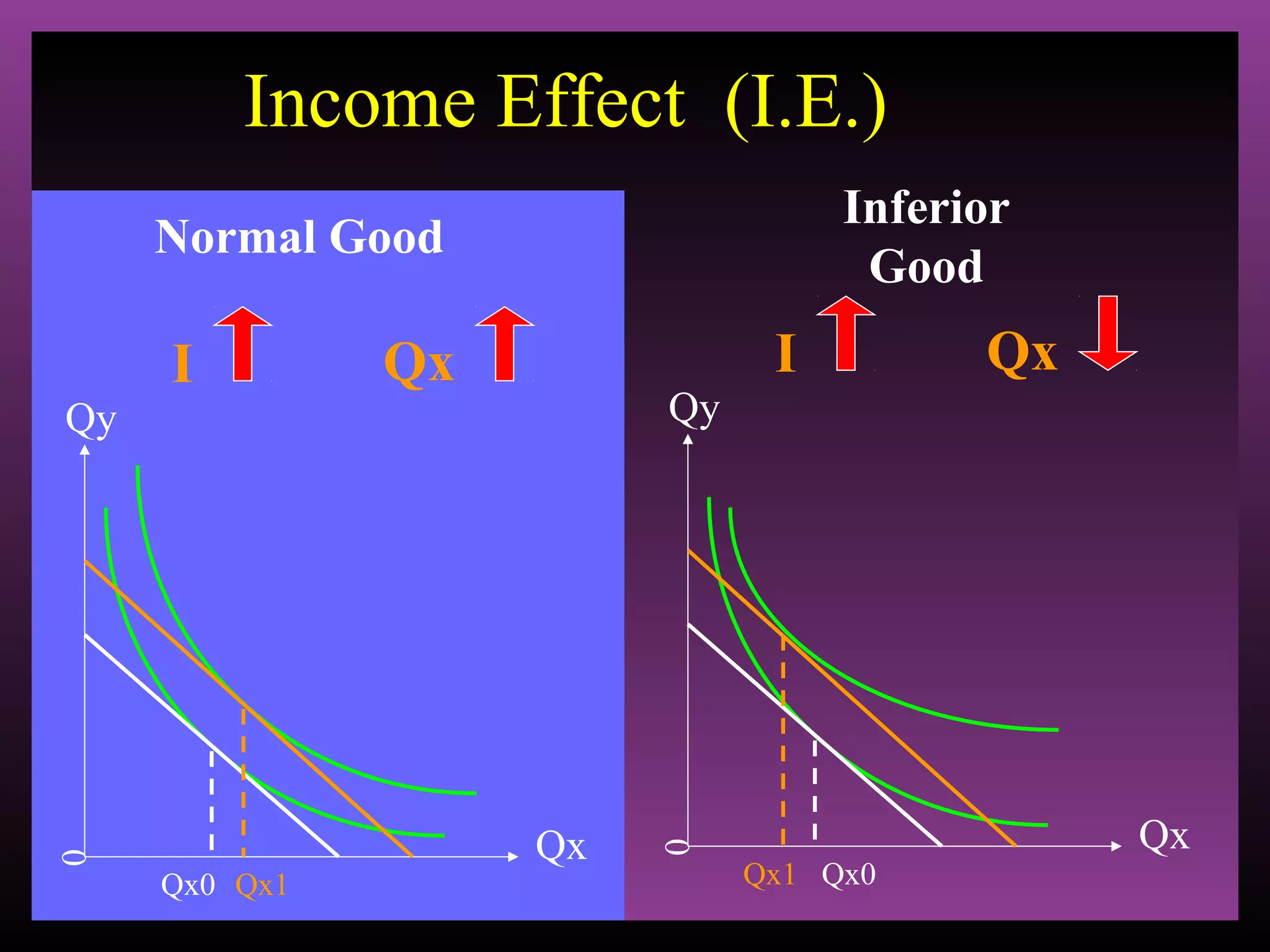
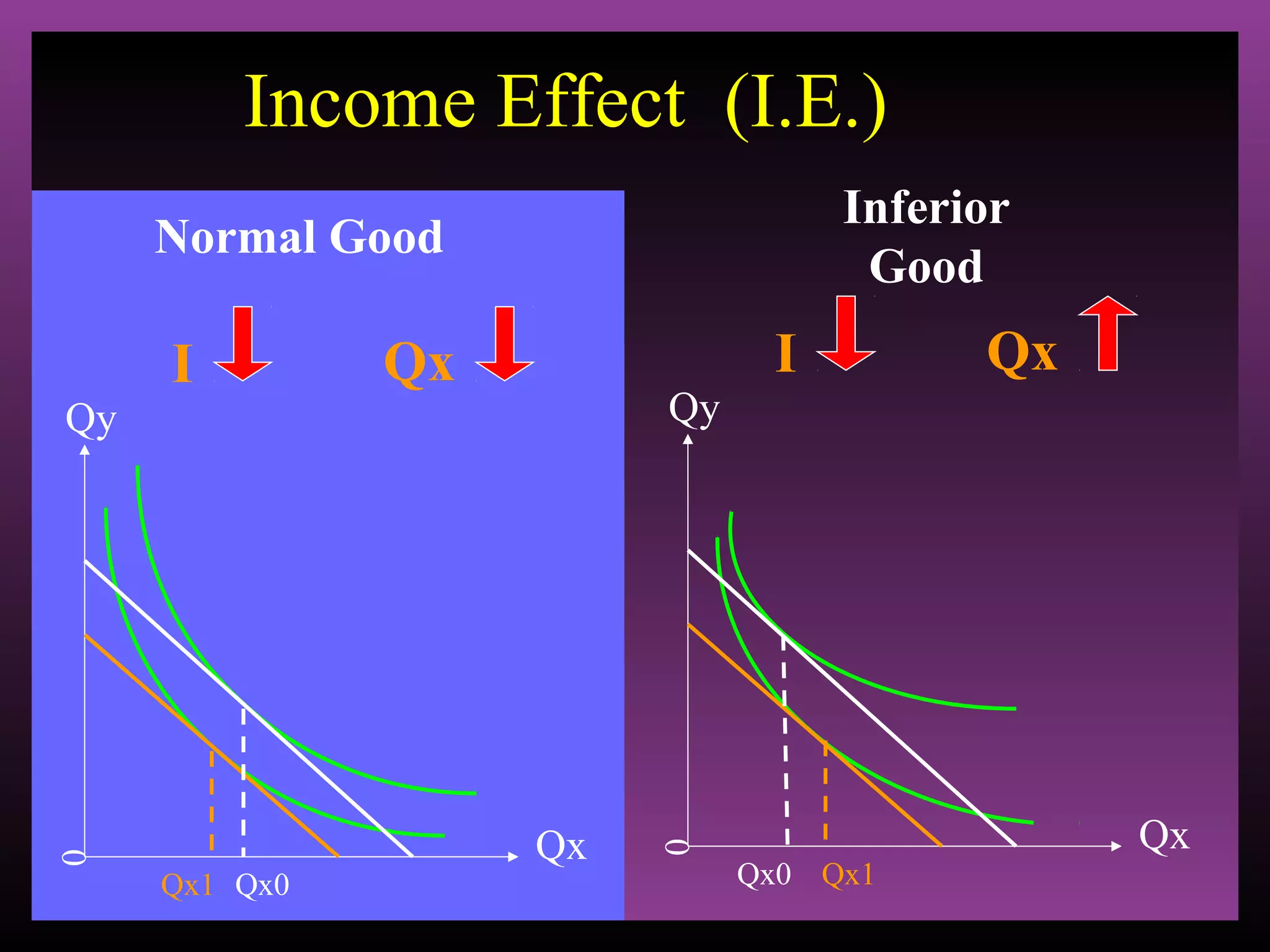
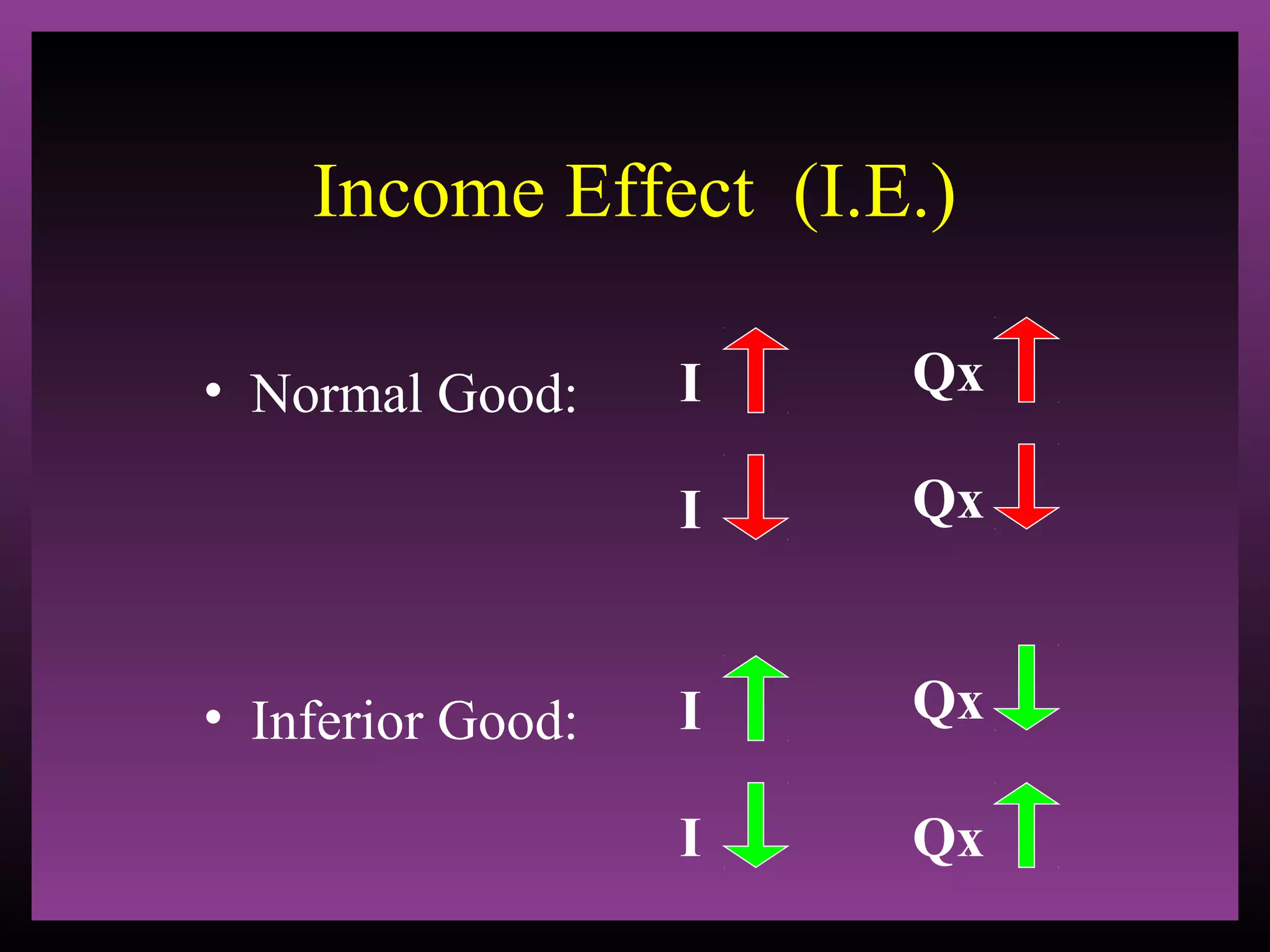
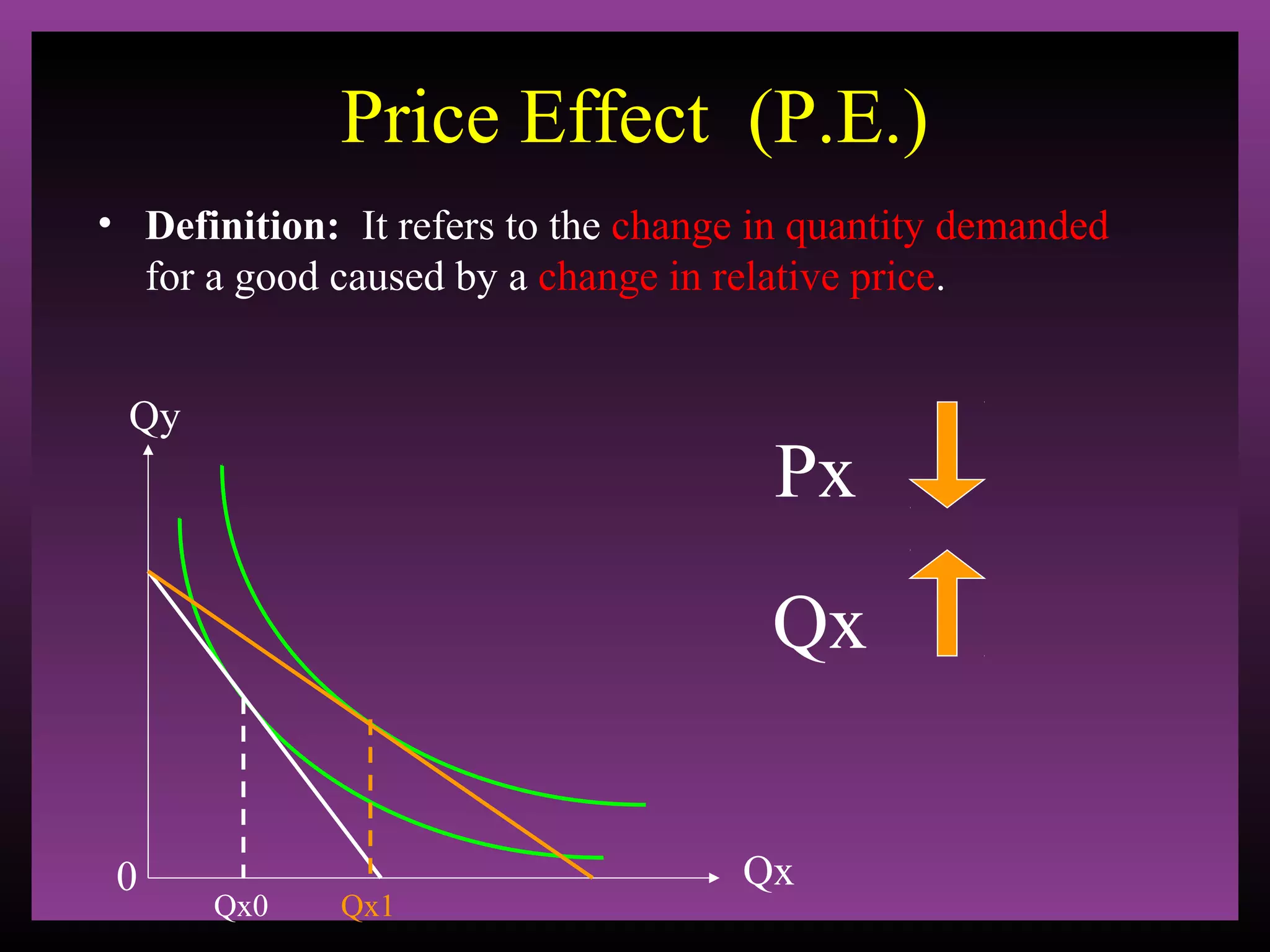
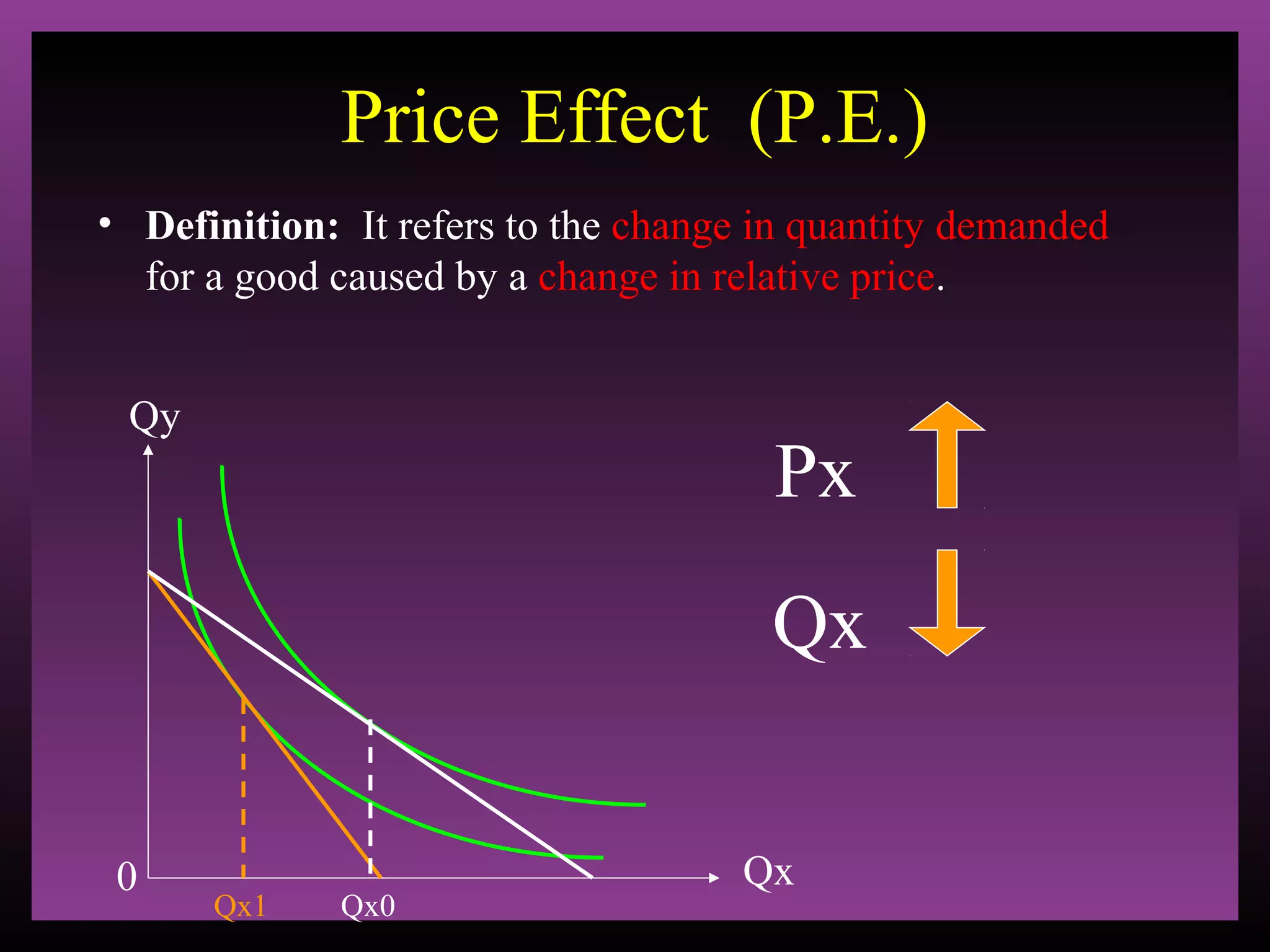
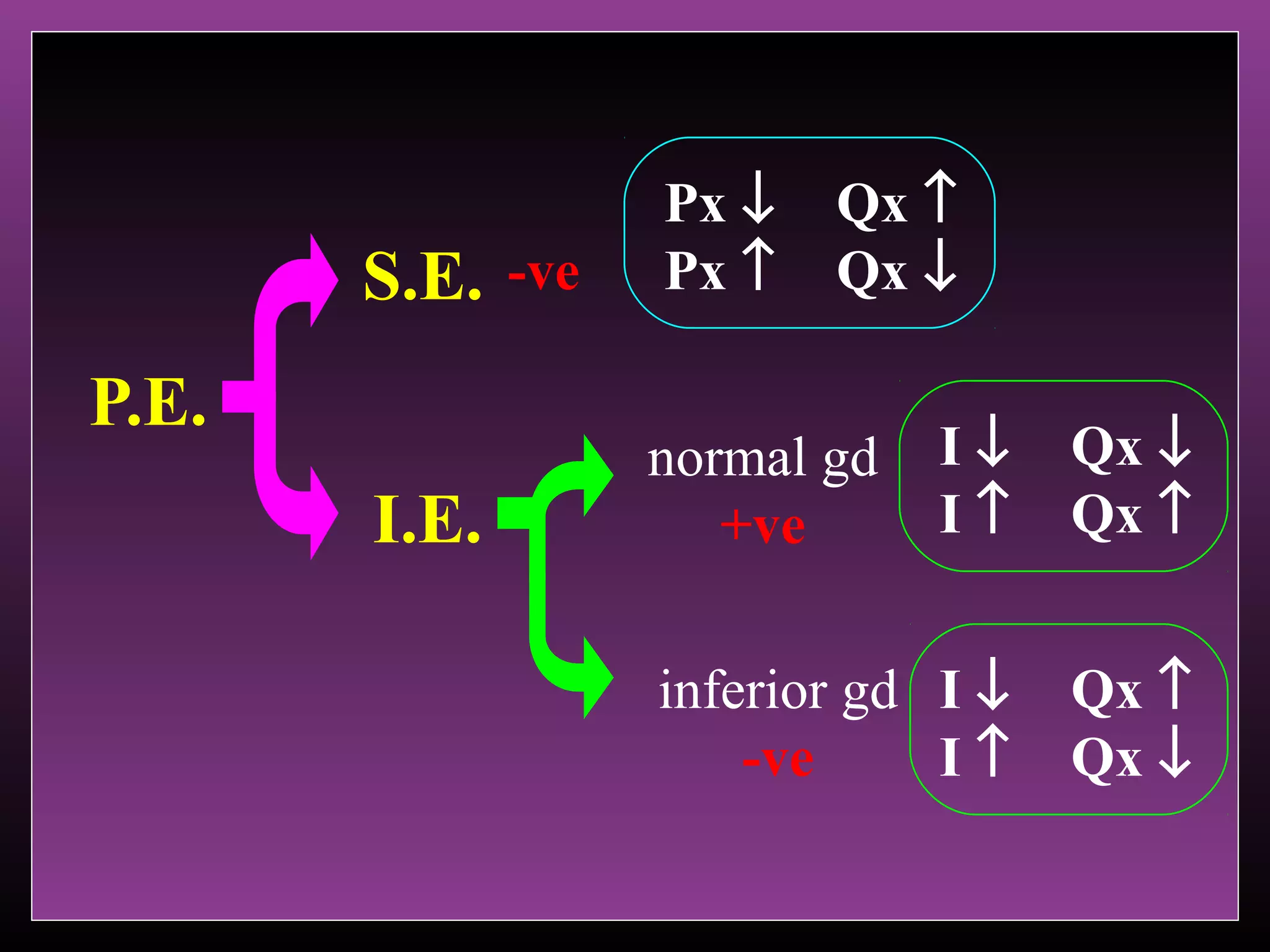
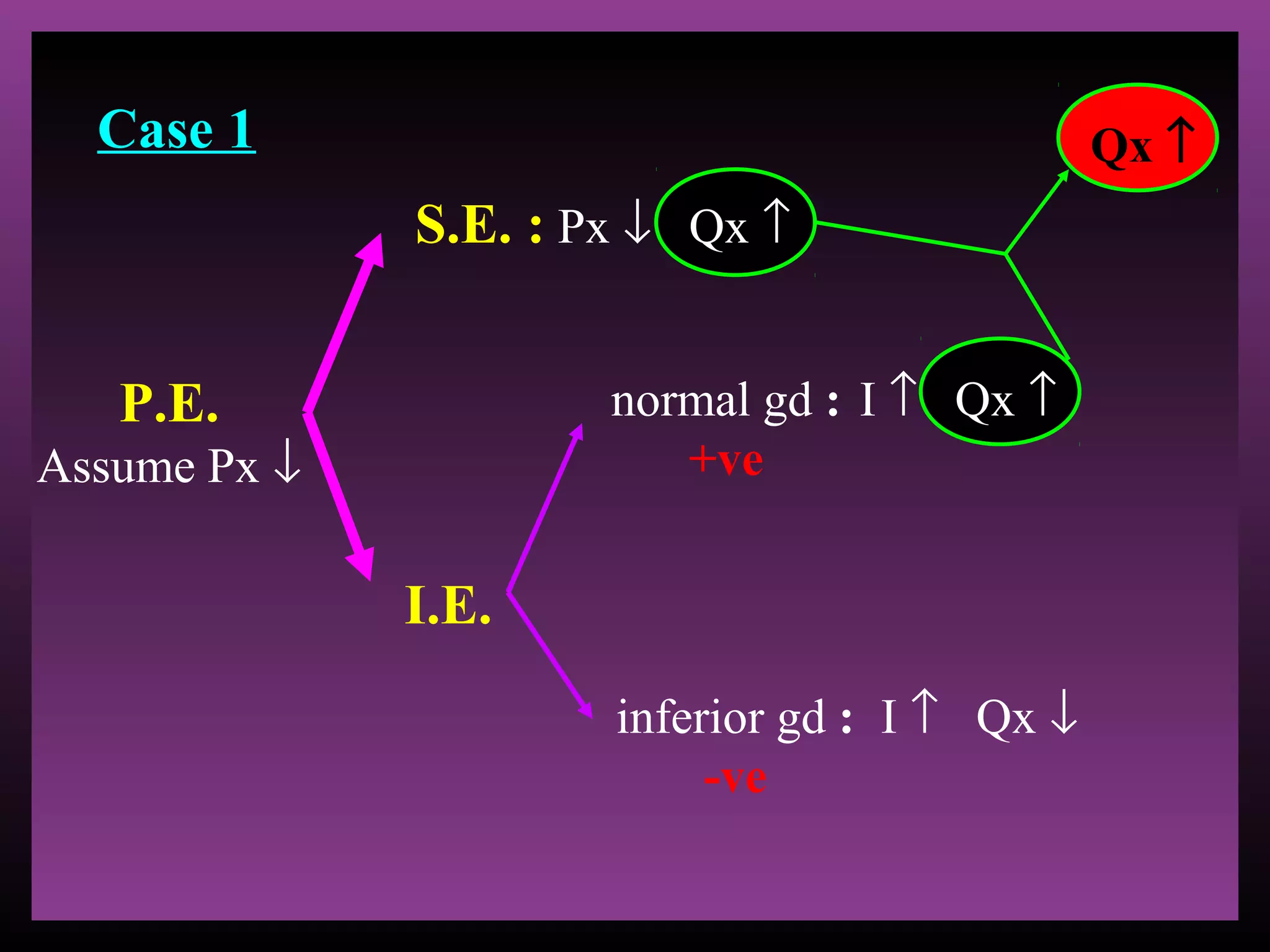
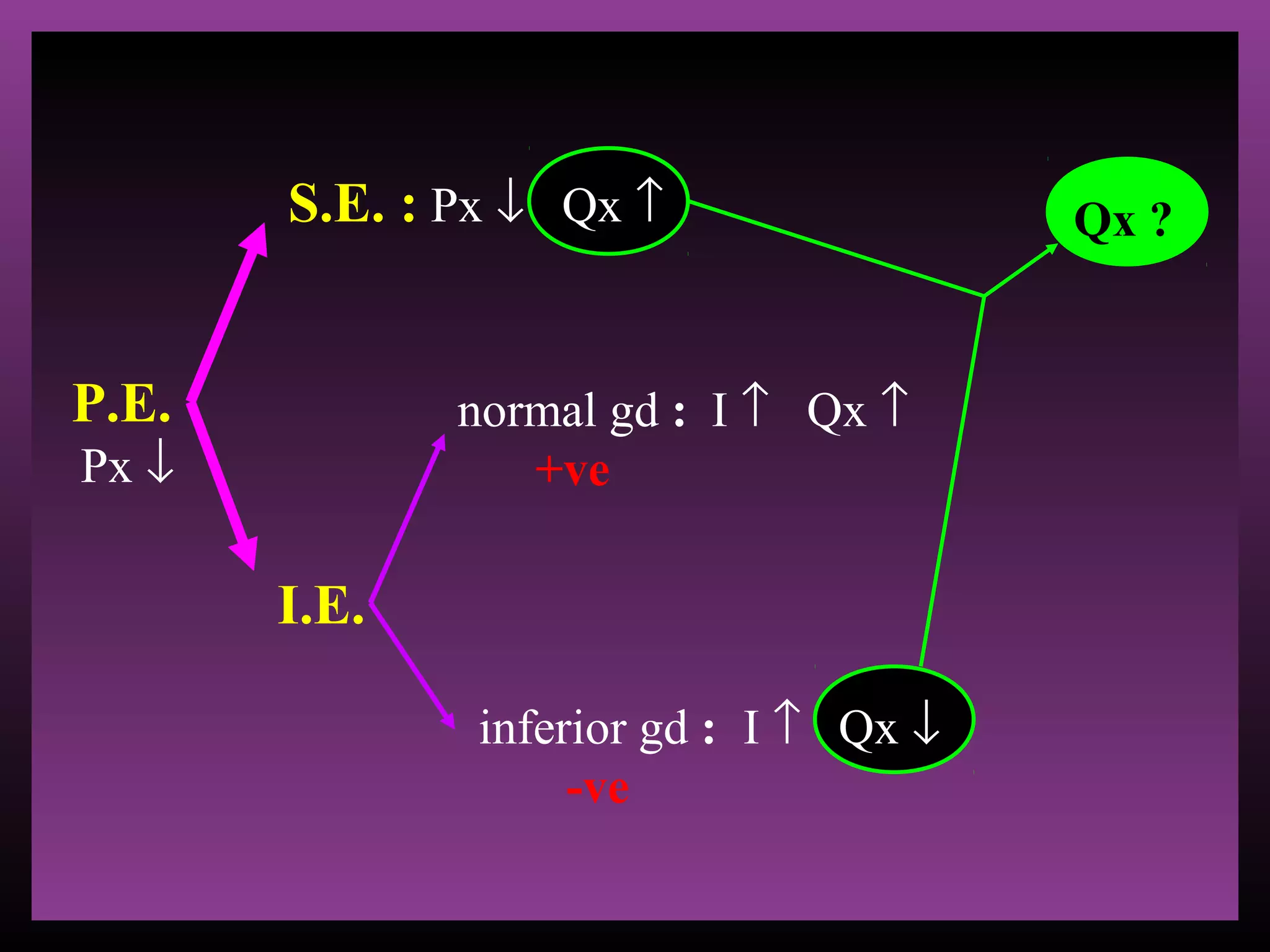
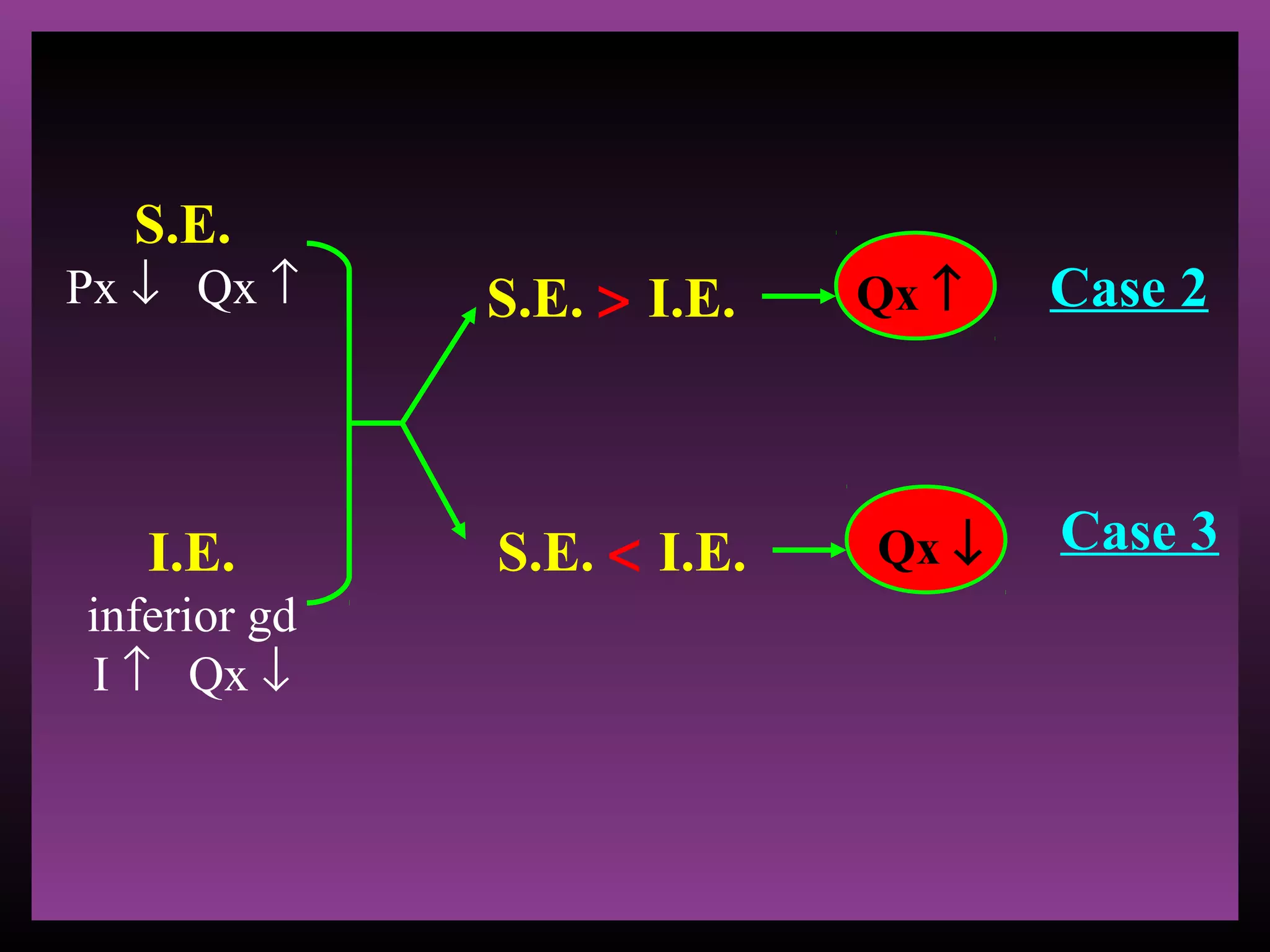
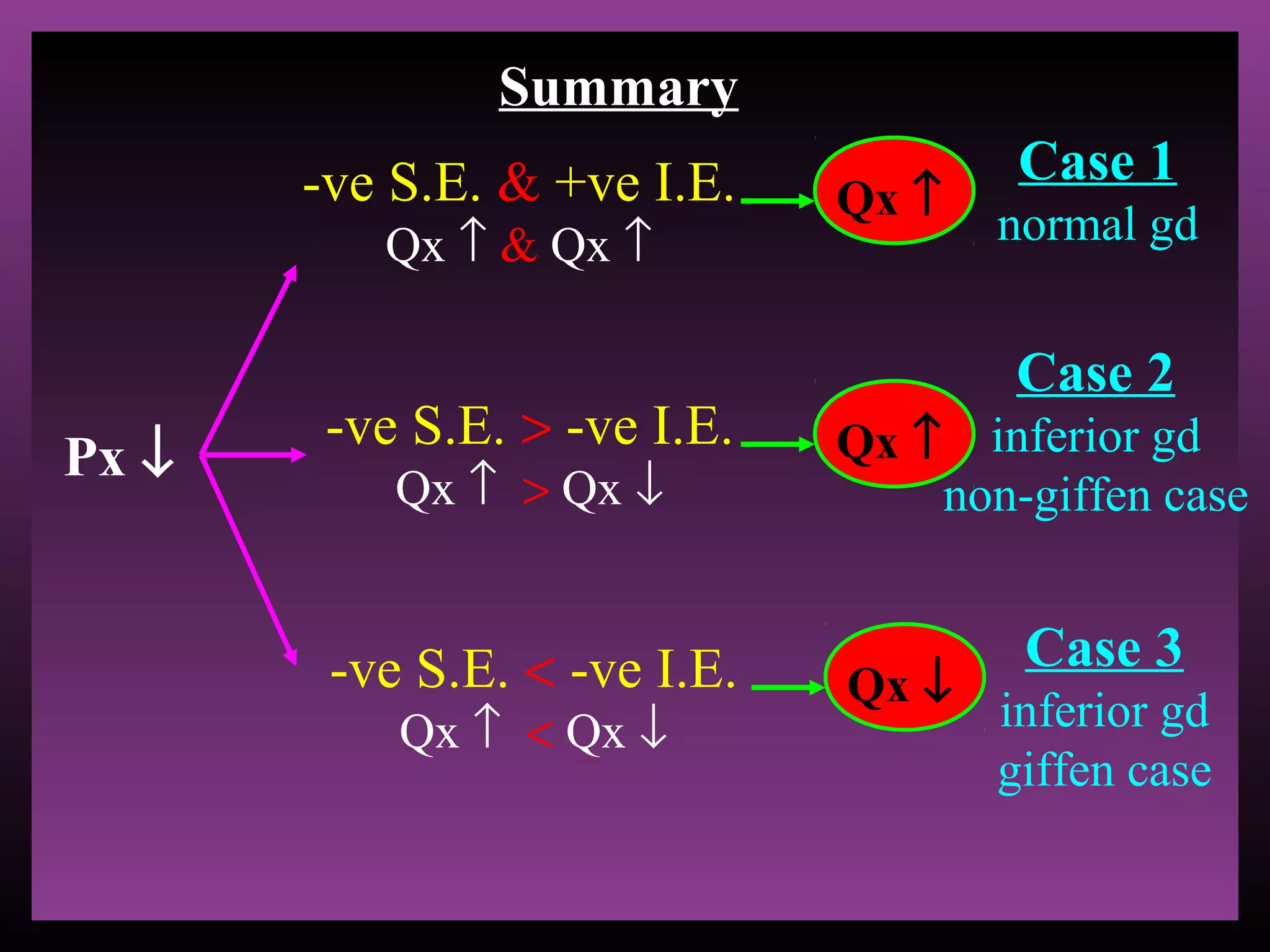
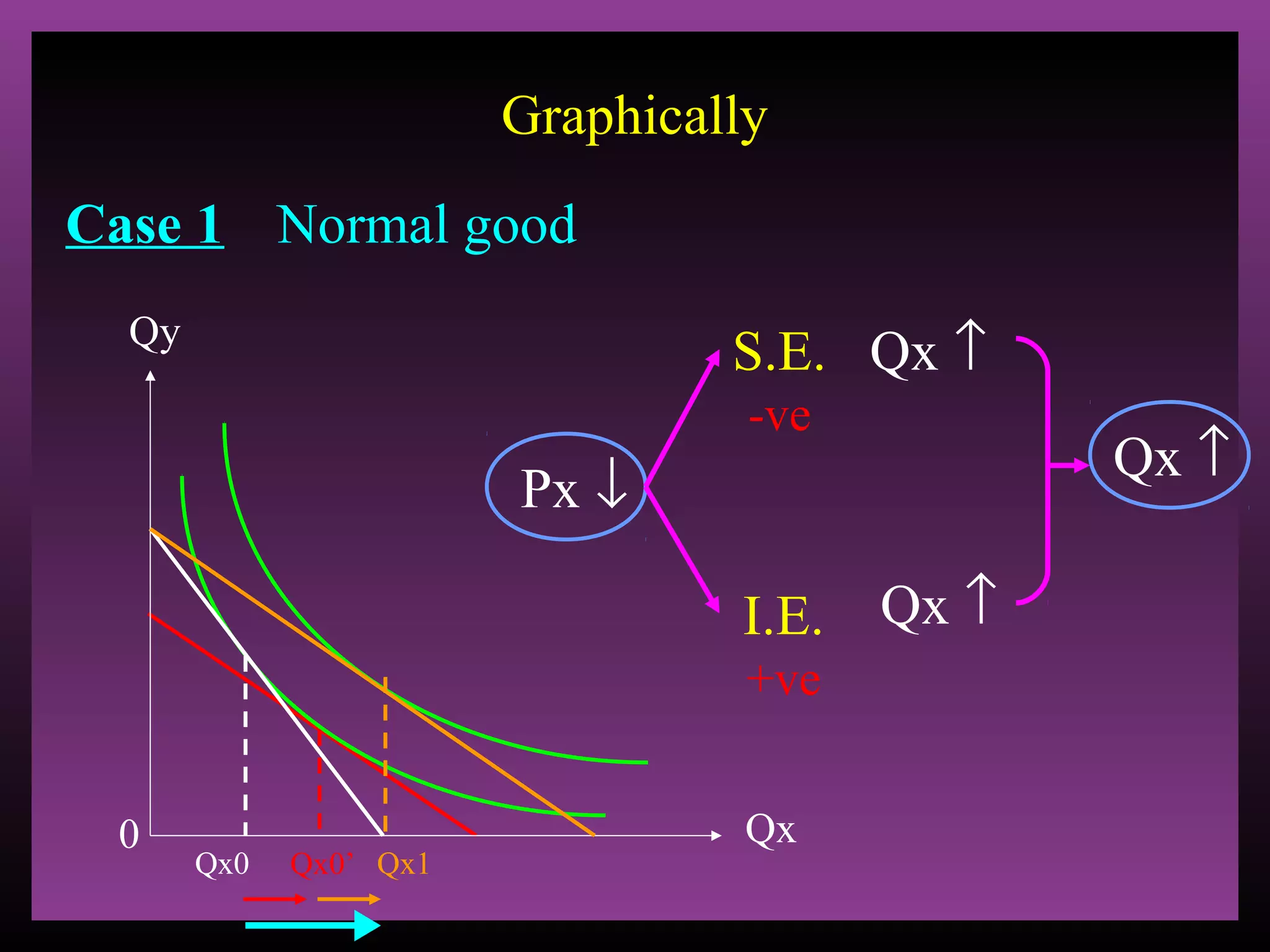
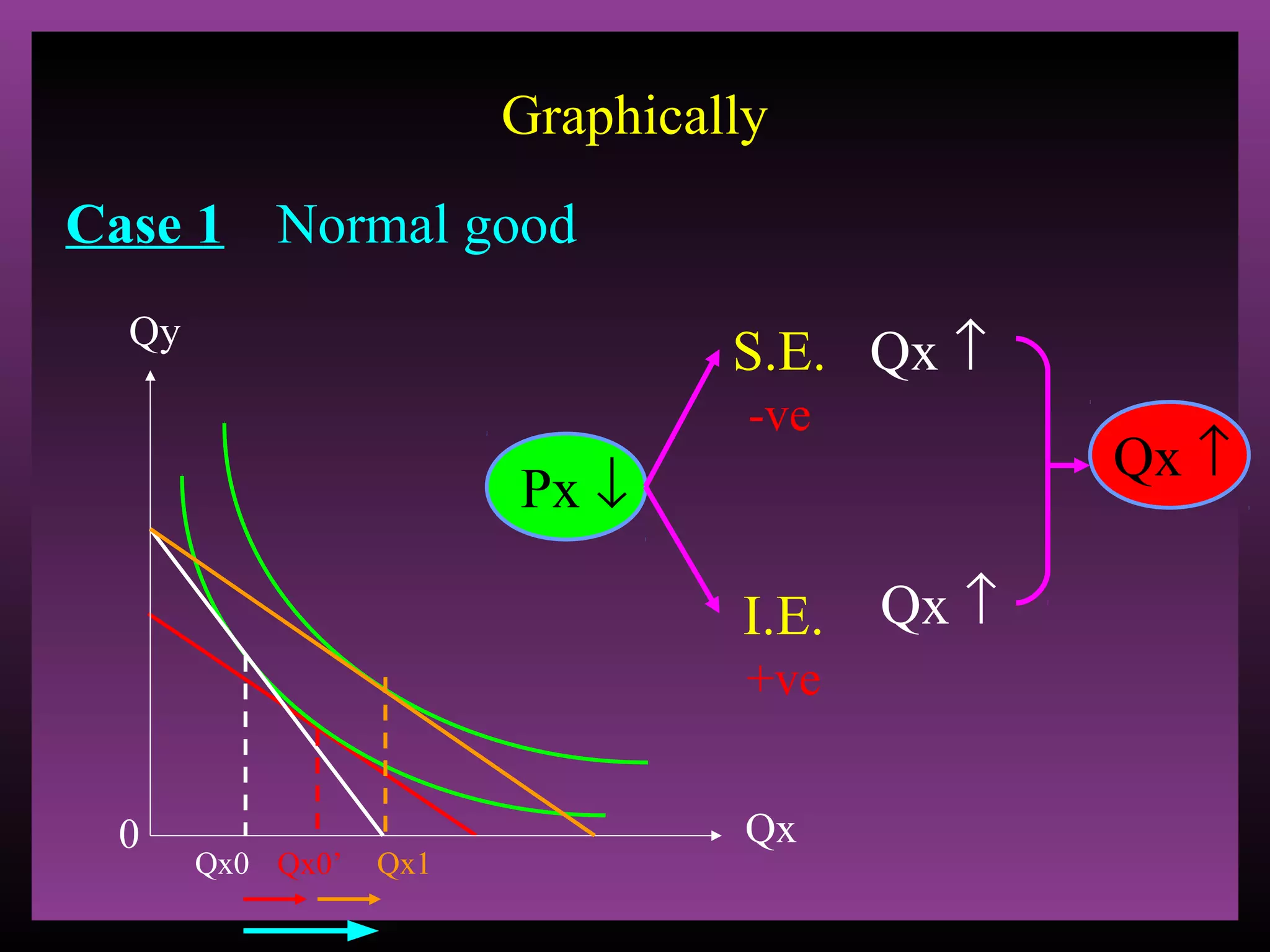
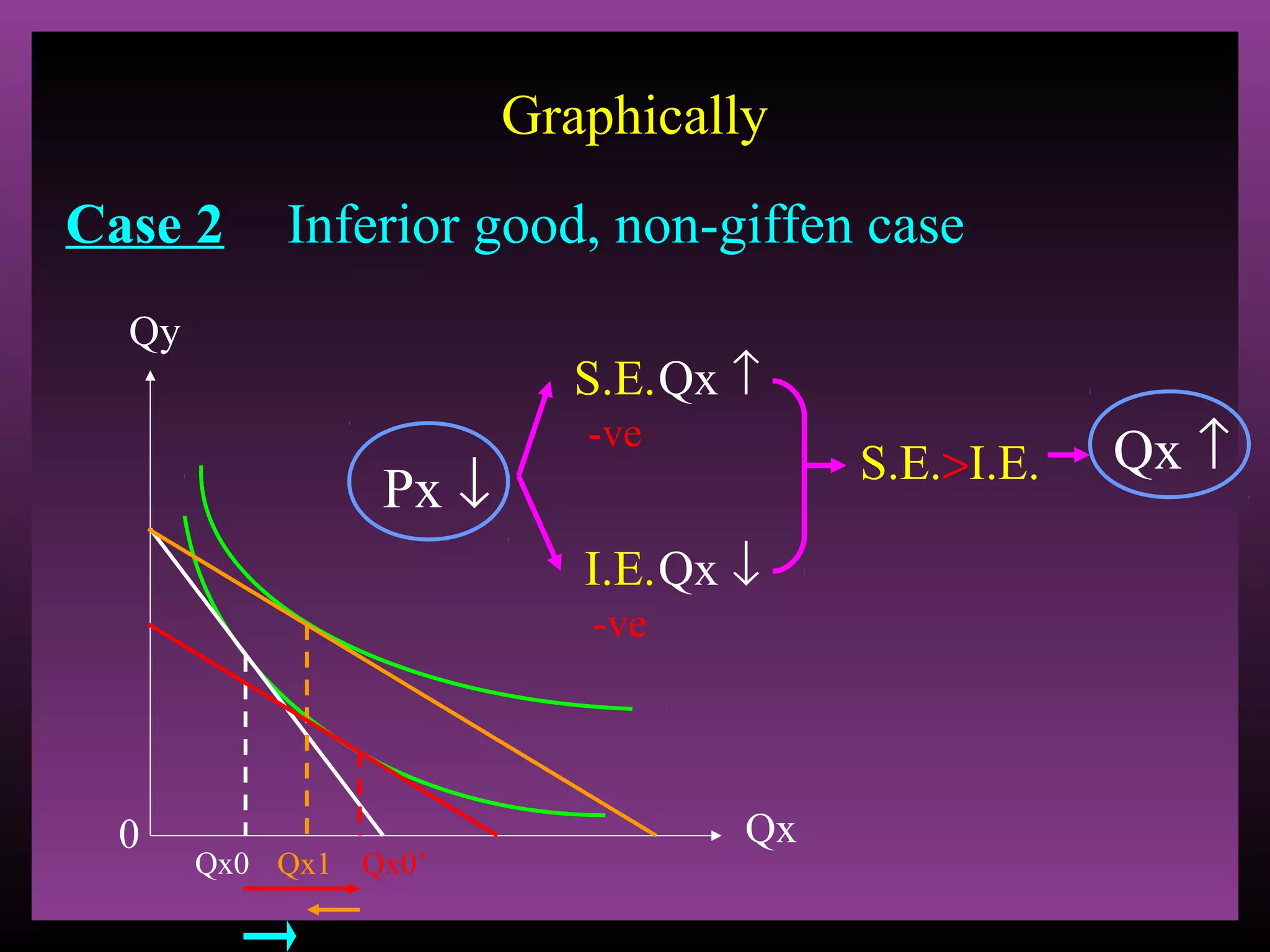
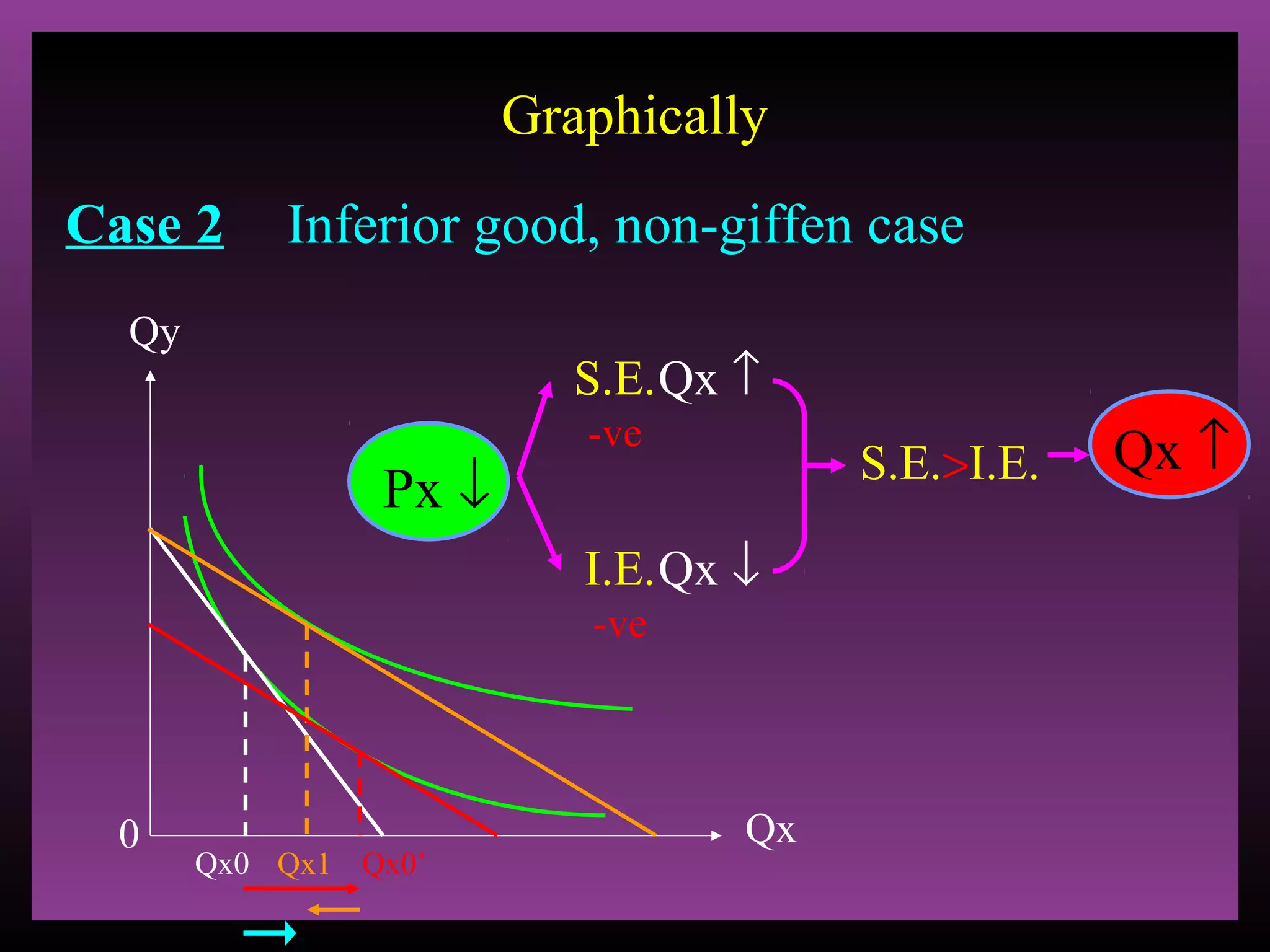
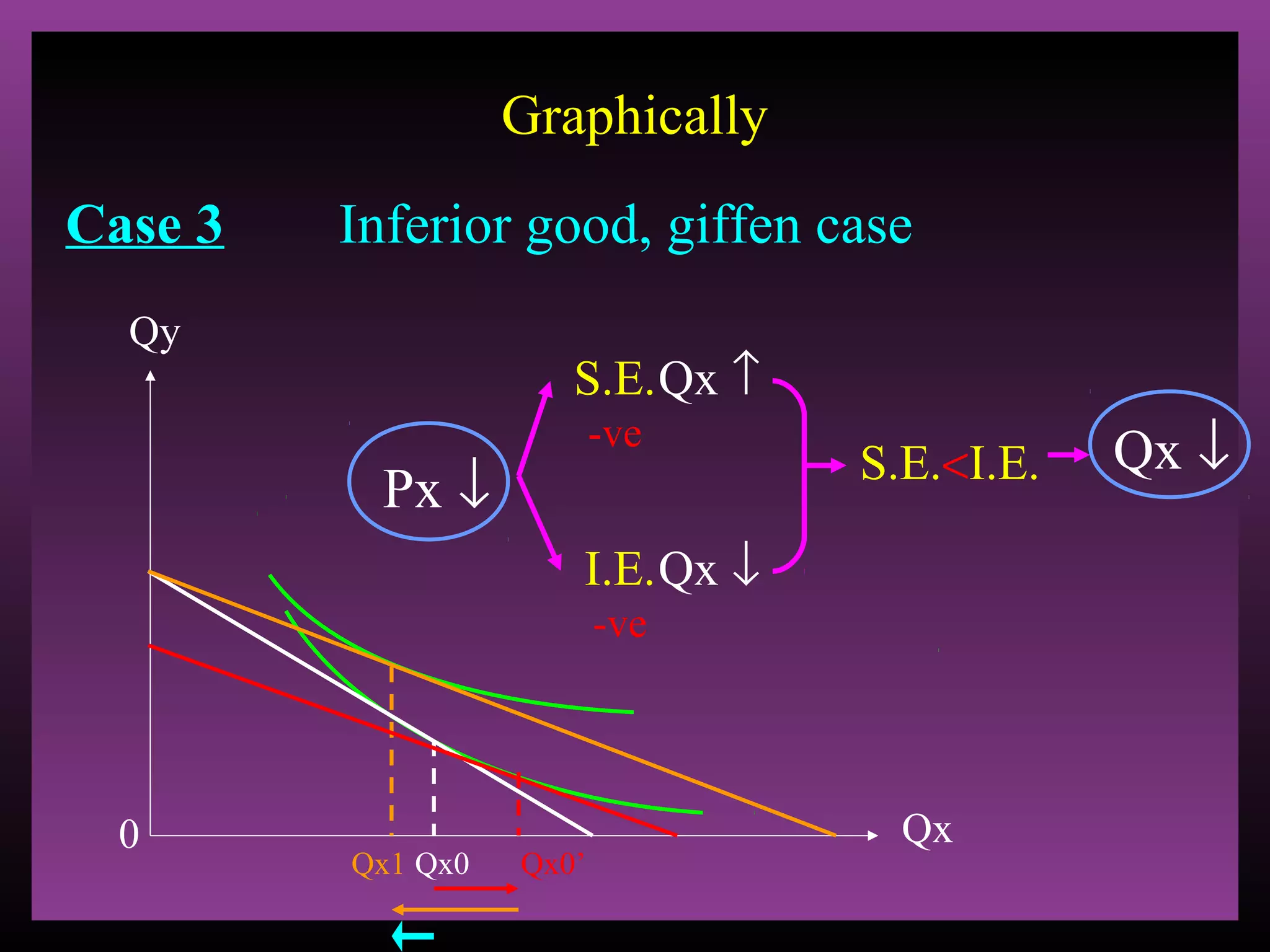
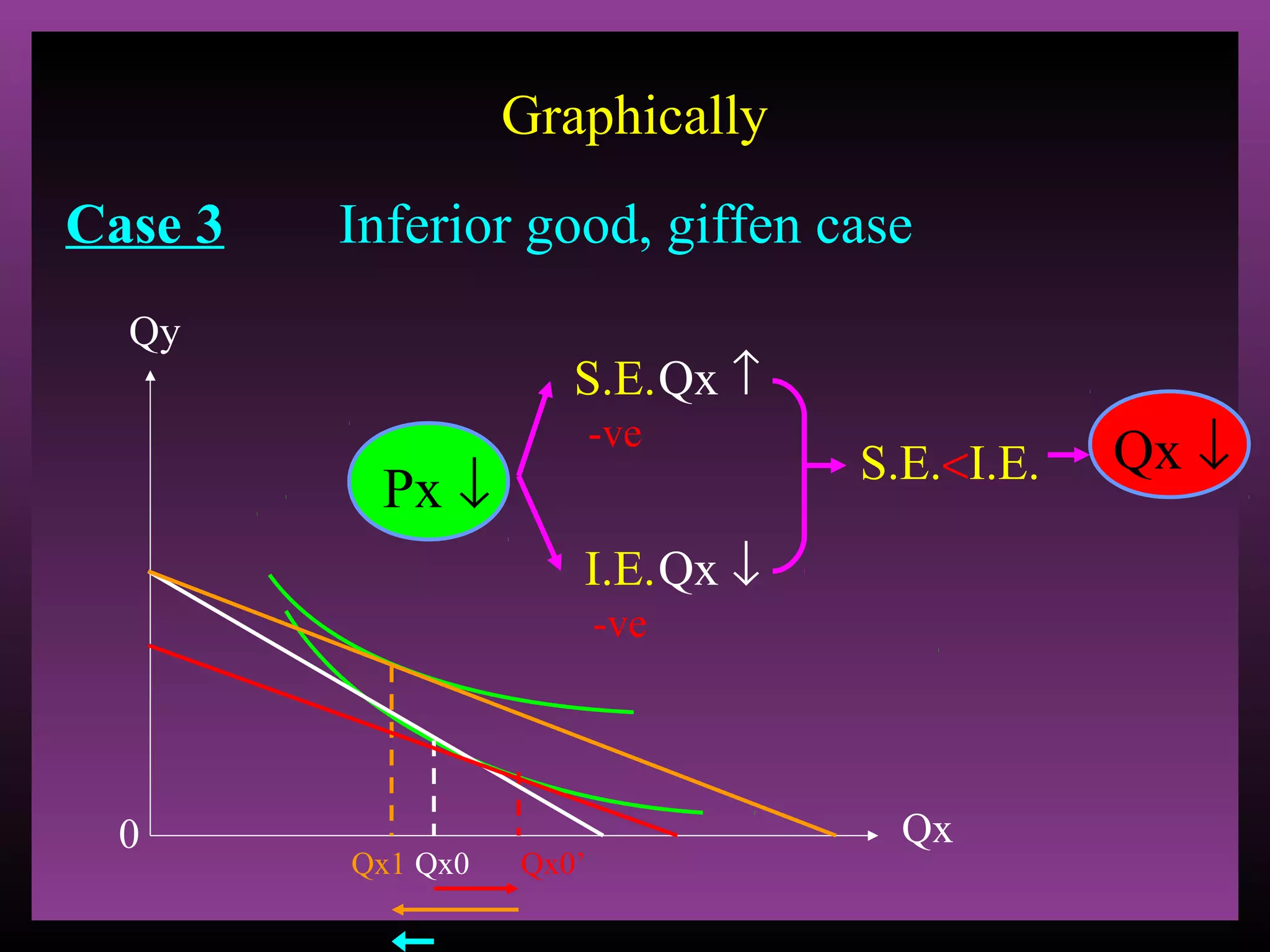
The document defines the substitution effect, income effect, and price effect. The substitution effect refers to changes in quantity demanded from a change in relative price holding income constant. The income effect refers to changes from a change in real income holding price constant. The price effect is the total change from a price change and equals the substitution effect plus the income effect. A price decrease can lead to an increase, decrease, or no change in quantity demanded depending on whether the good is normal or inferior and the relative magnitude of the substitution and income effects.