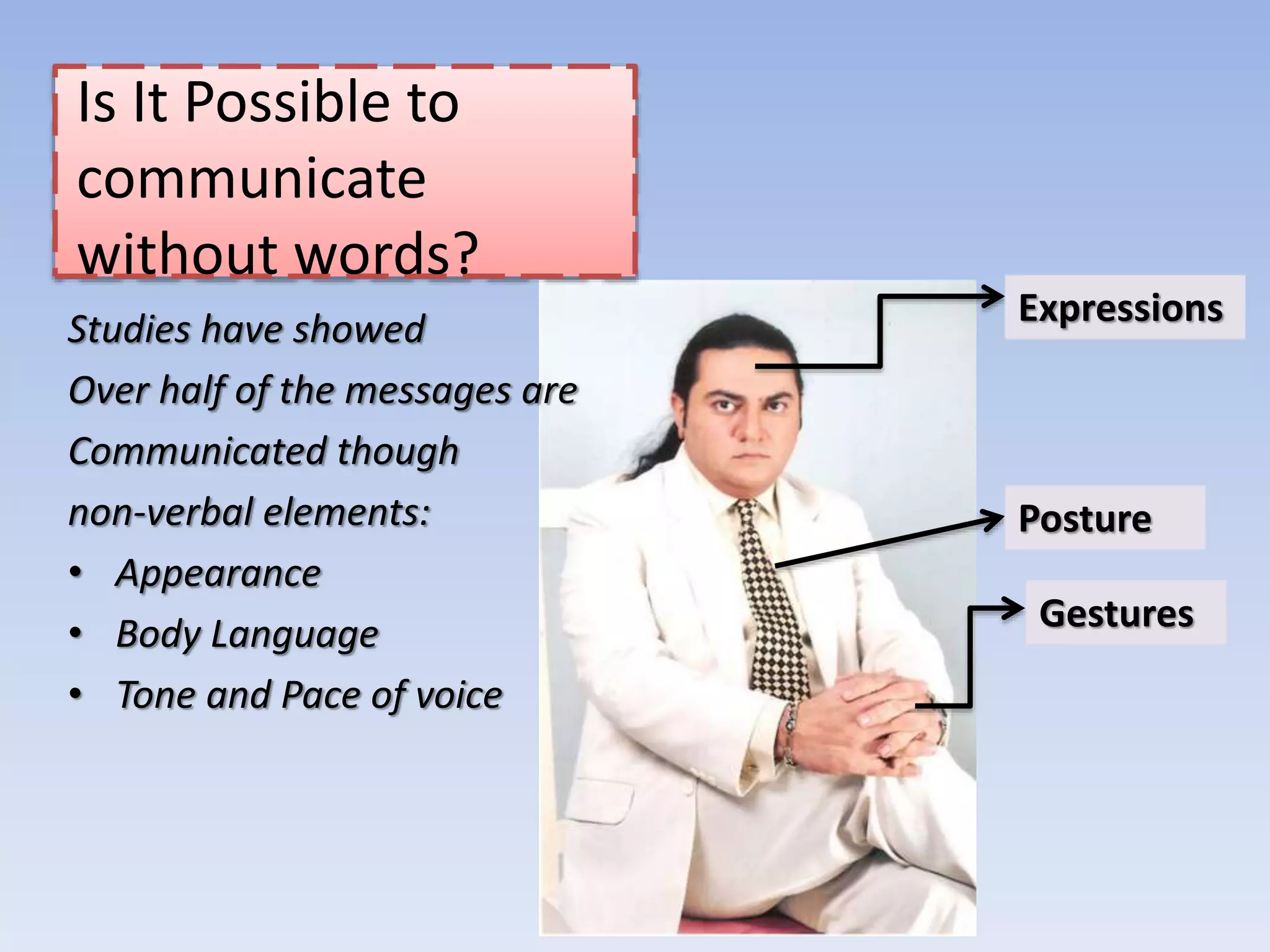
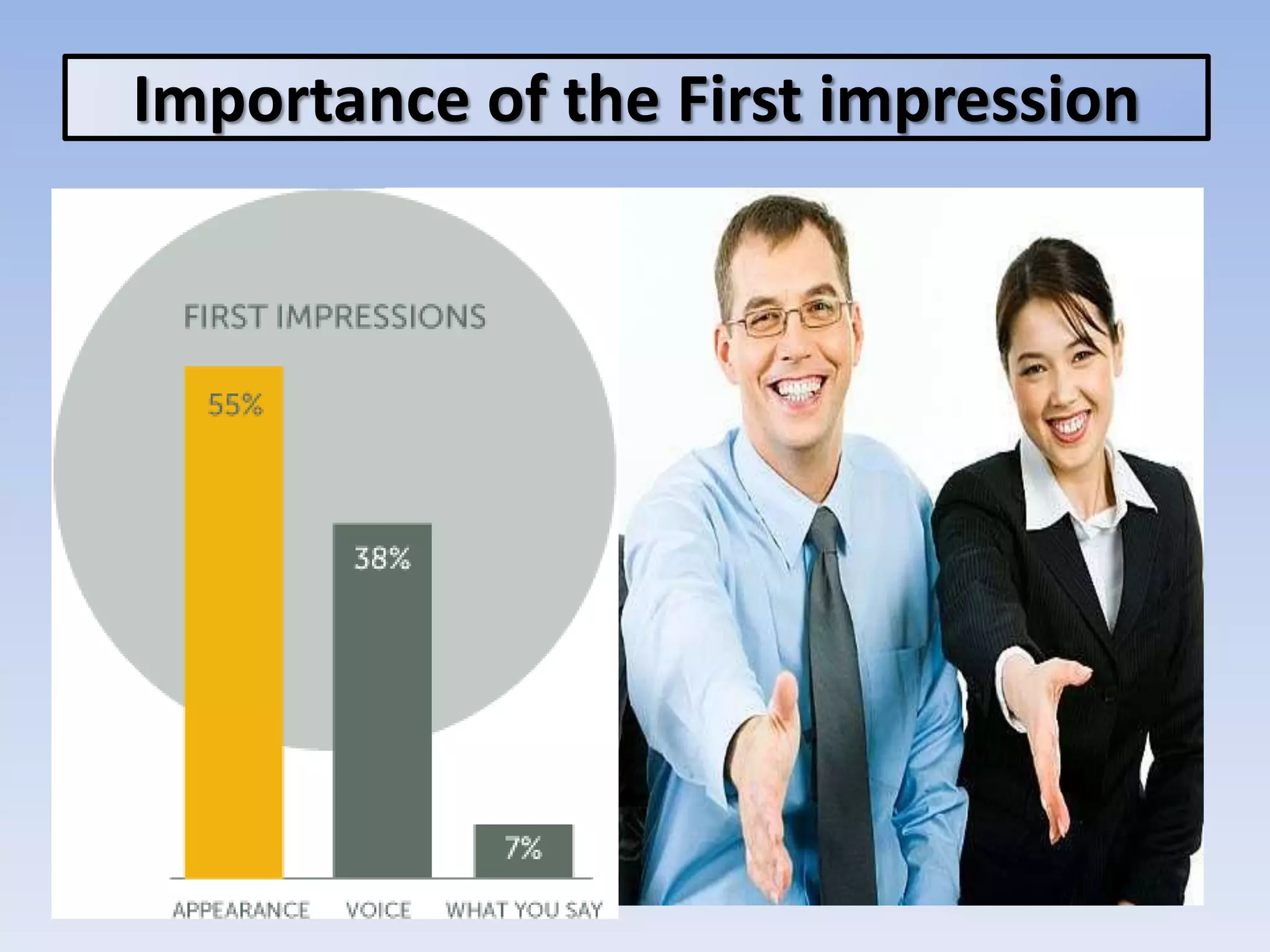
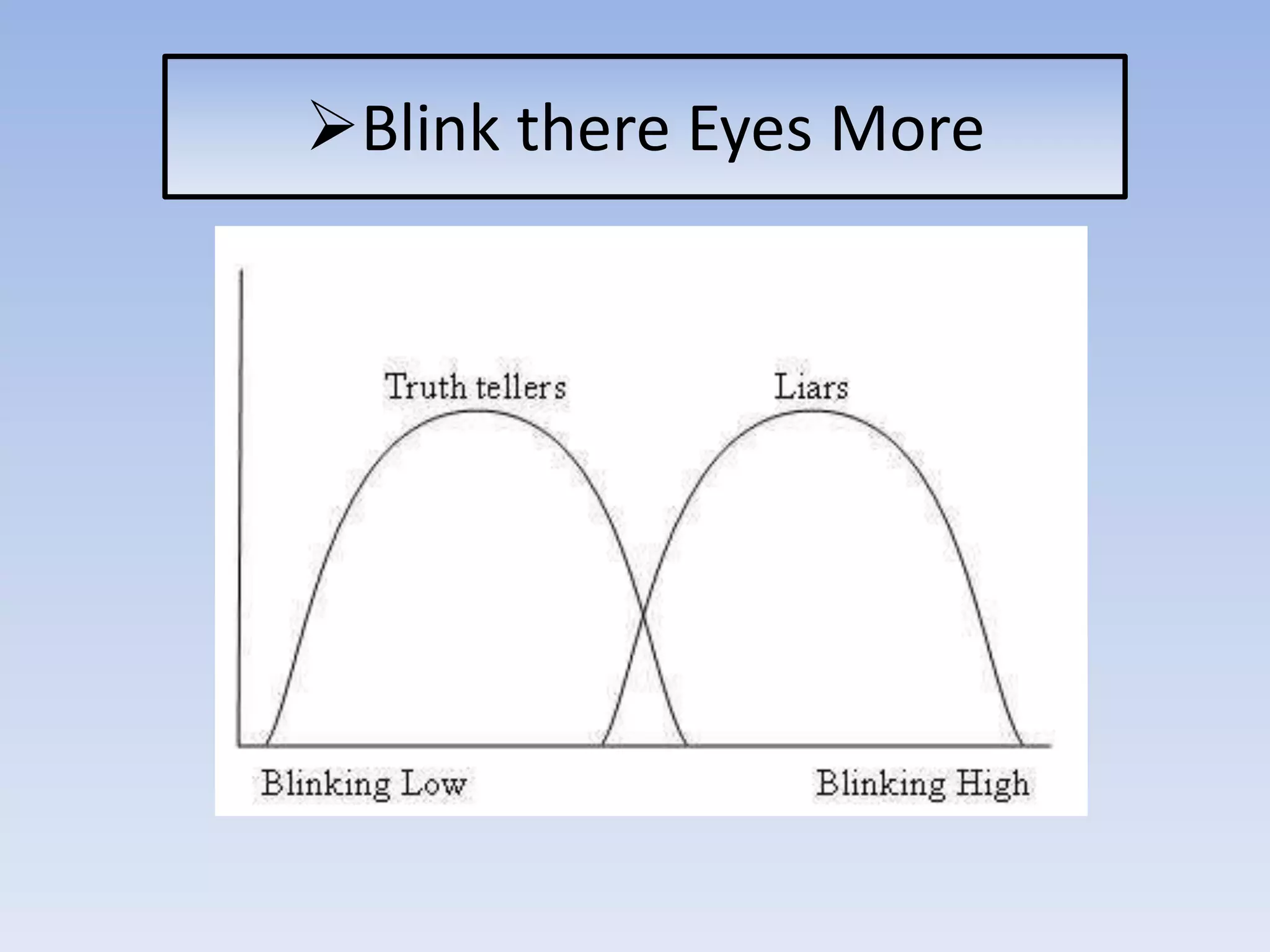
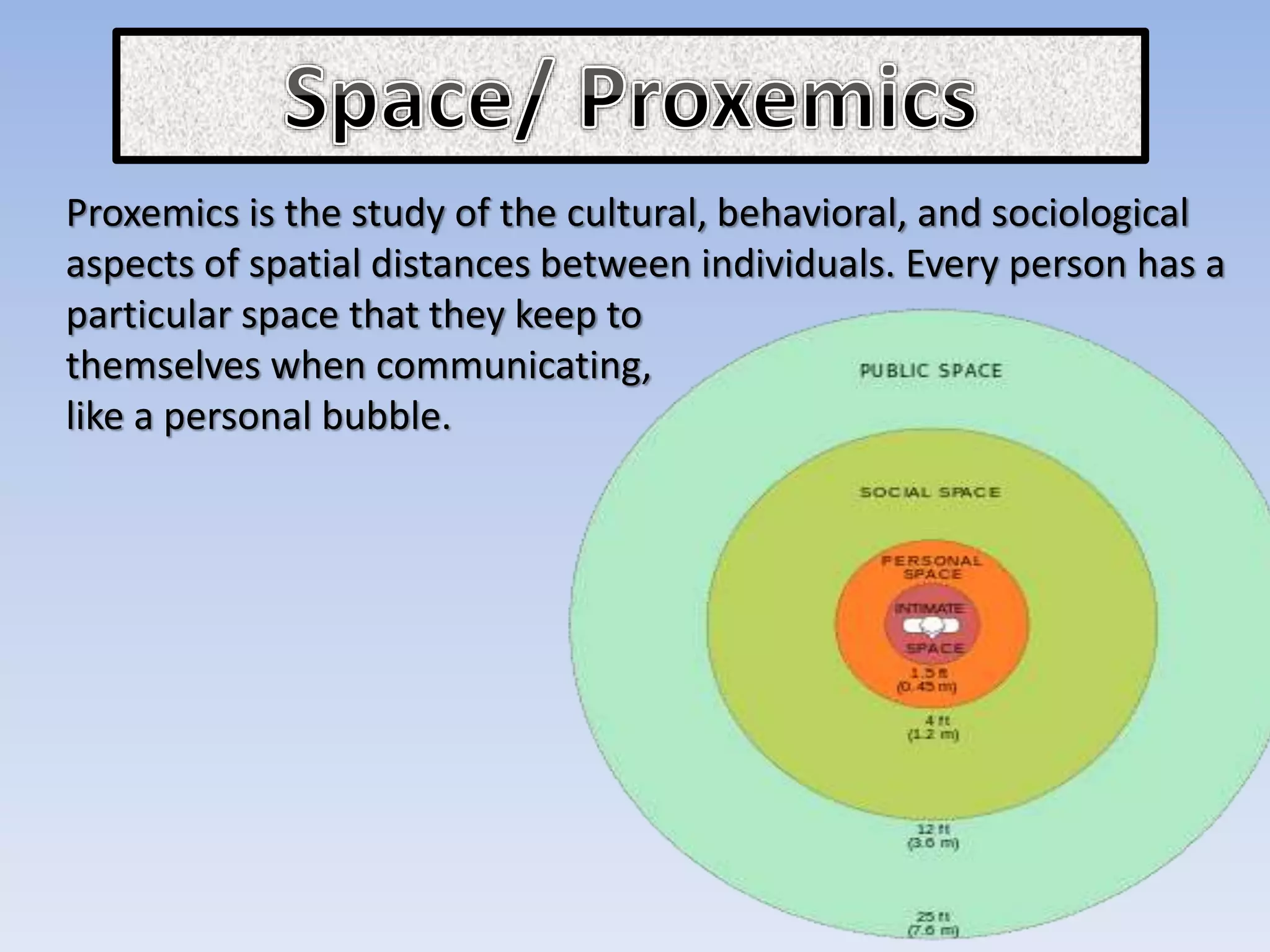
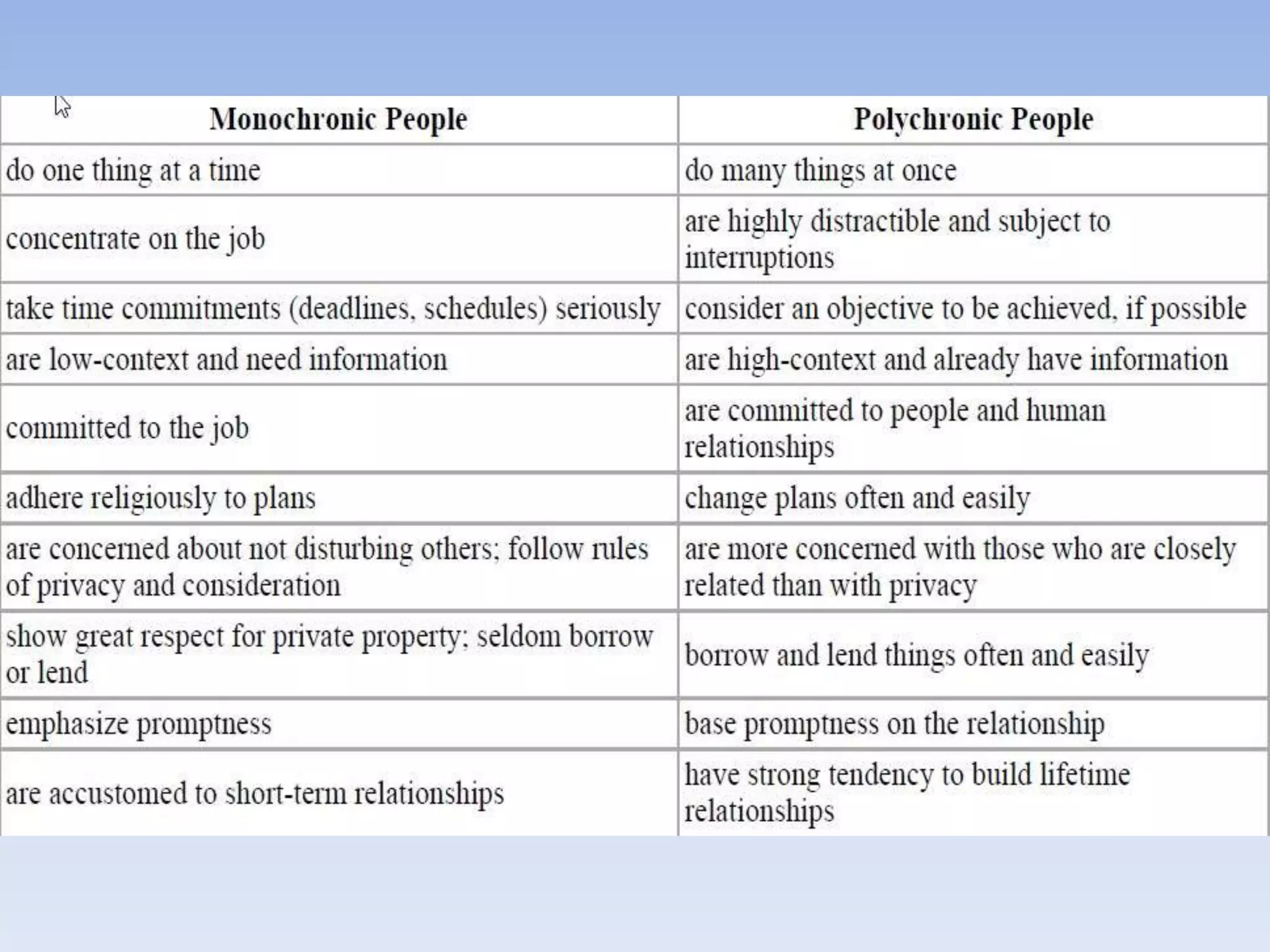
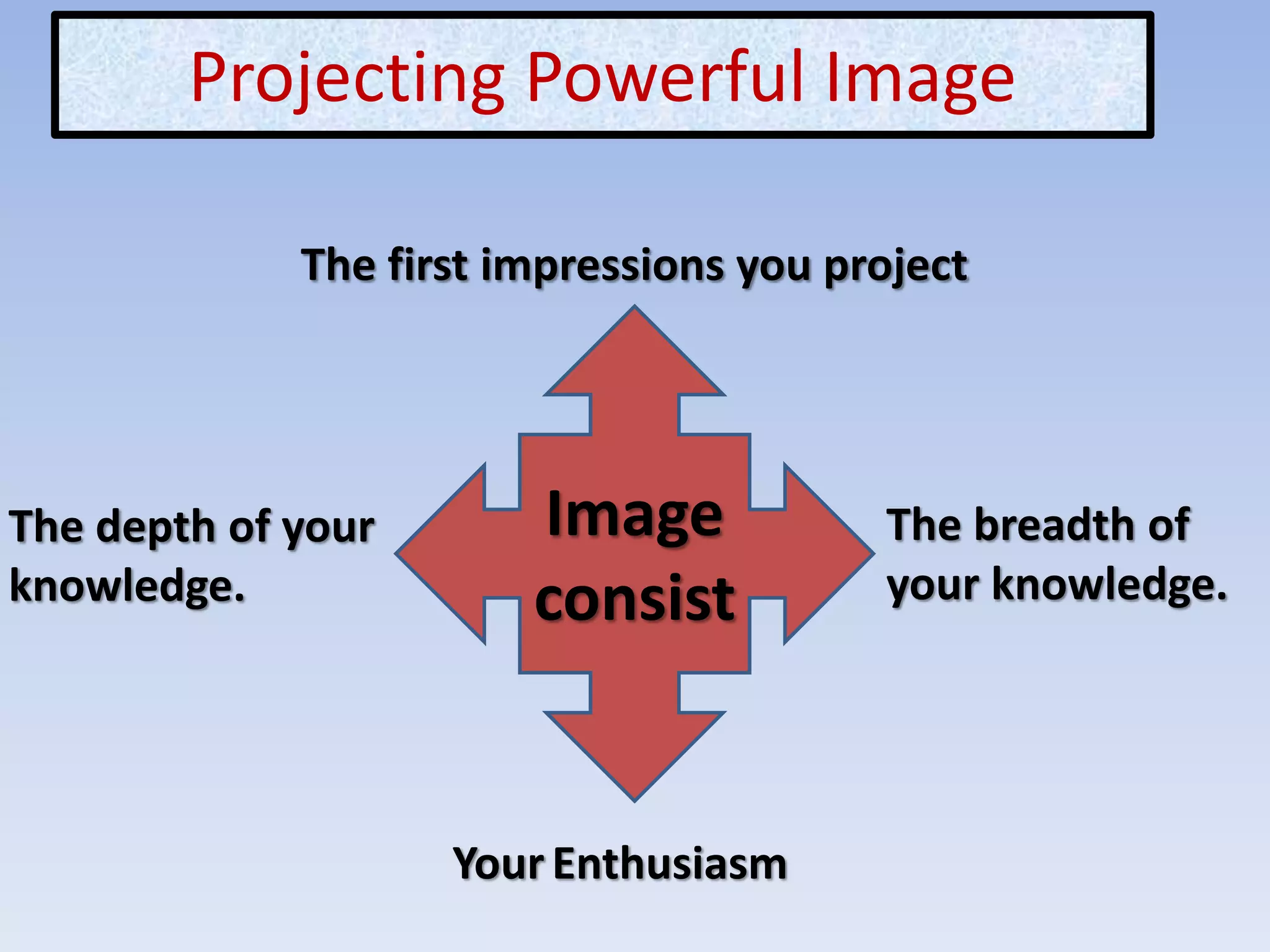
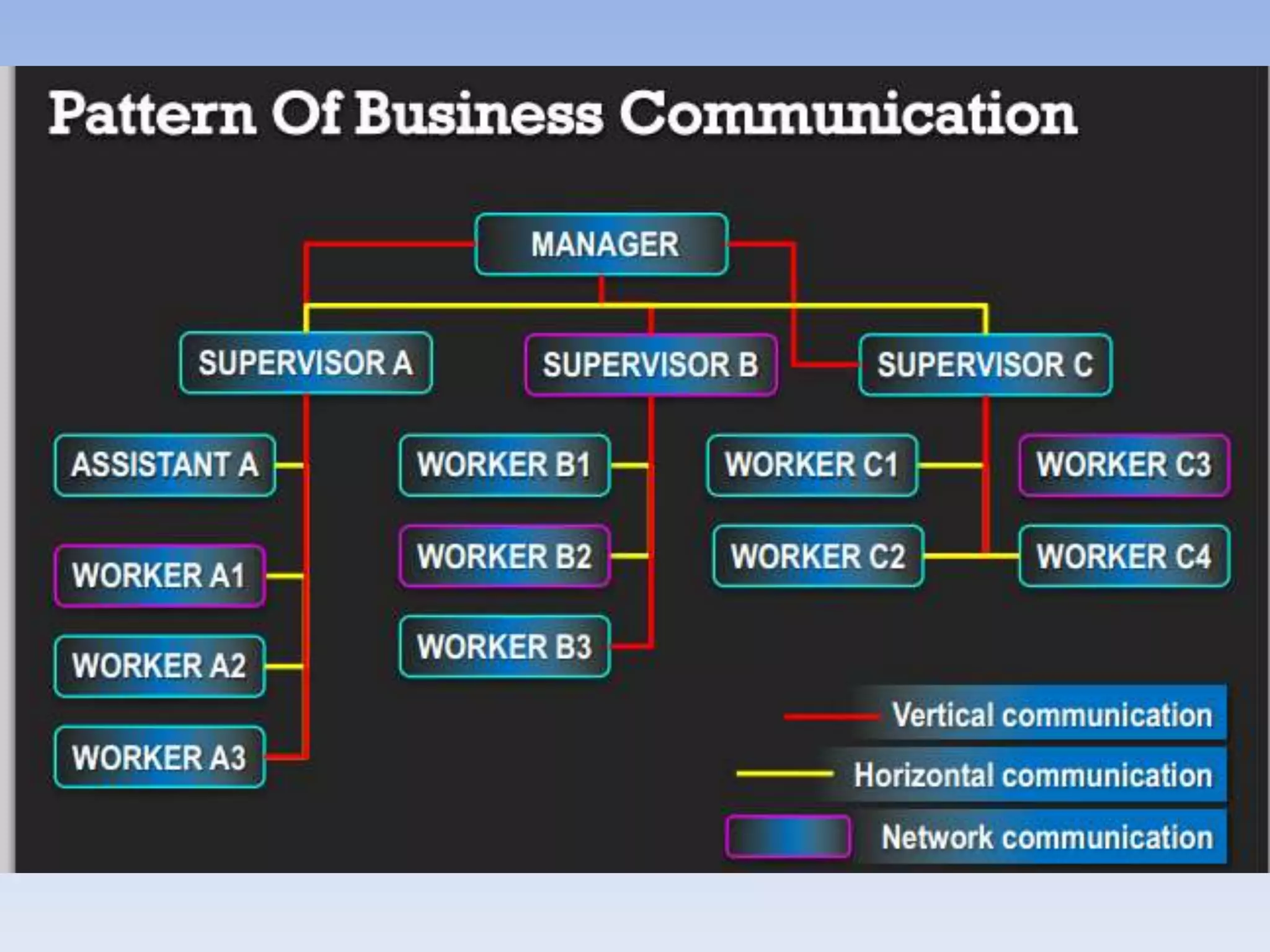
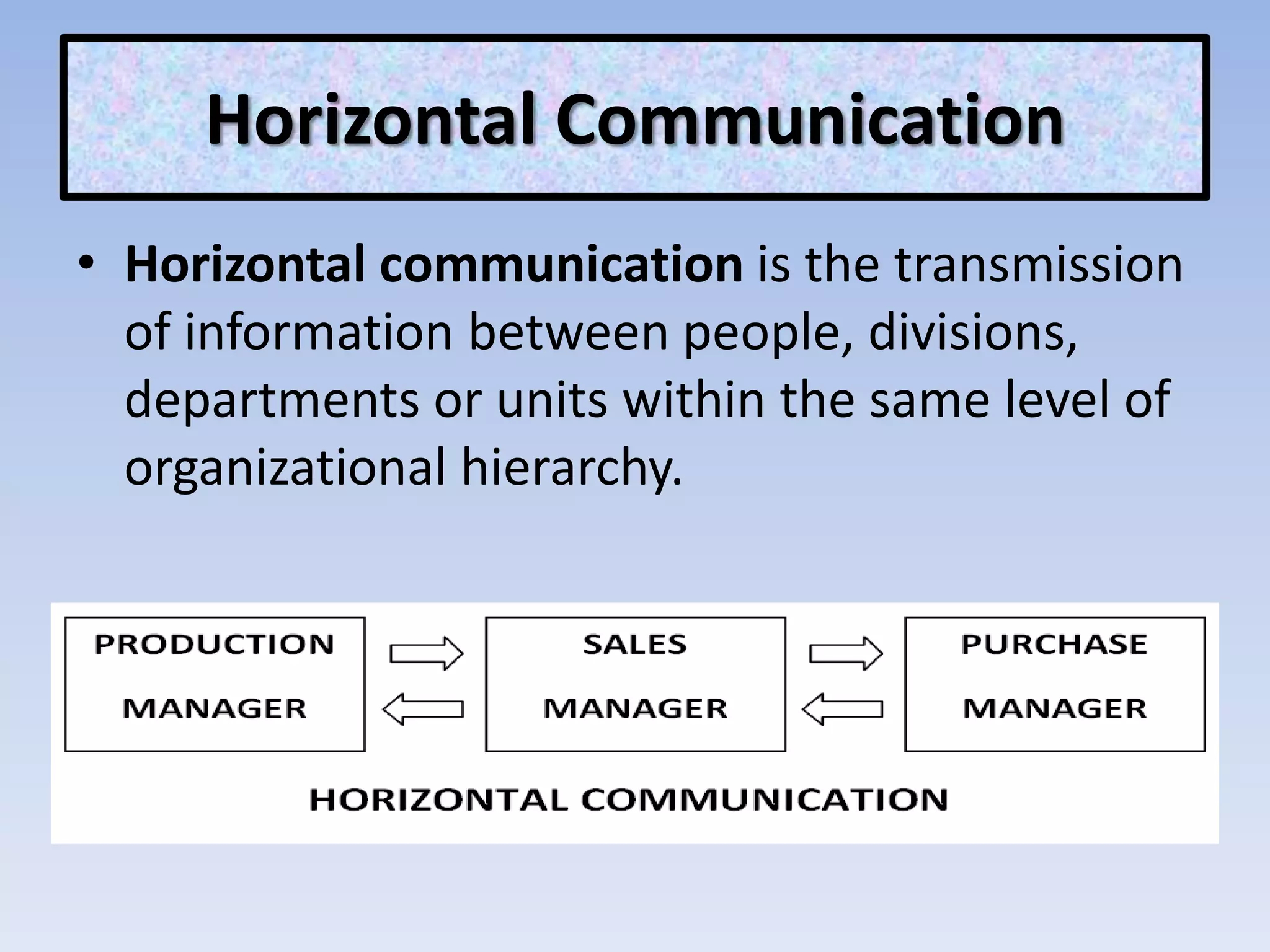
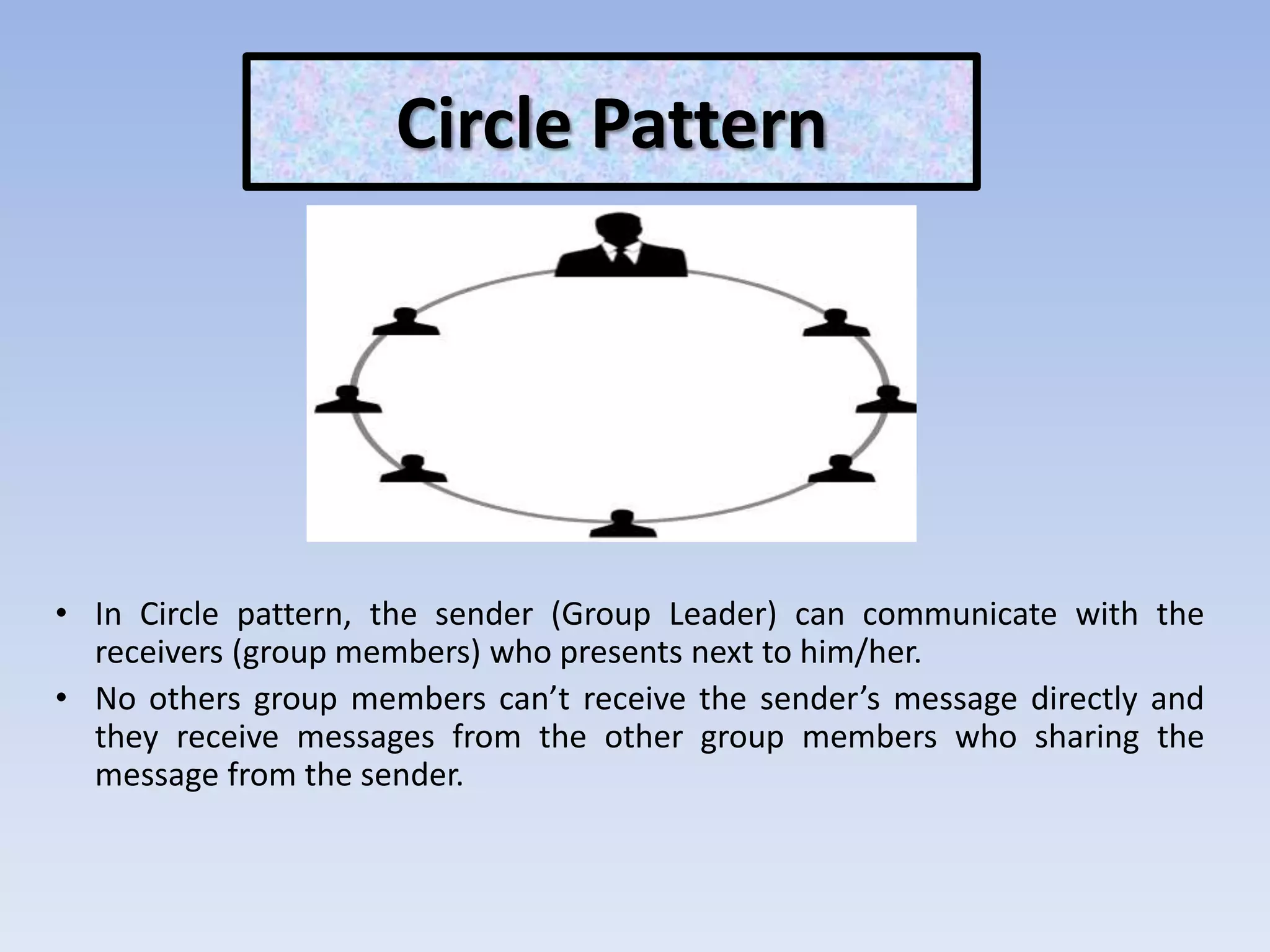
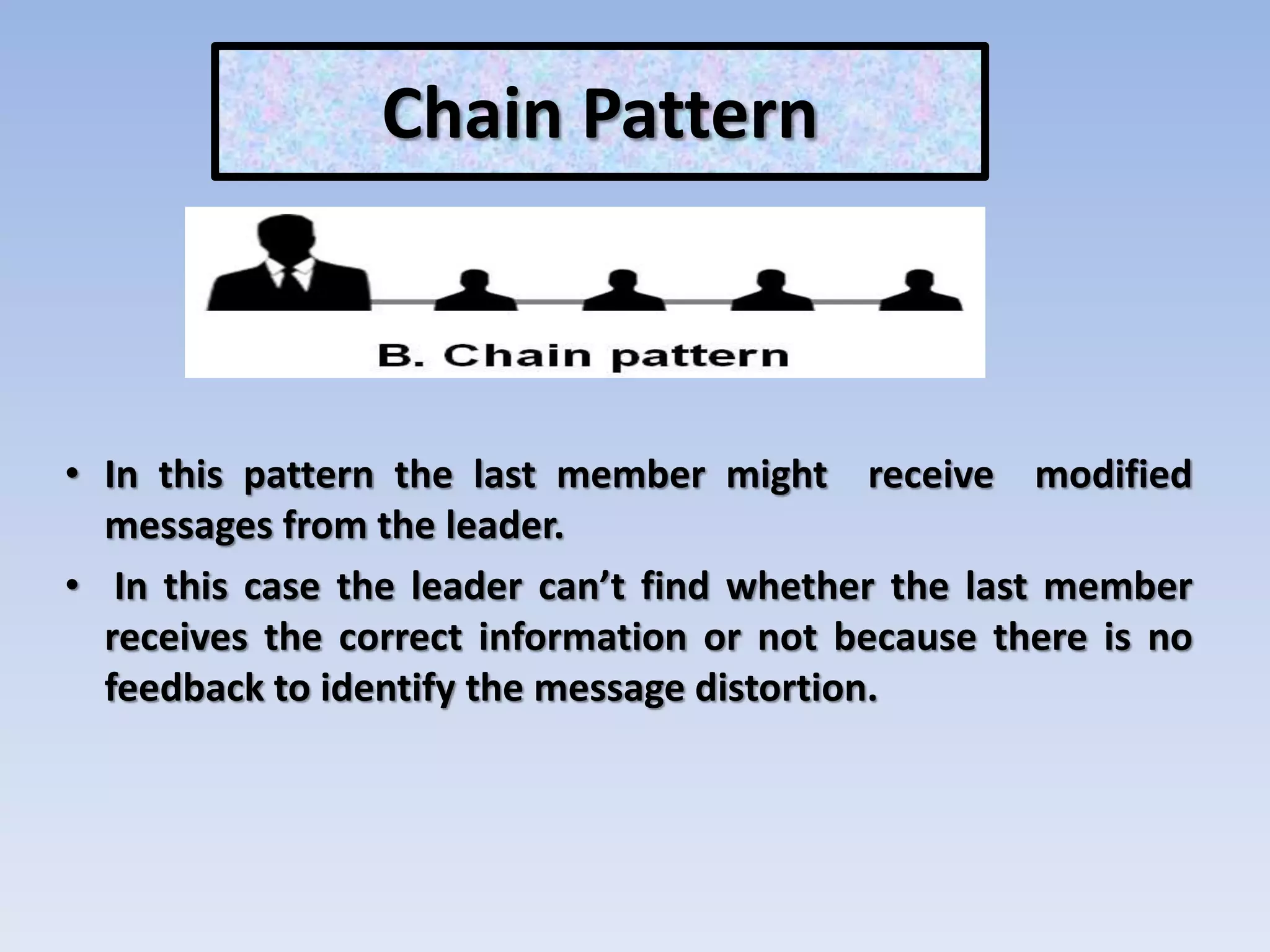
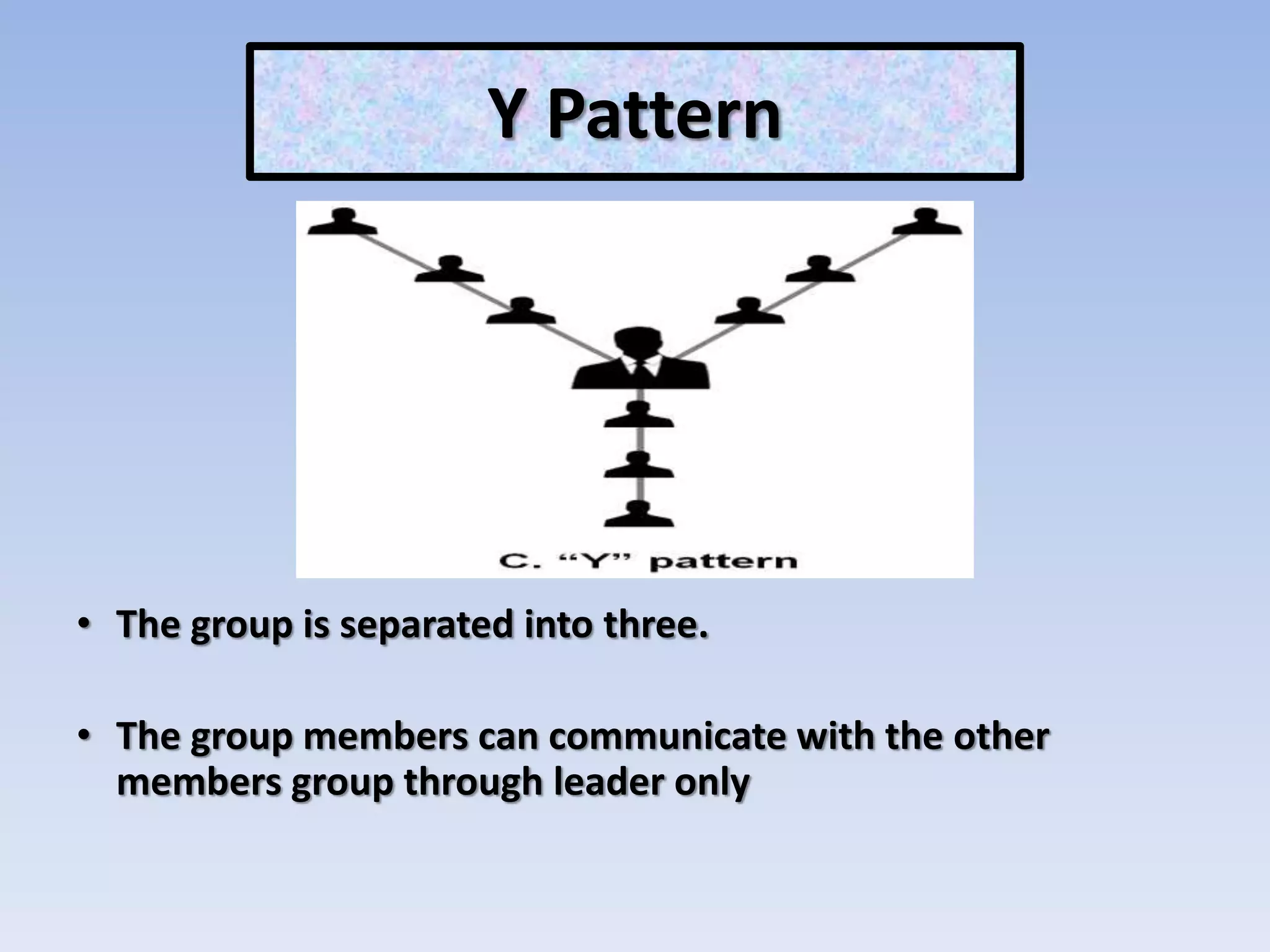
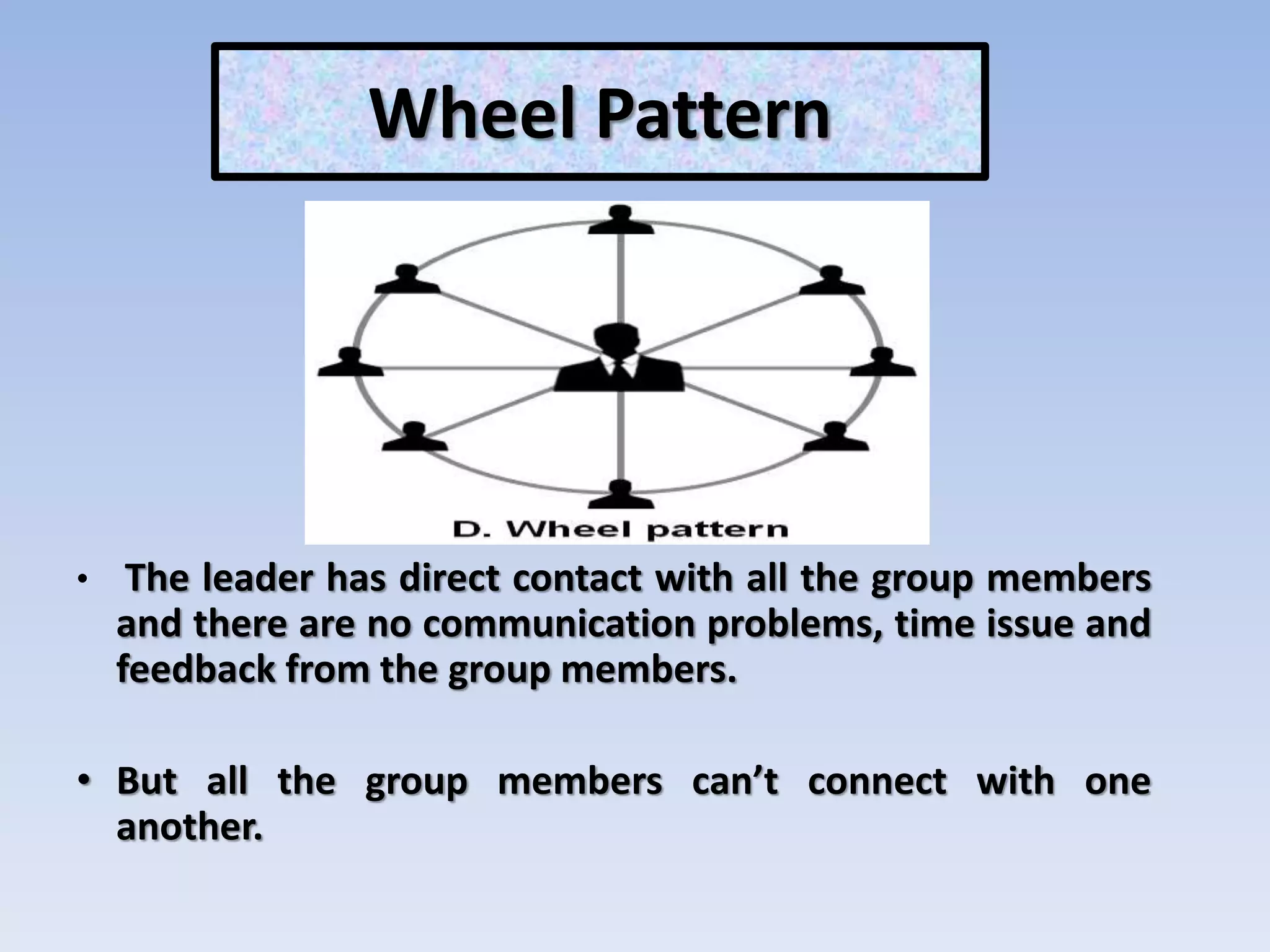
The document discusses various aspects of non-verbal communication including principles, types of non-verbal cues, and patterns of communication. It covers how over half of communication is non-verbal through cues like body language, tone, and expressions. Principles discussed include non-verbal messages being ambiguous and having cultural influences. Types of non-verbal cues explained are proxemics, chronemics, appearance, environment, and projecting a powerful image through factors like voice, knowledge, and enthusiasm. Patterns of communication described are horizontal, vertical, and in groups through circle, chain, wheel, and Y patterns.