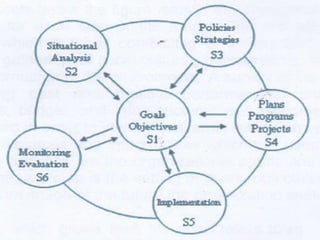
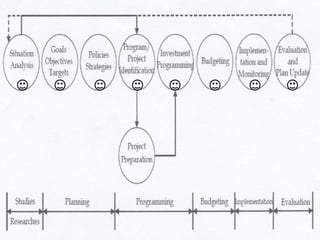
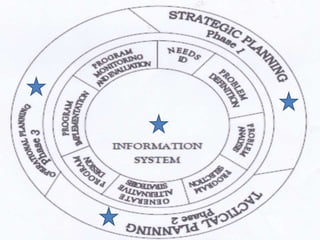
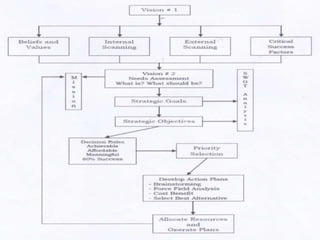
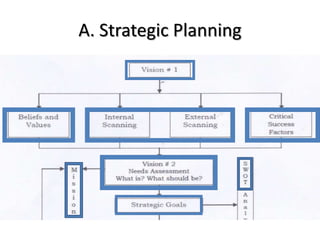
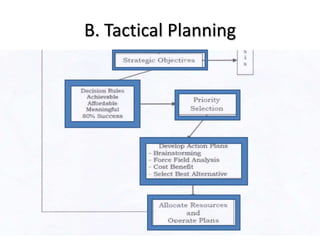
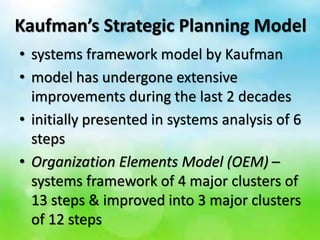
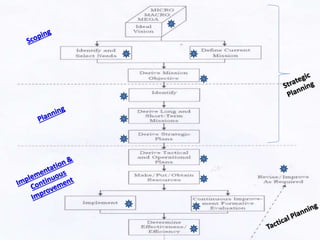
The document outlines various educational planning models, detailing the processes and steps involved in effective planning, including situational analysis, goal-setting, policy development, program prioritization, budgeting, implementation, and evaluation. It introduces models like Bell's, Herman's, Kaufman's, and Franco's, each providing frameworks for strategic, tactical, and operational planning in educational contexts. Emphasis is placed on continuous improvement and adaptation to both internal and external environments to achieve desired educational outcomes.