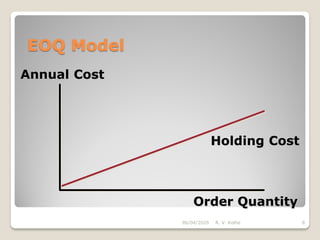
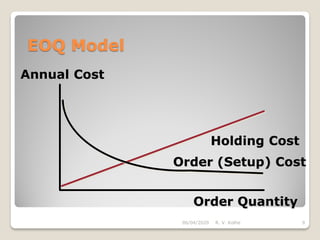
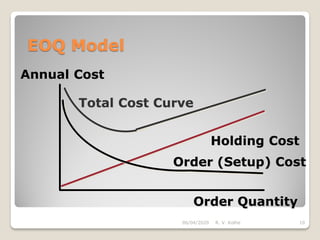
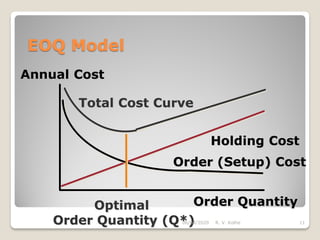
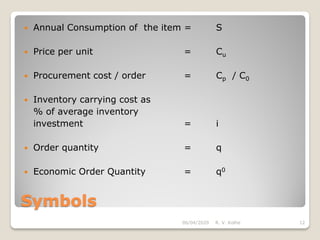
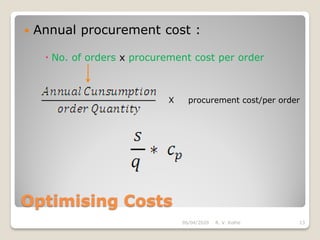
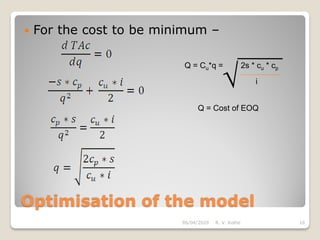
This document discusses the economic order quantity (EOQ) model, which helps determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. It describes the different types of inventory costs, including carrying costs, ordering costs, and shortage costs. The EOQ model balances these costs - large orders reduce ordering costs but increase carrying costs, while small orders are the opposite. The document provides the formula for calculating the EOQ and defines the symbols used. It also shows graphs depicting how total costs vary with order quantity and how the EOQ is the quantity that minimizes total costs.