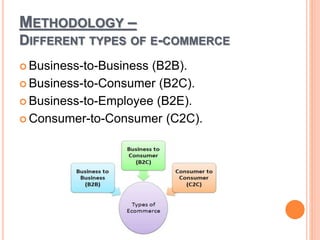
This document discusses e-commerce and its various types and aspects. It begins with introducing commerce and e-commerce. It then outlines the objectives of e-commerce like high reachability, conversions, customer satisfaction, and social popularity. The methodology section explains different types of e-commerce like B2B, B2C, B2E, and C2C. It also discusses topics like advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce and customer intimacy. The document presents findings from a study and provides recommendations to improve e-commerce adoption. It concludes that e-commerce has significantly grown the economy by changing consumer purchasing behavior.