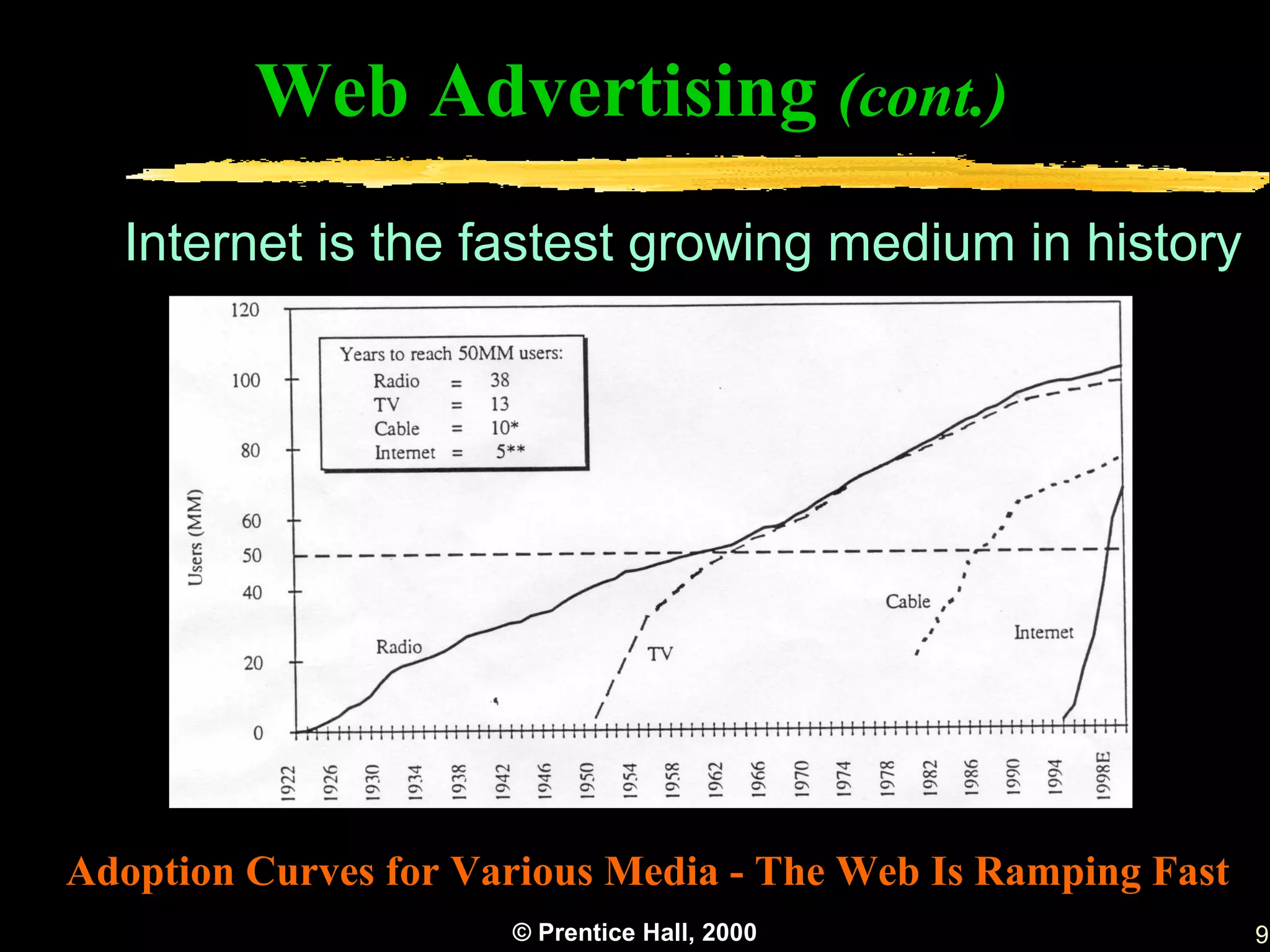
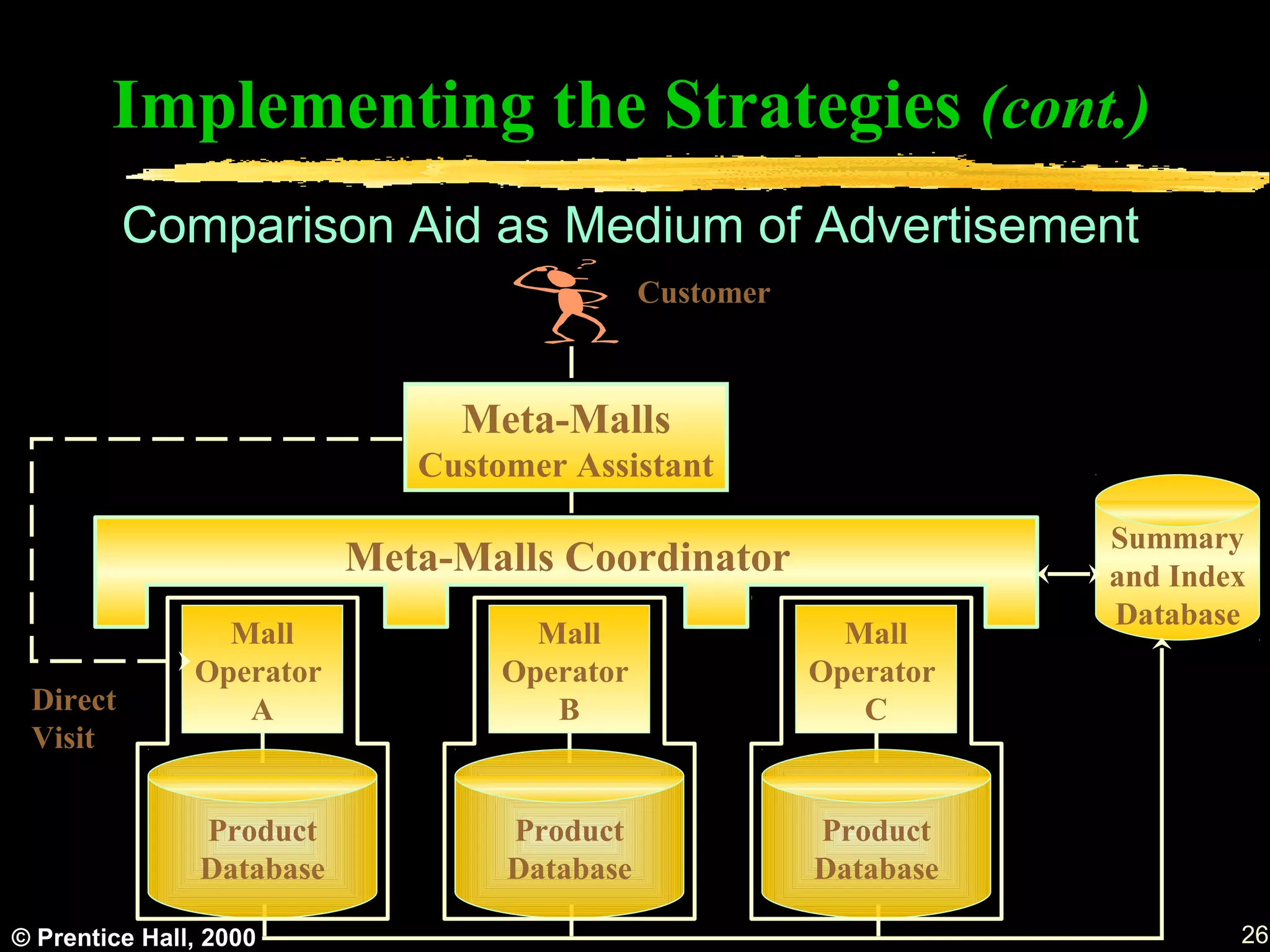
This document discusses various topics related to advertisement in electronic commerce, including objectives, types of ads, strategies, and methods. It describes common ad formats like banners, e-mail marketing, and push technology. It also covers measuring ad effectiveness, customized catalogs, and managing web traffic and standards. The overall aim is to introduce key concepts in online advertising.