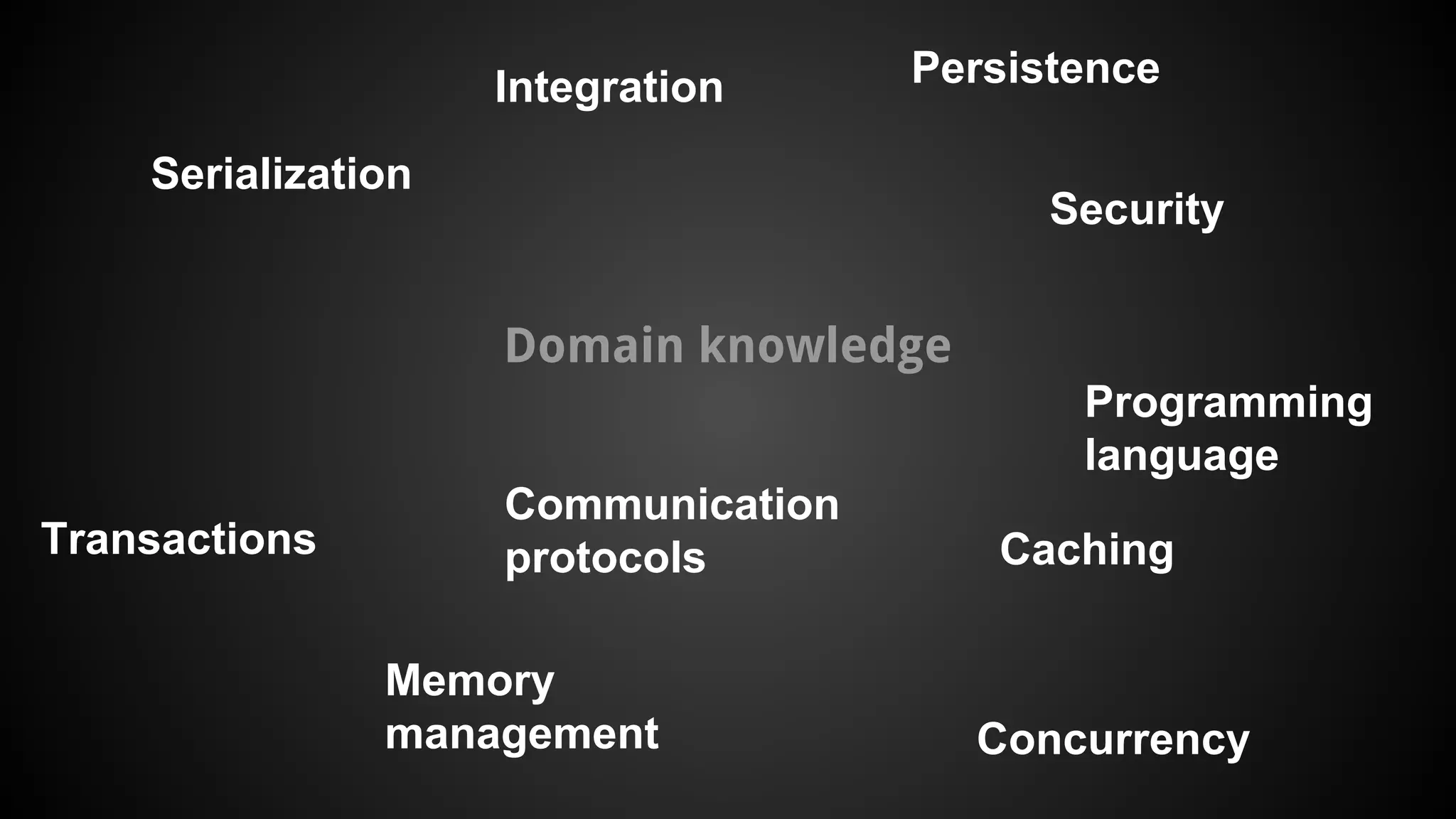
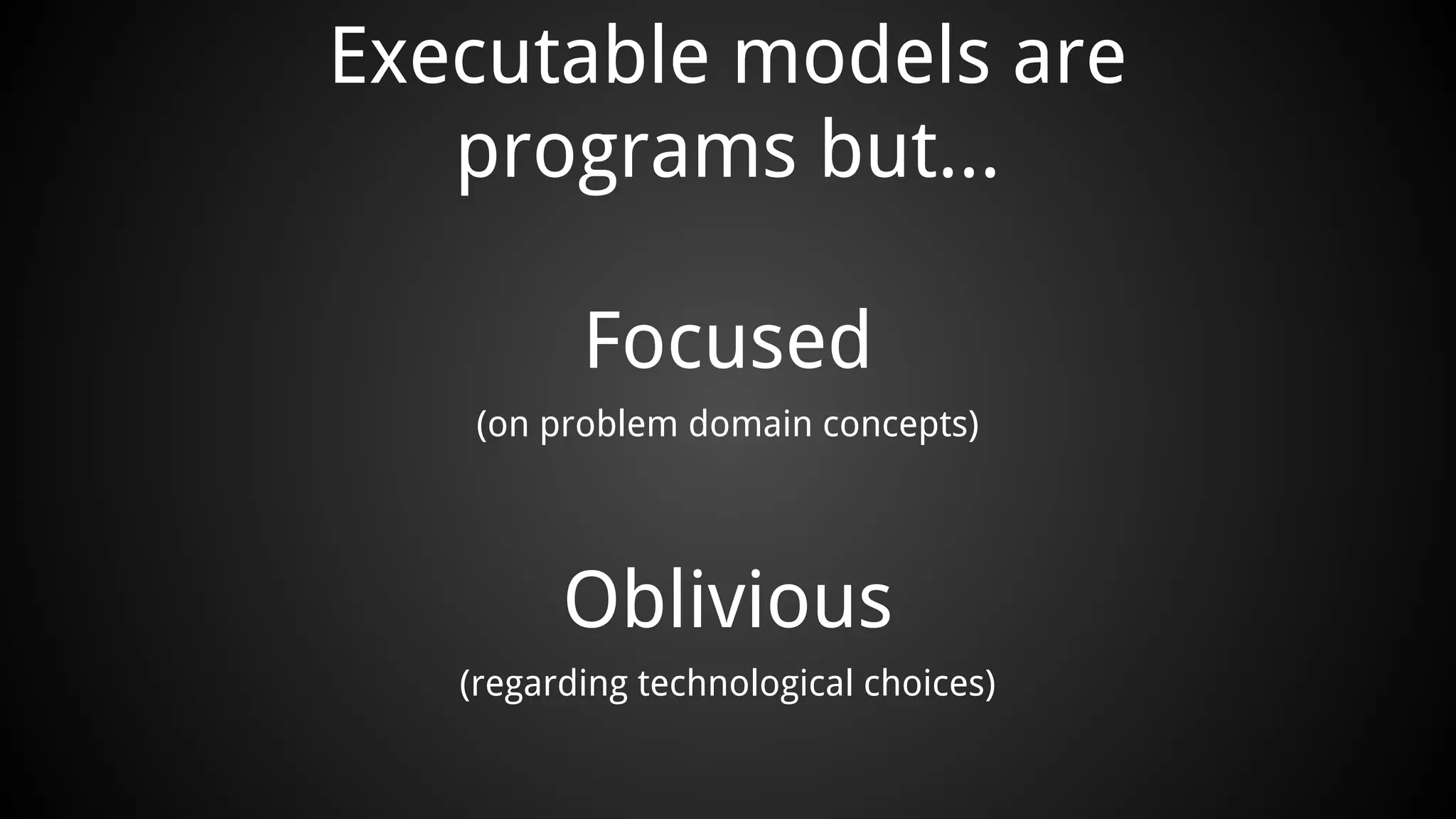
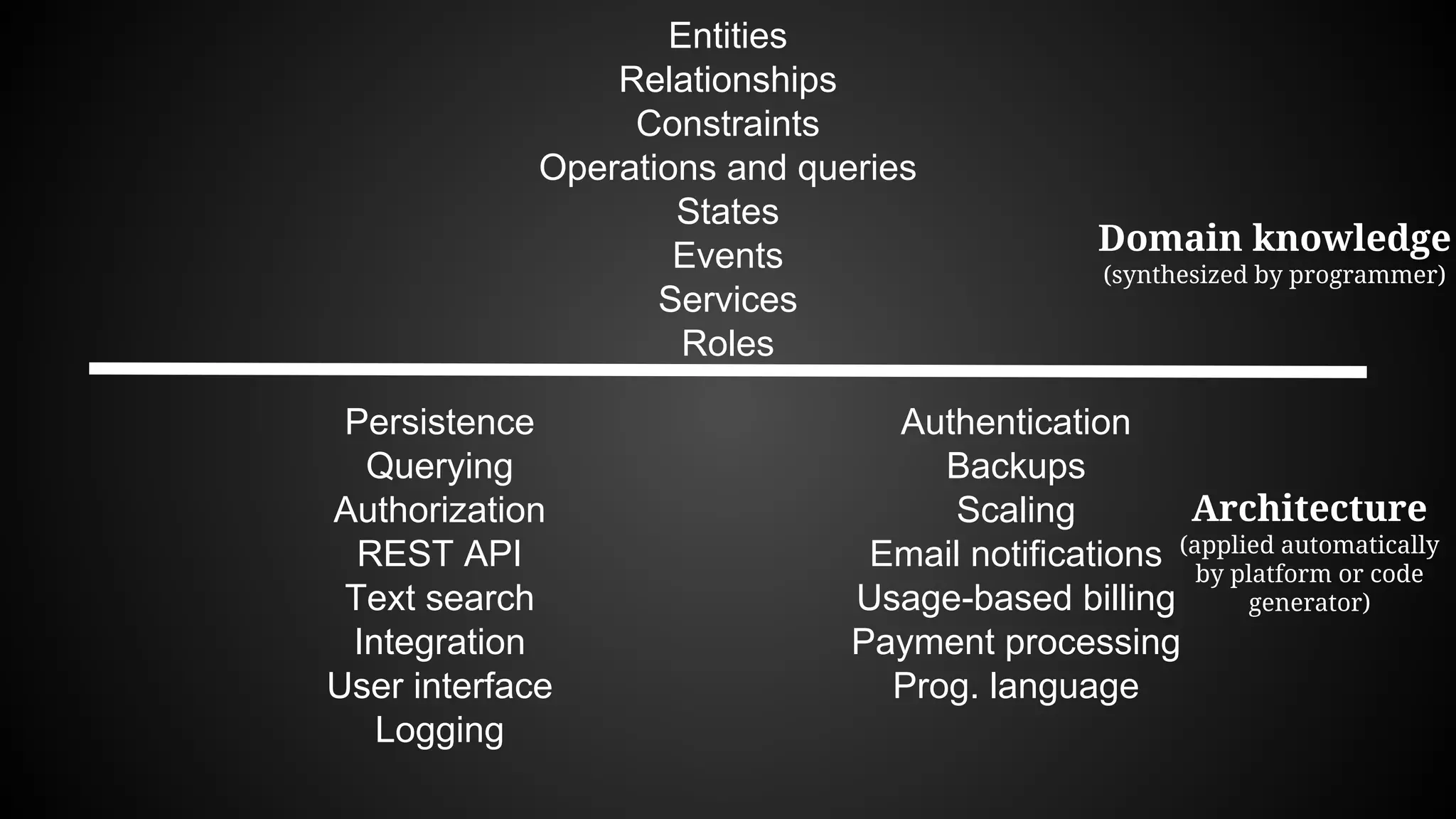
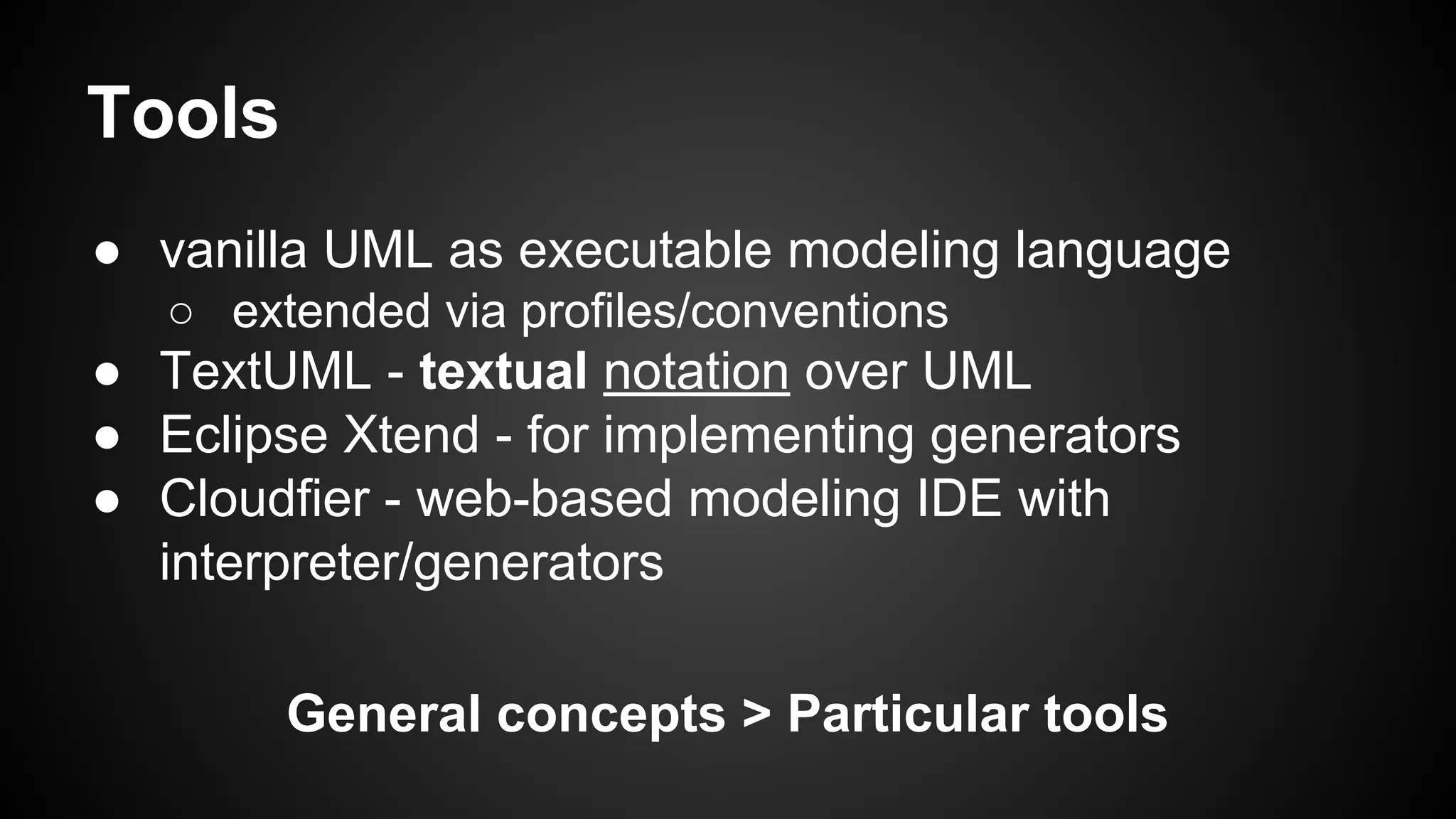
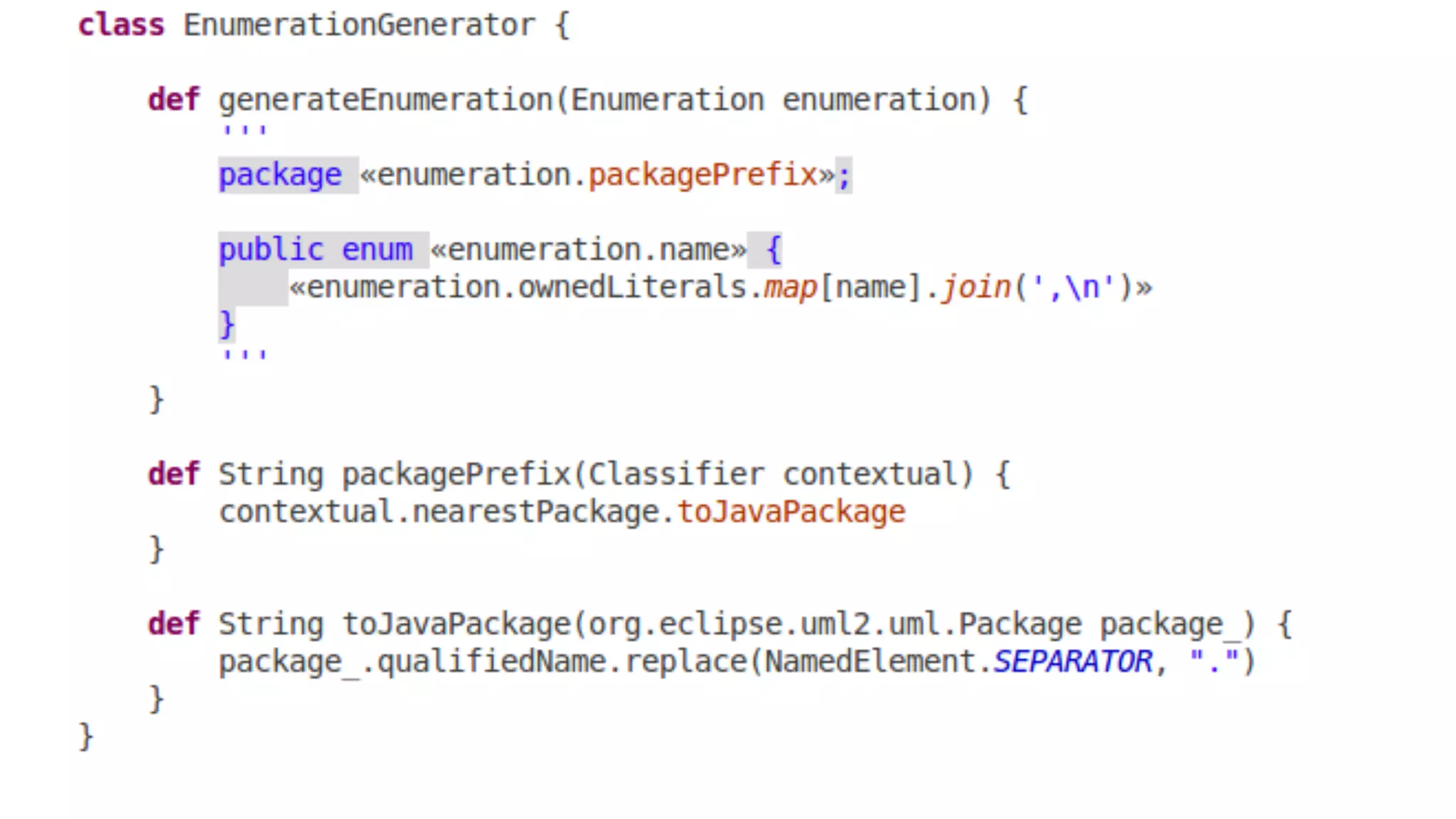
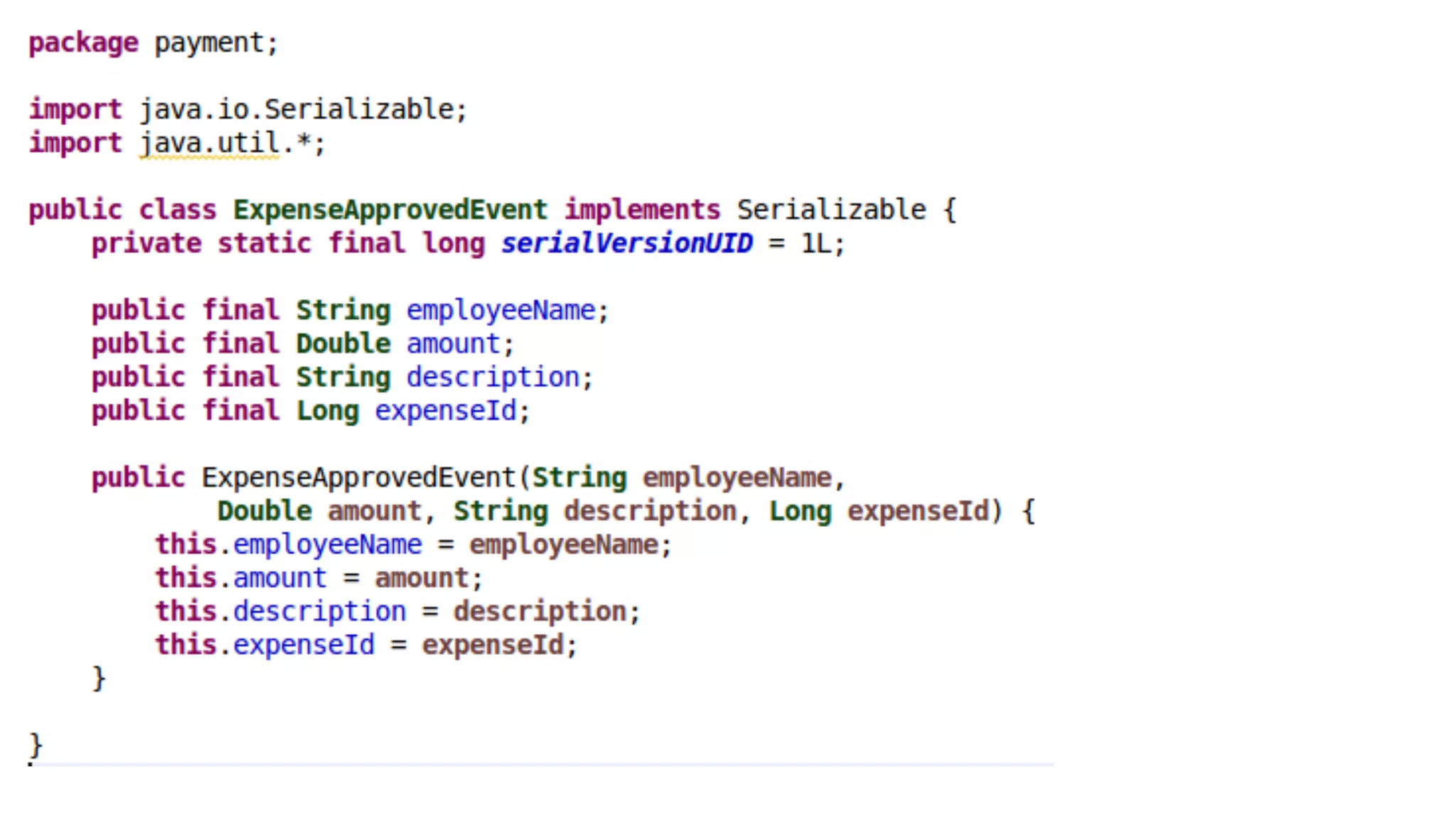
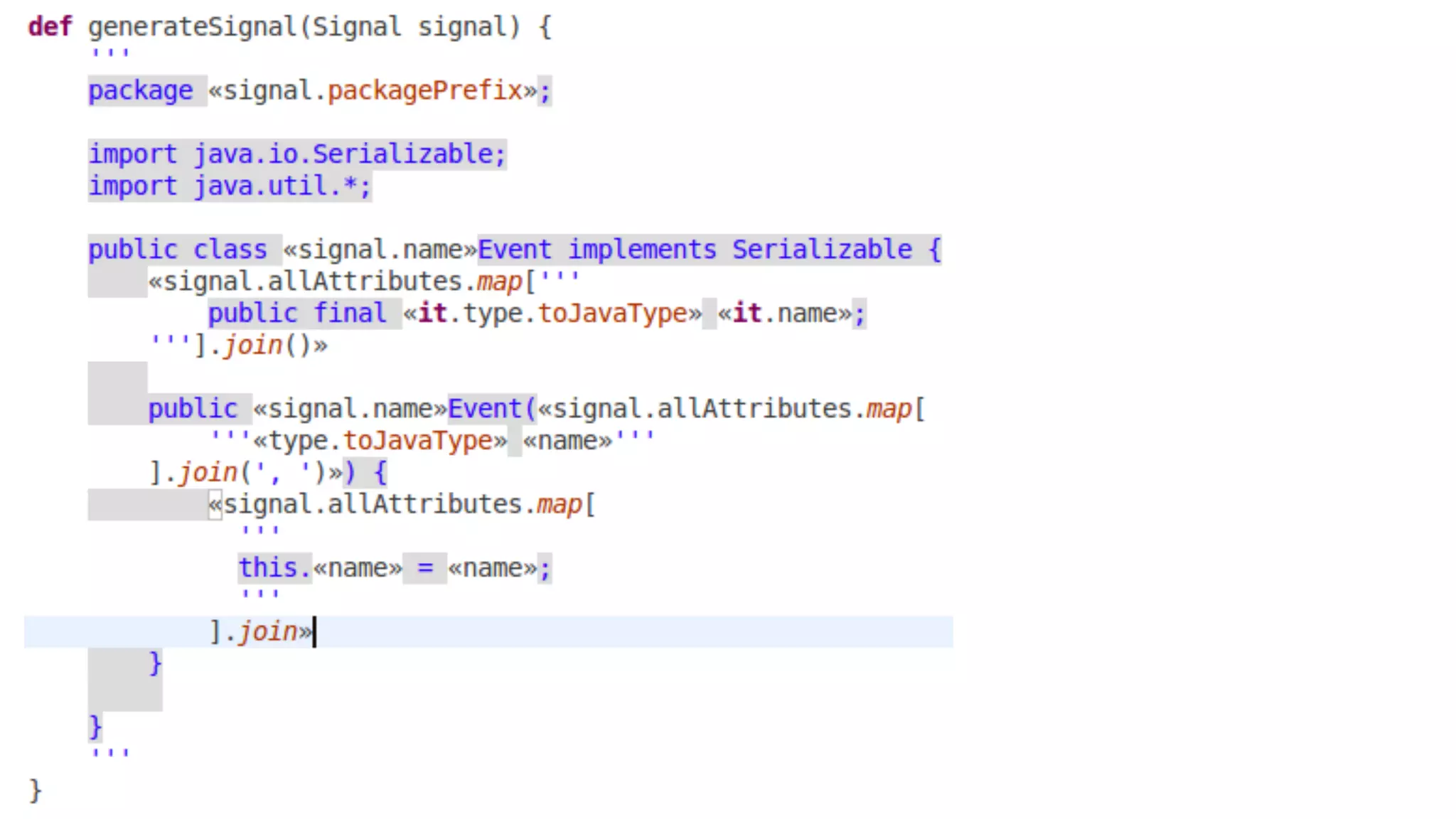
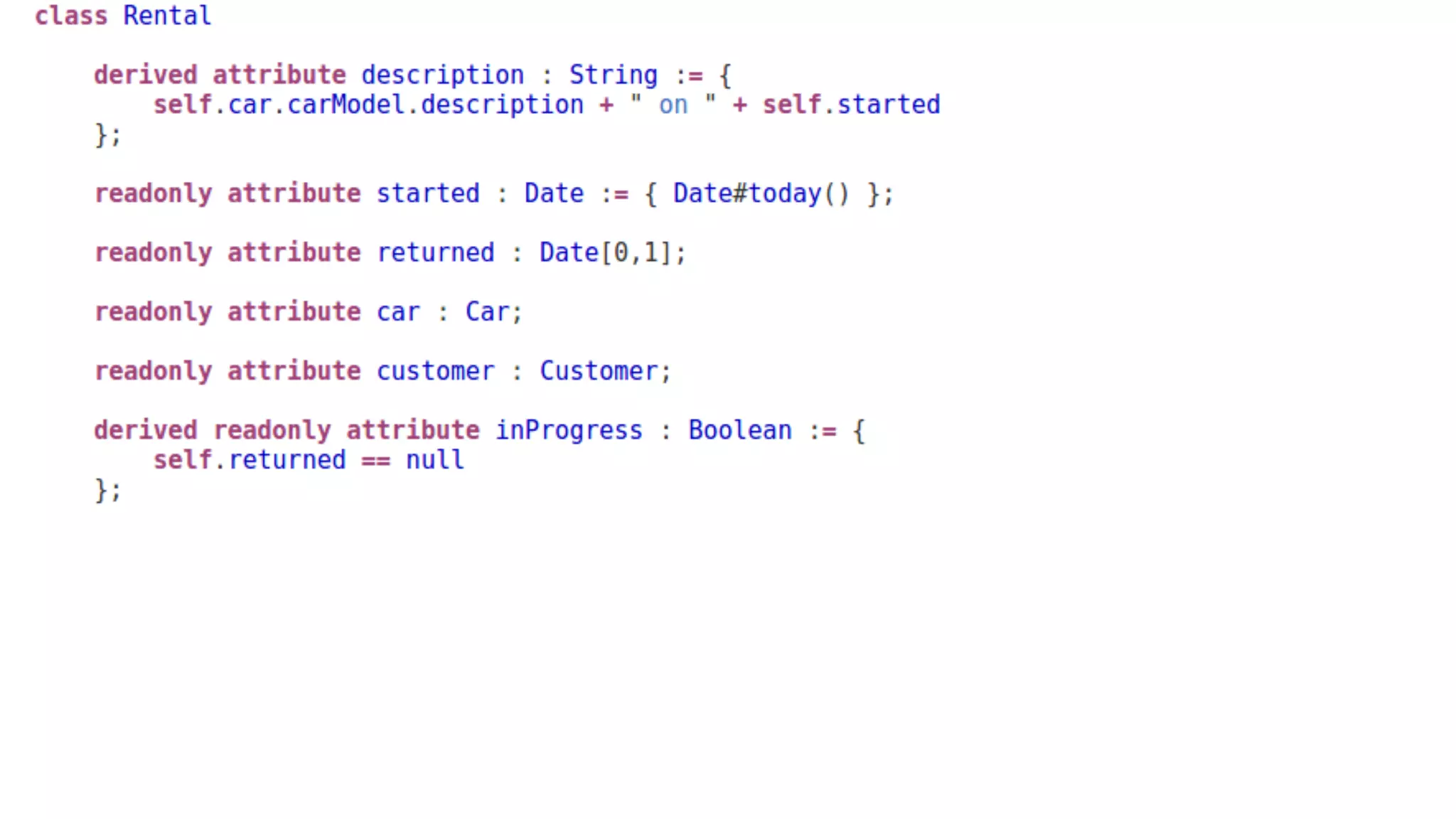
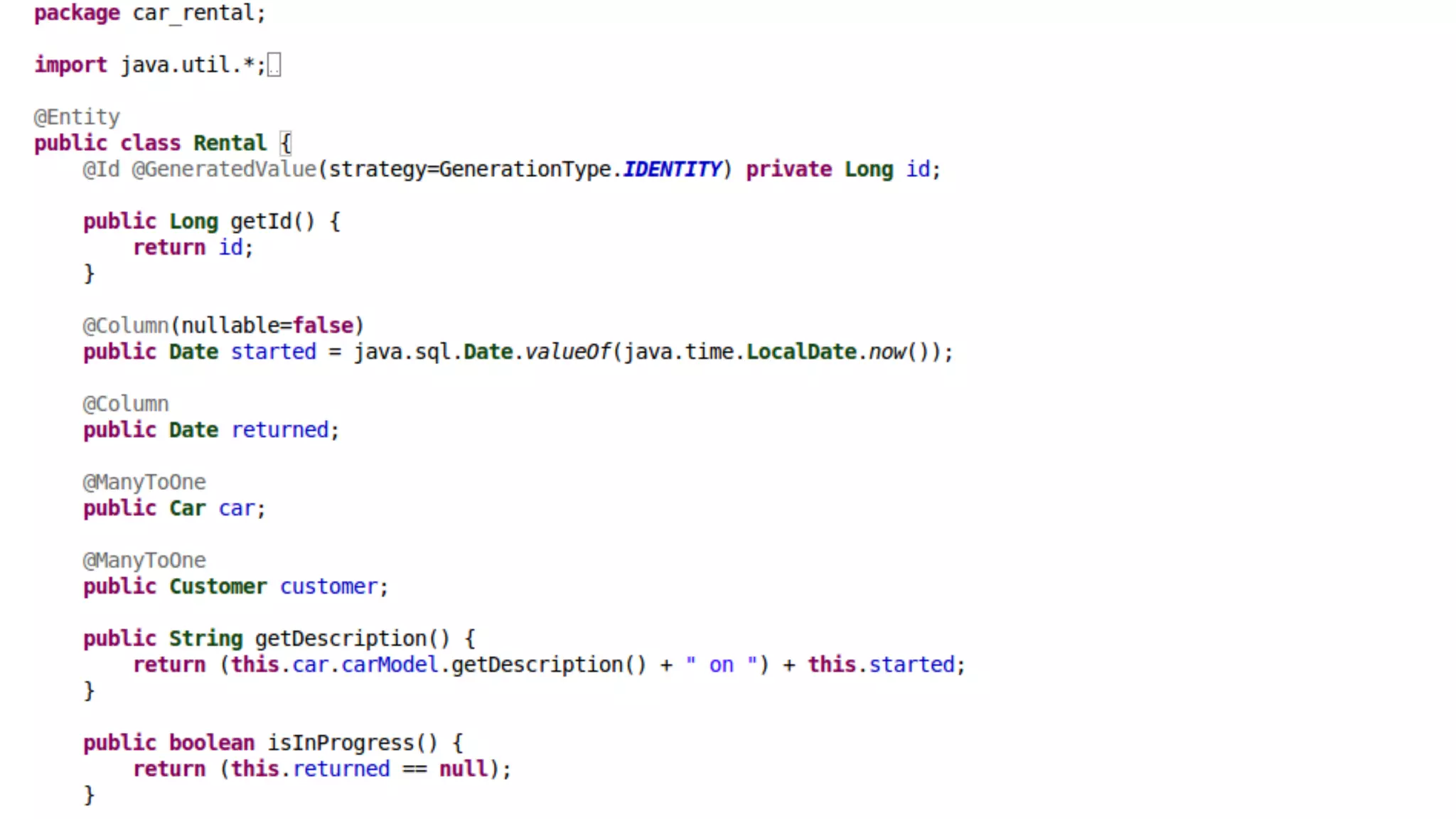
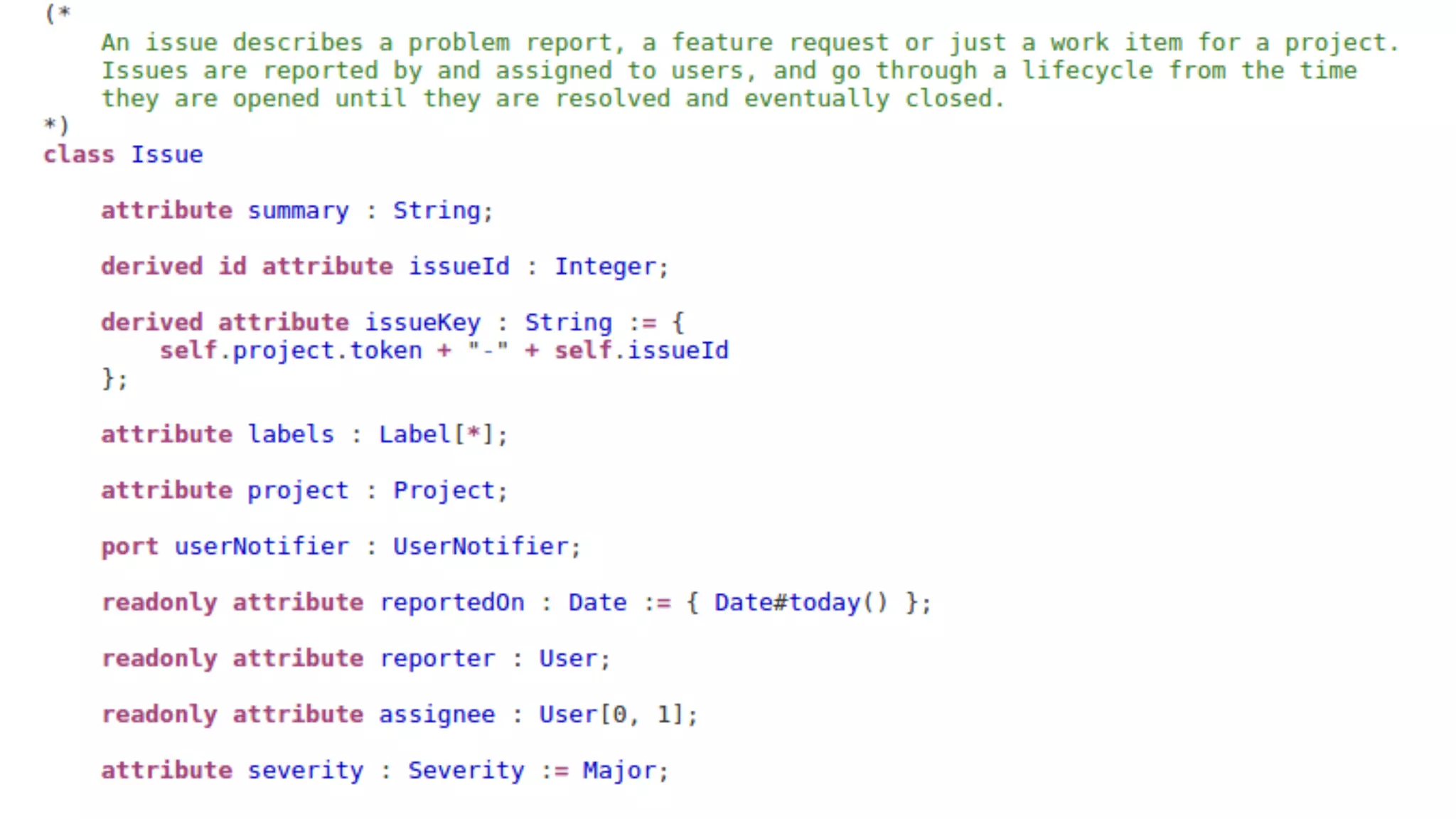
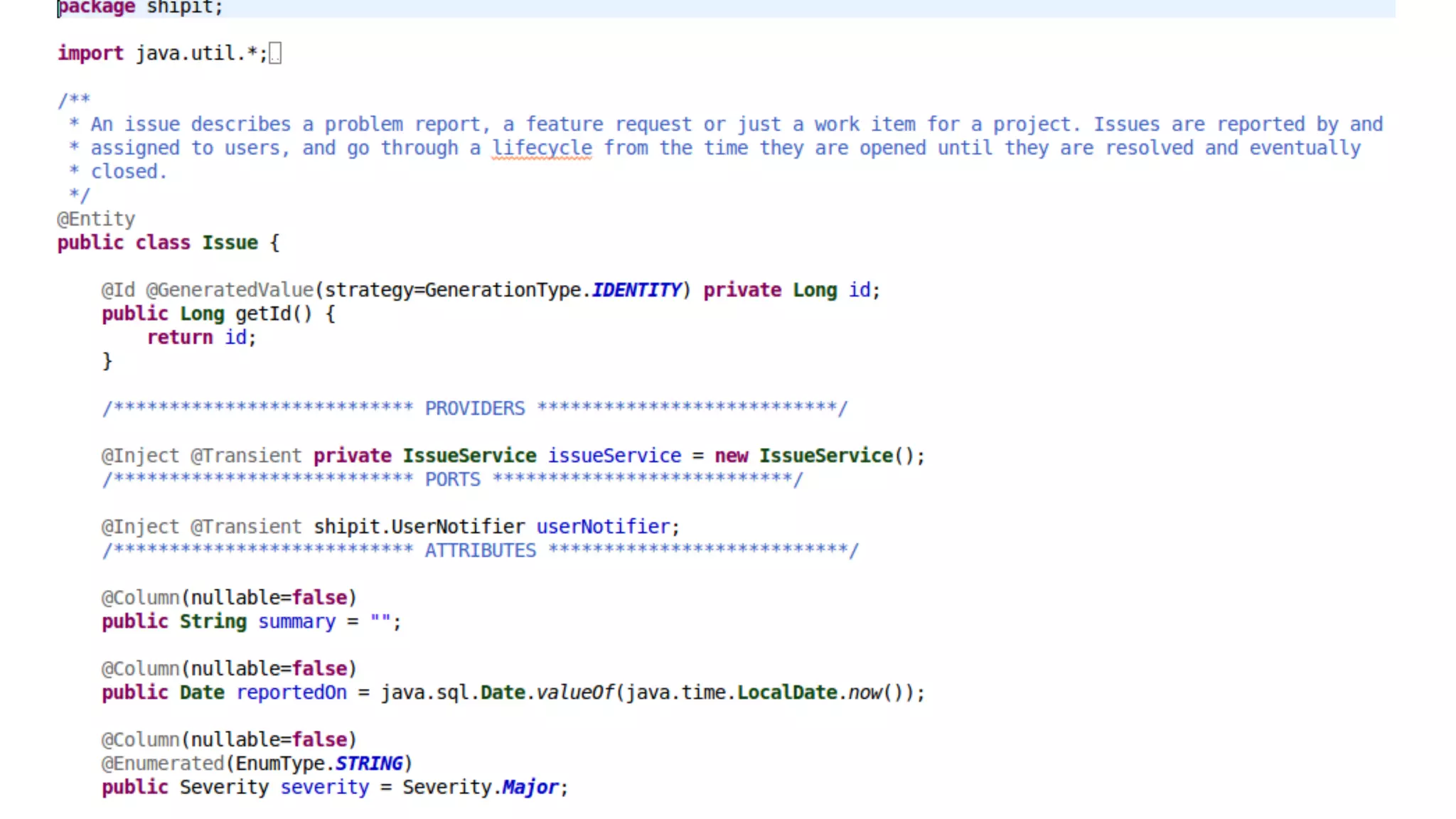
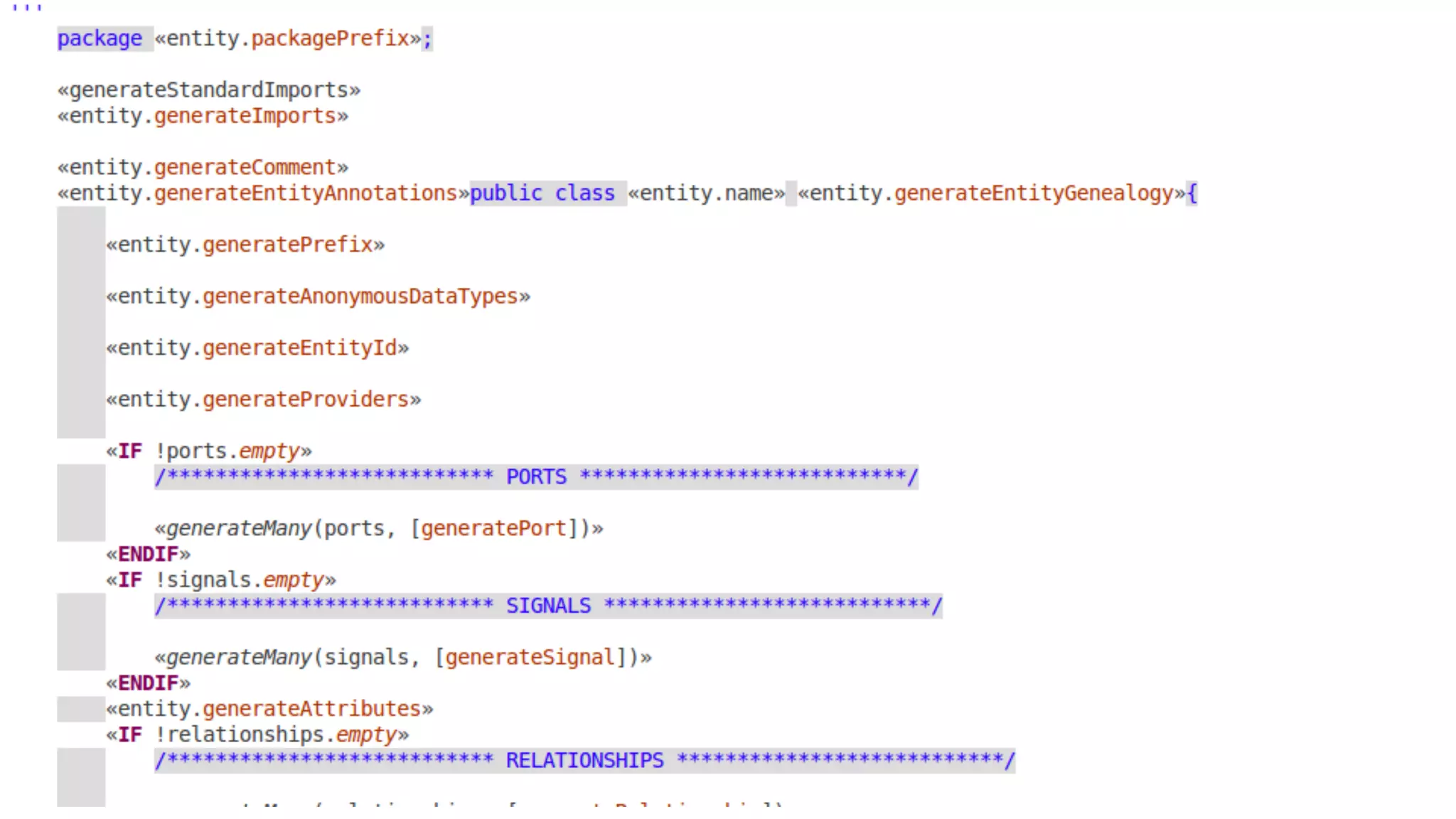
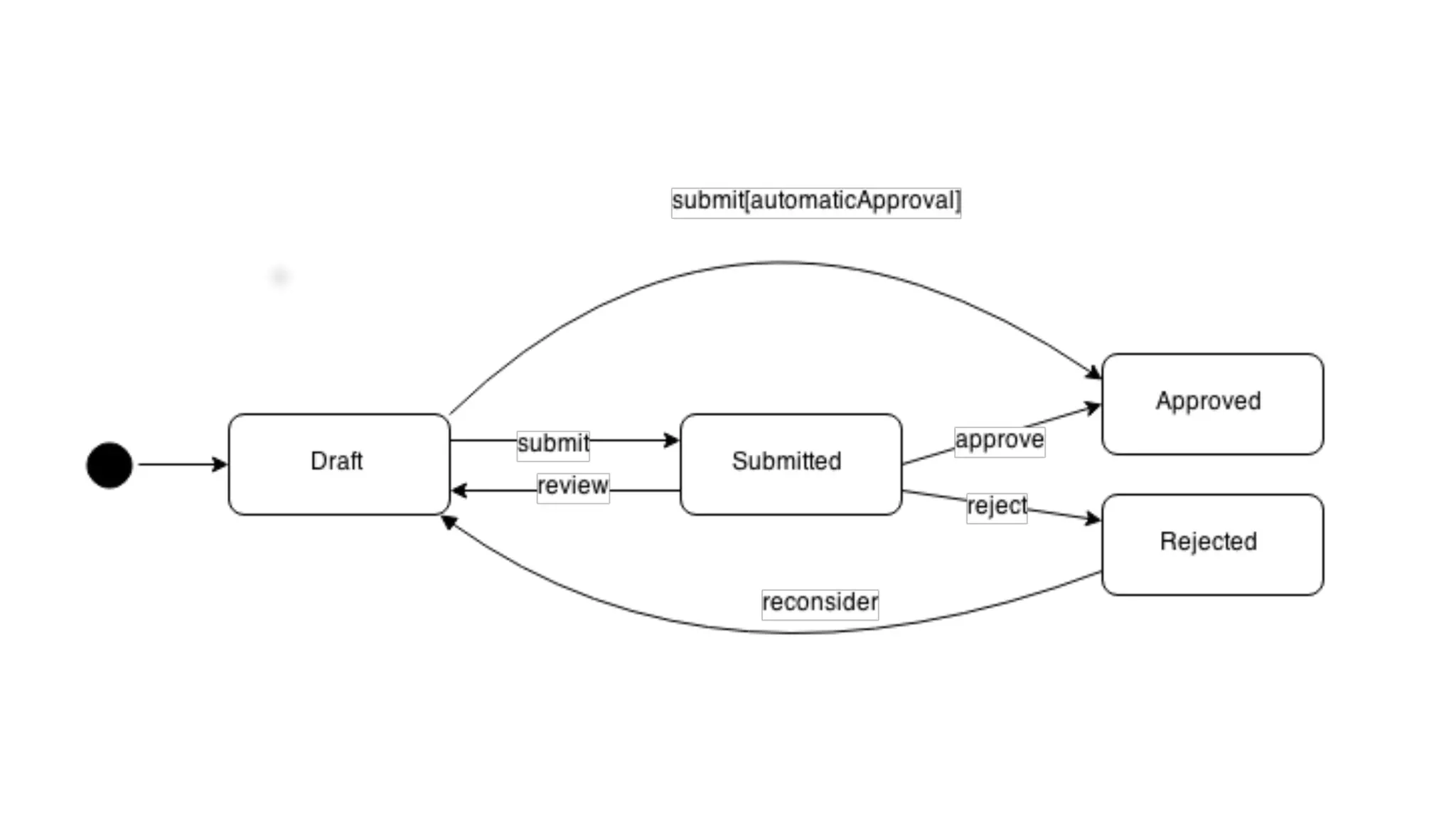
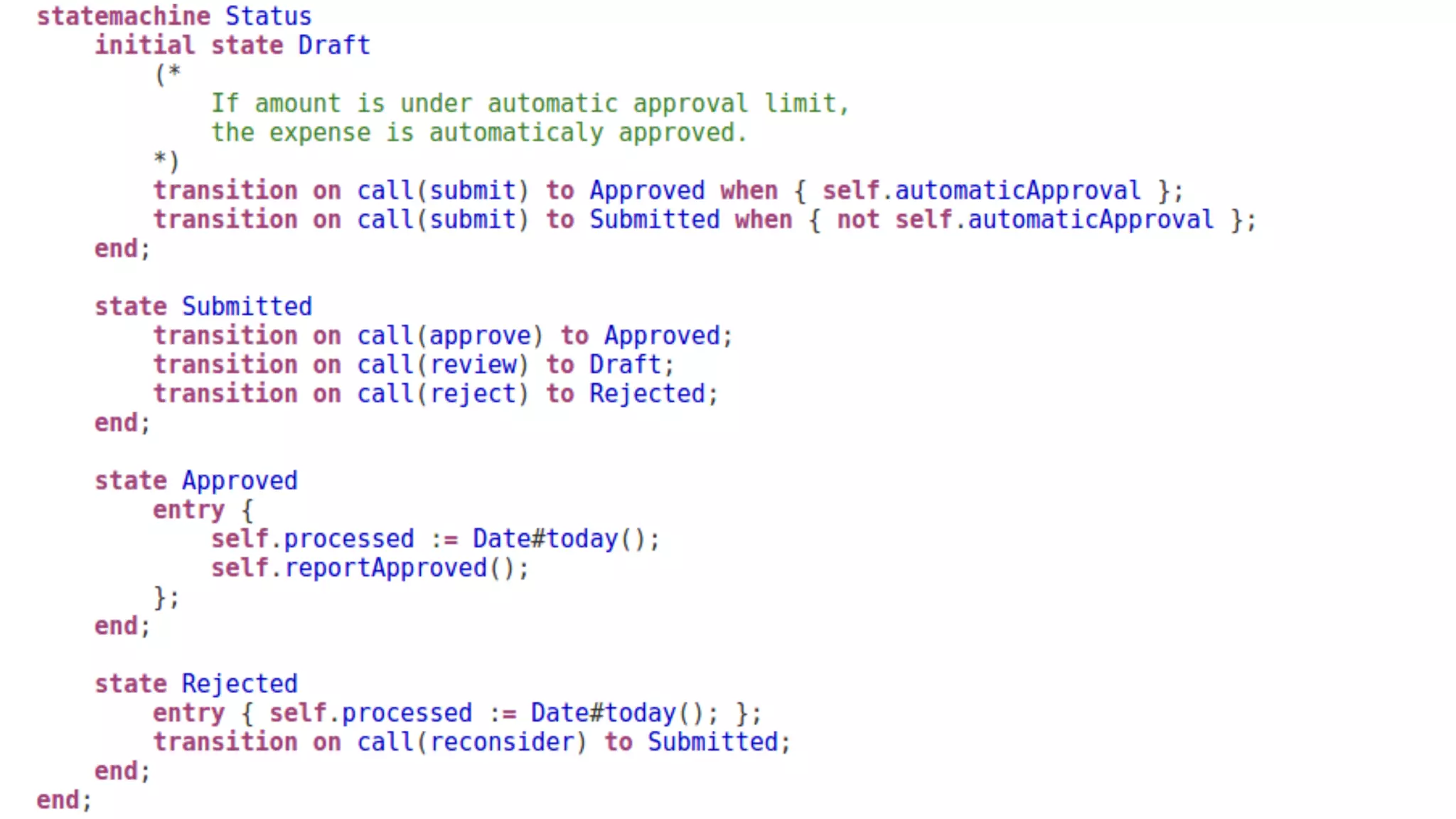
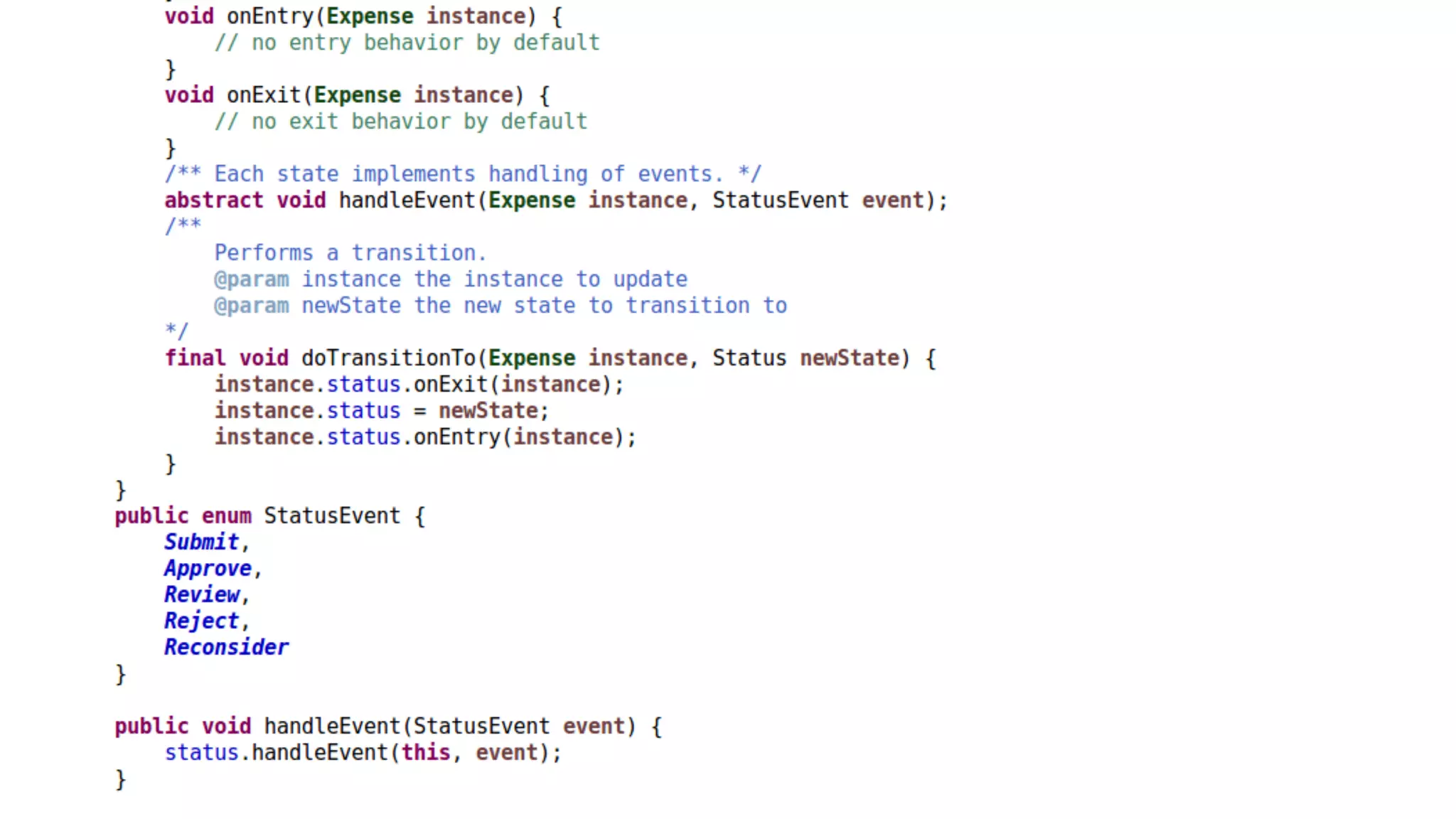
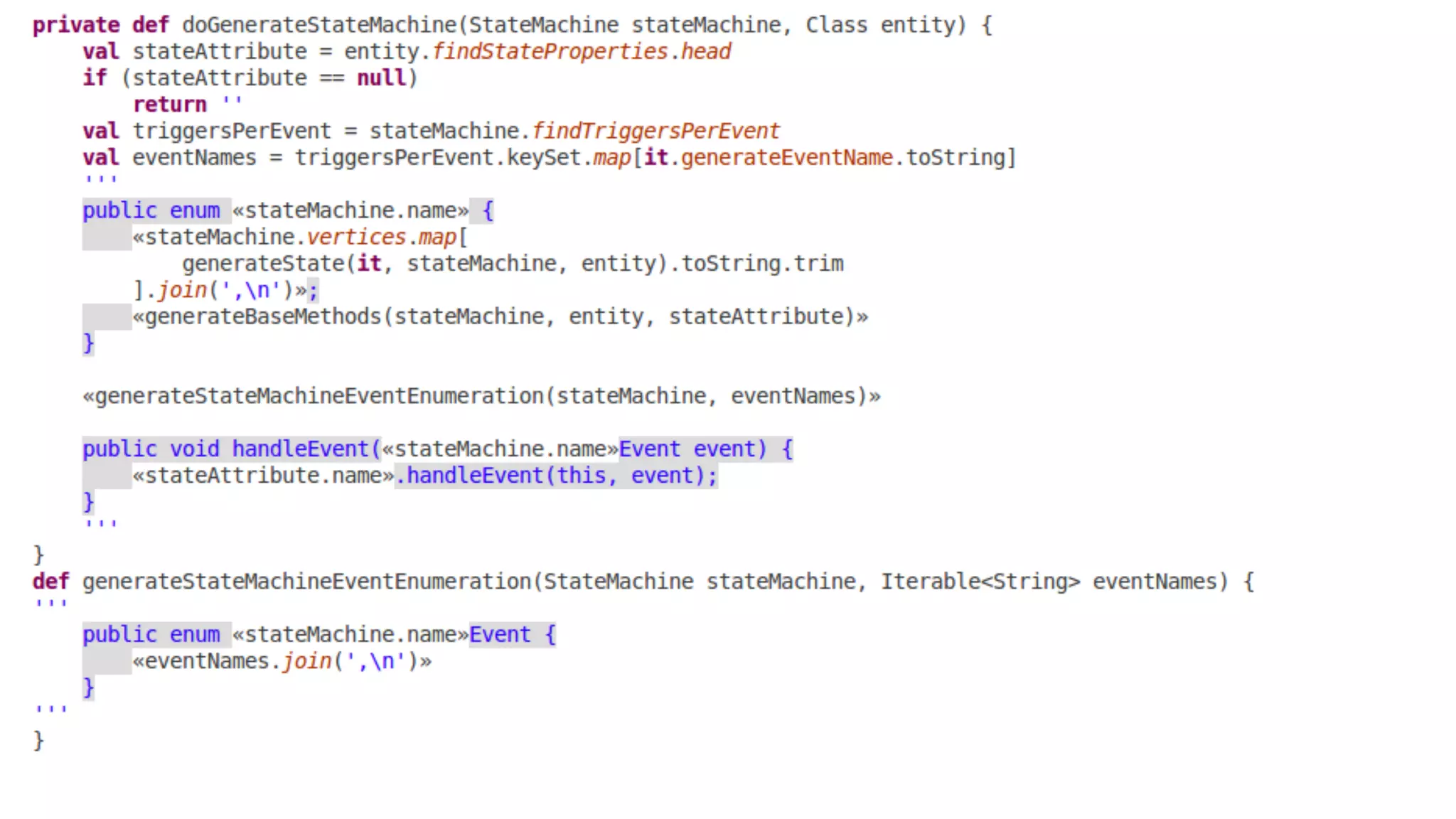
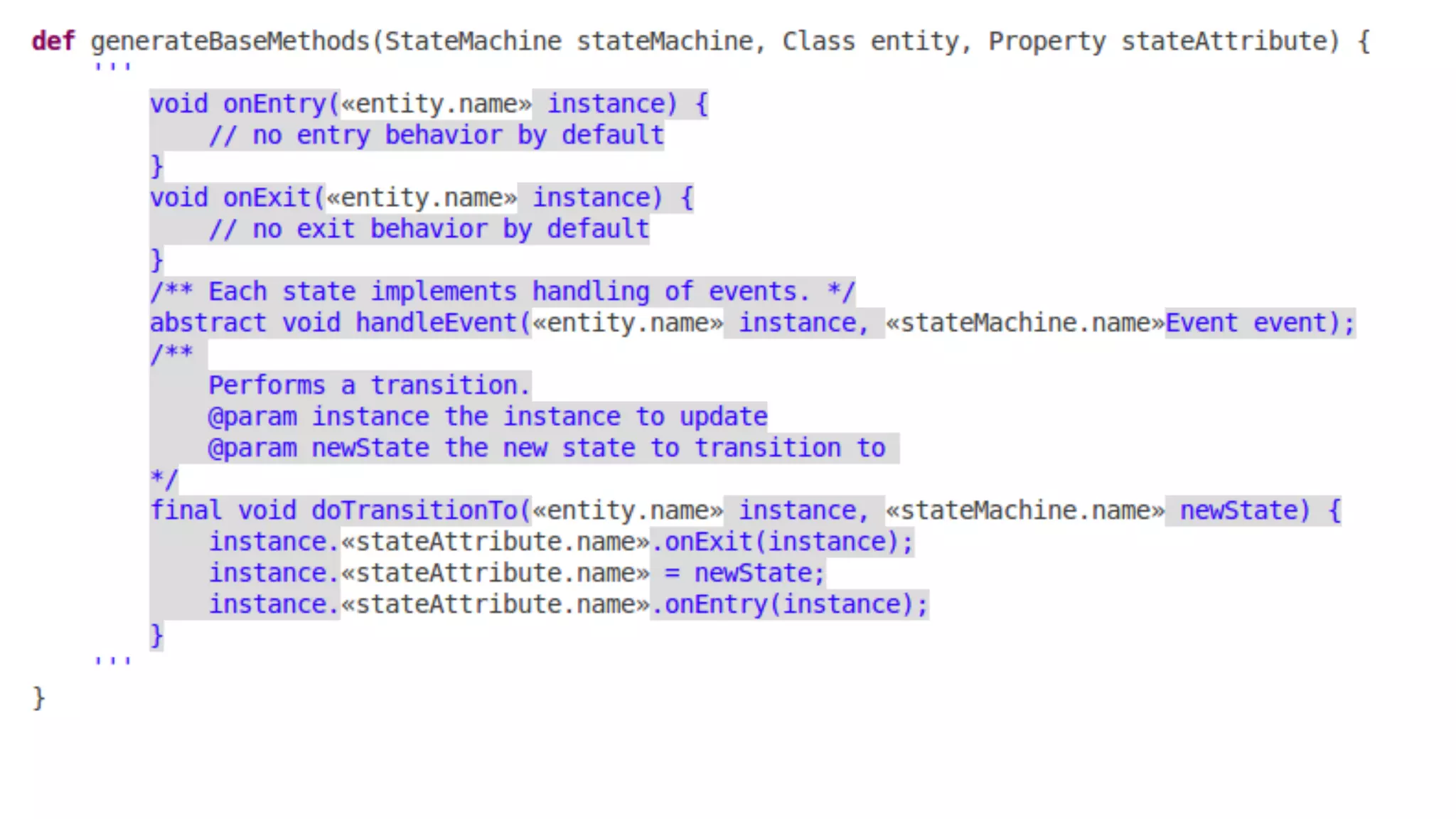
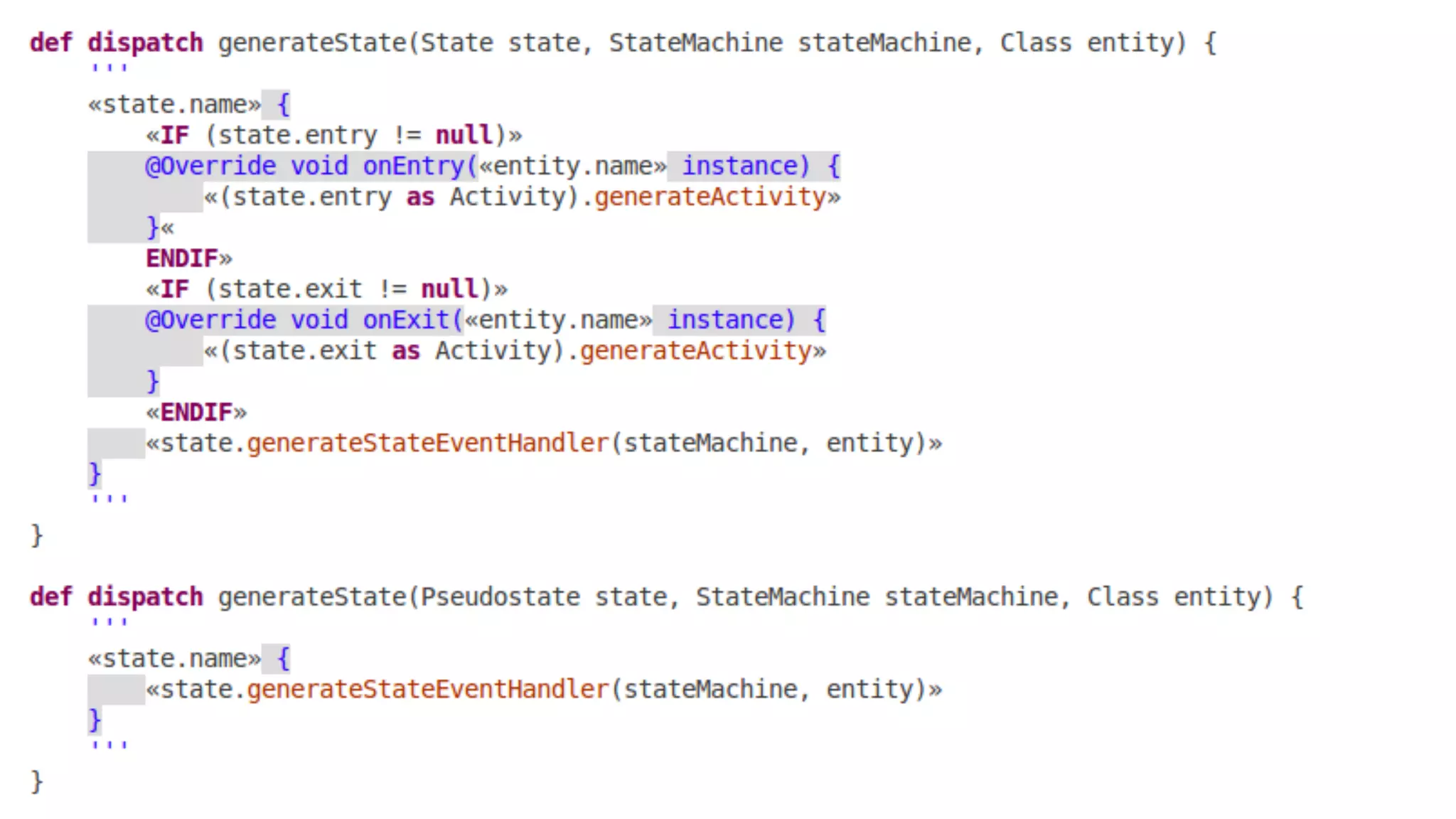
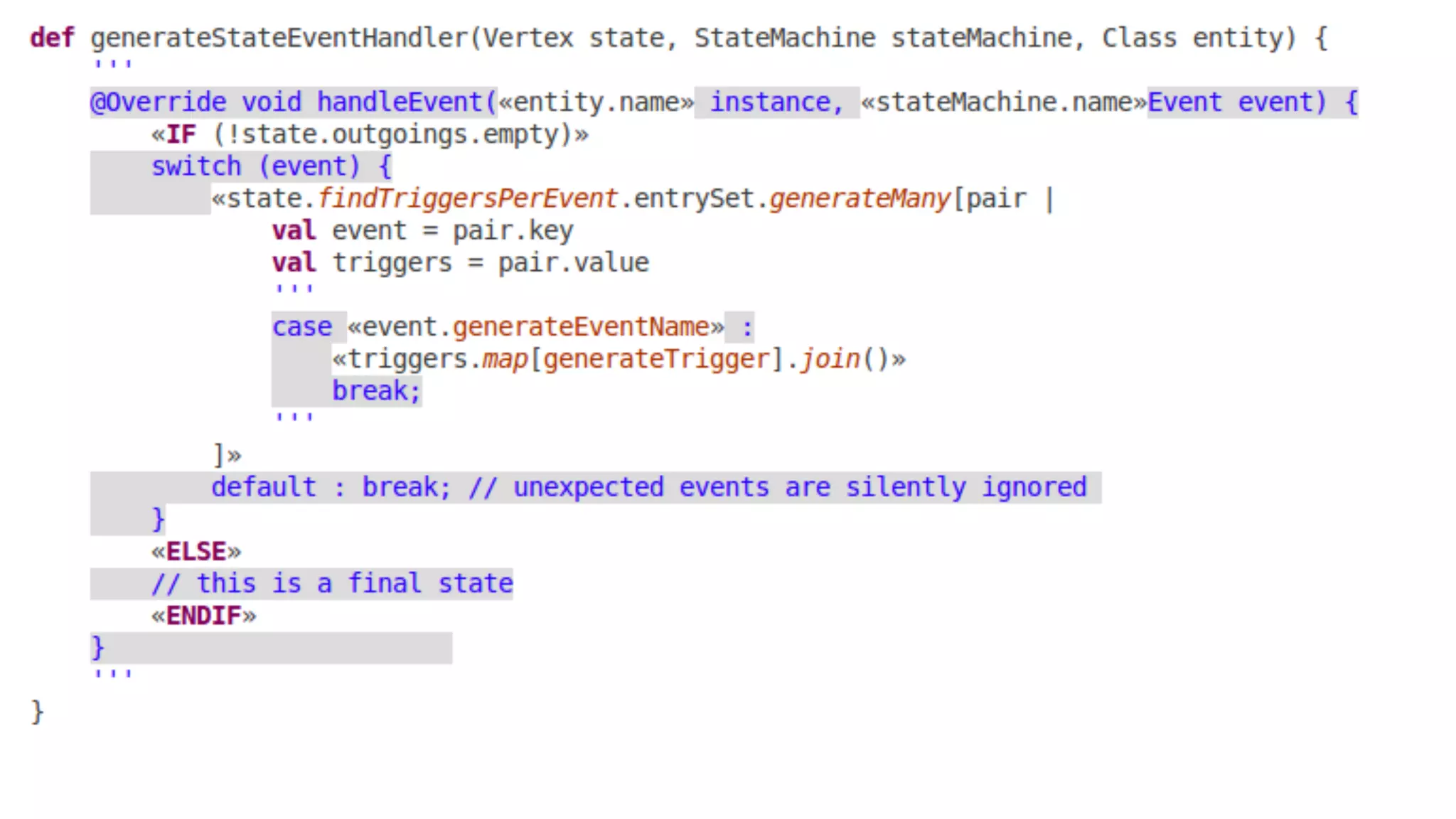
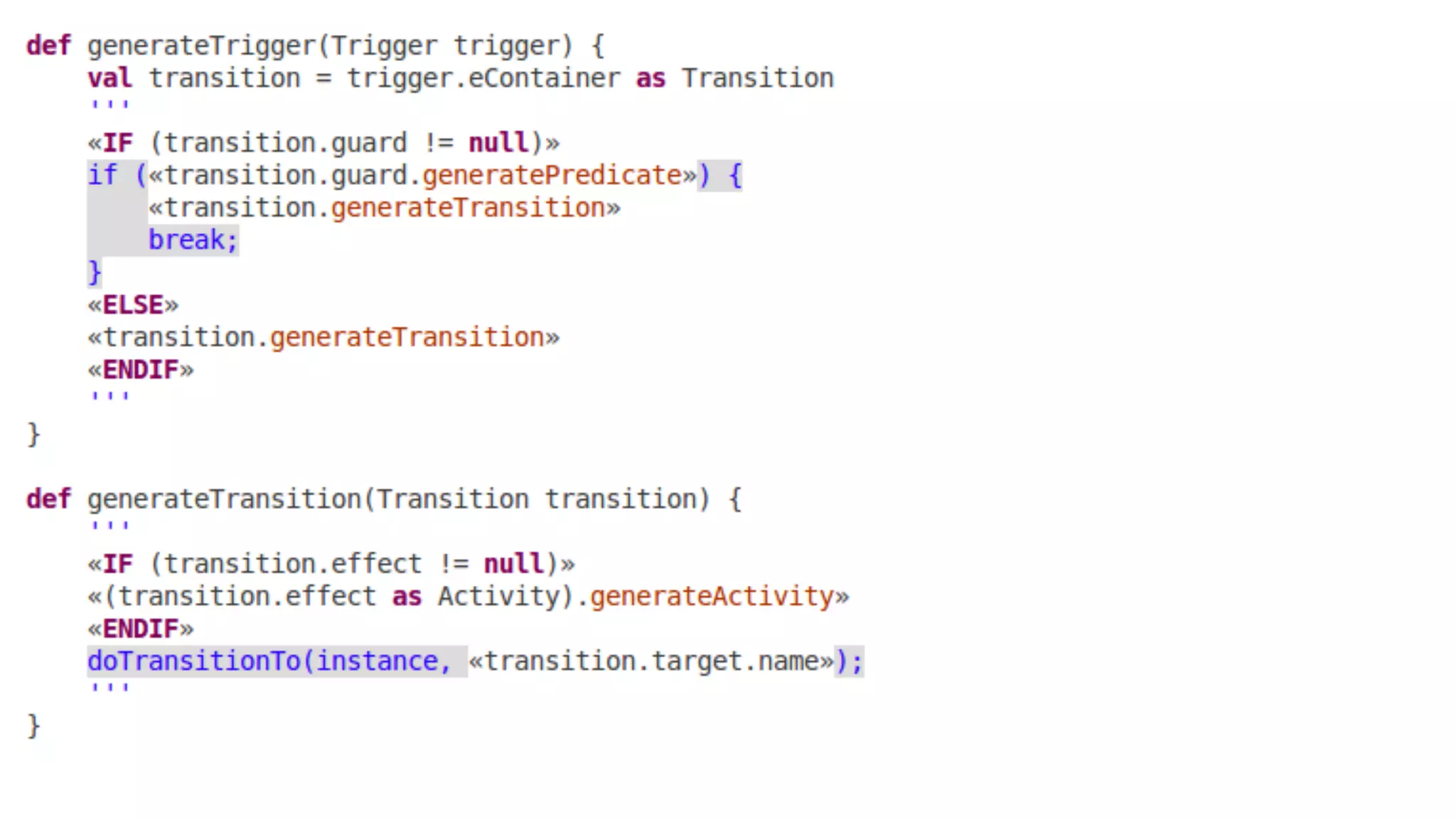
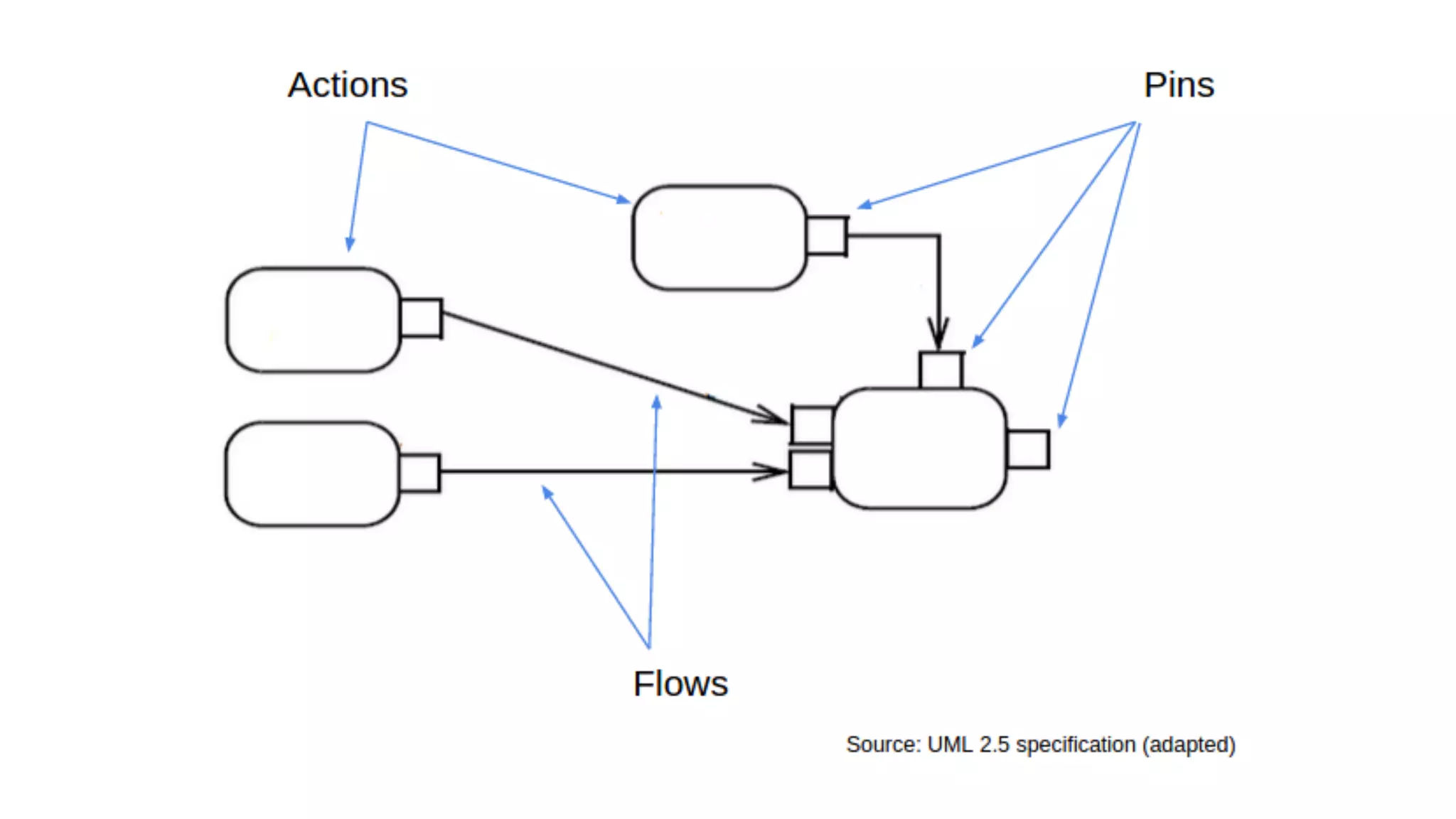
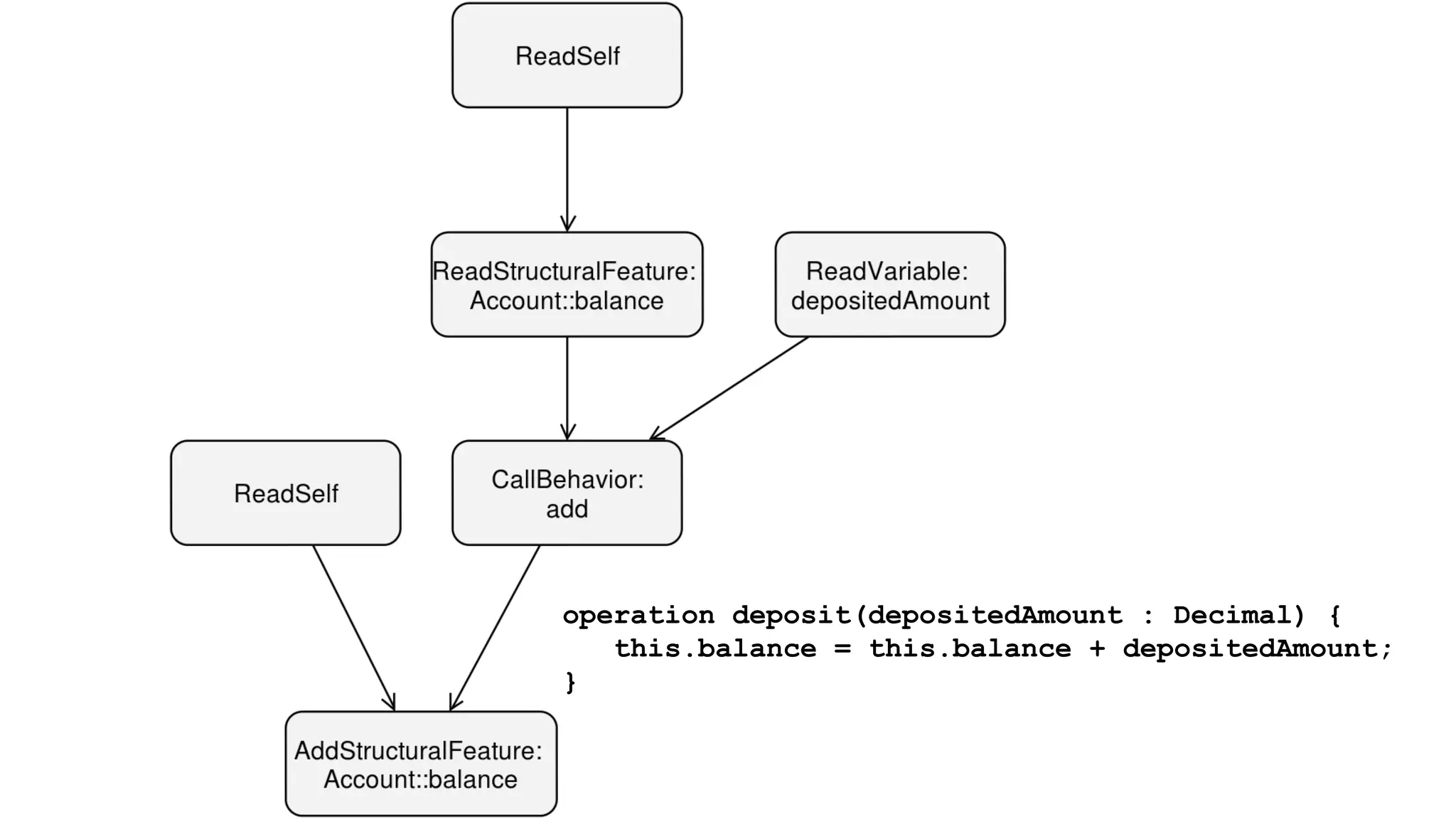
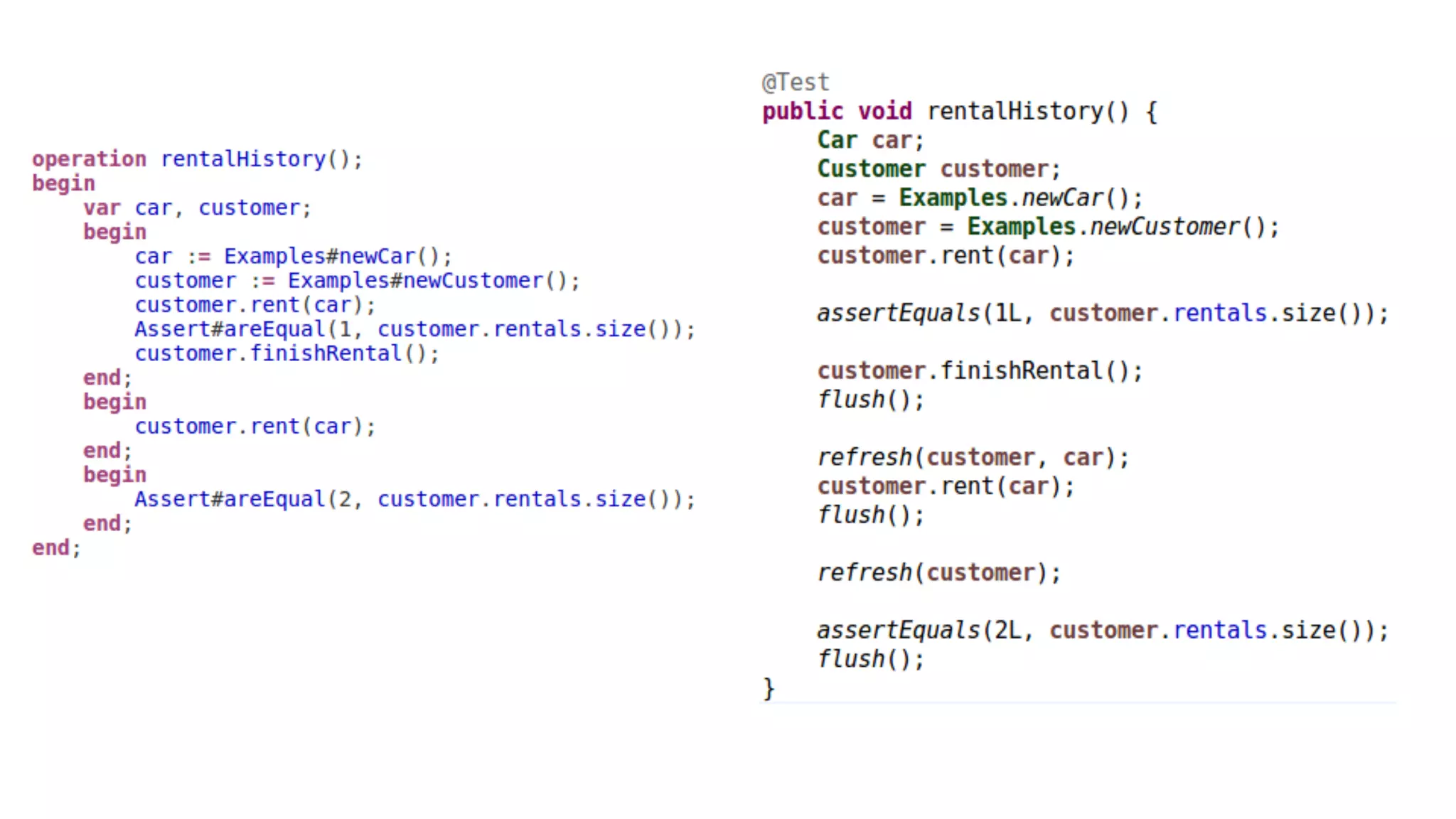
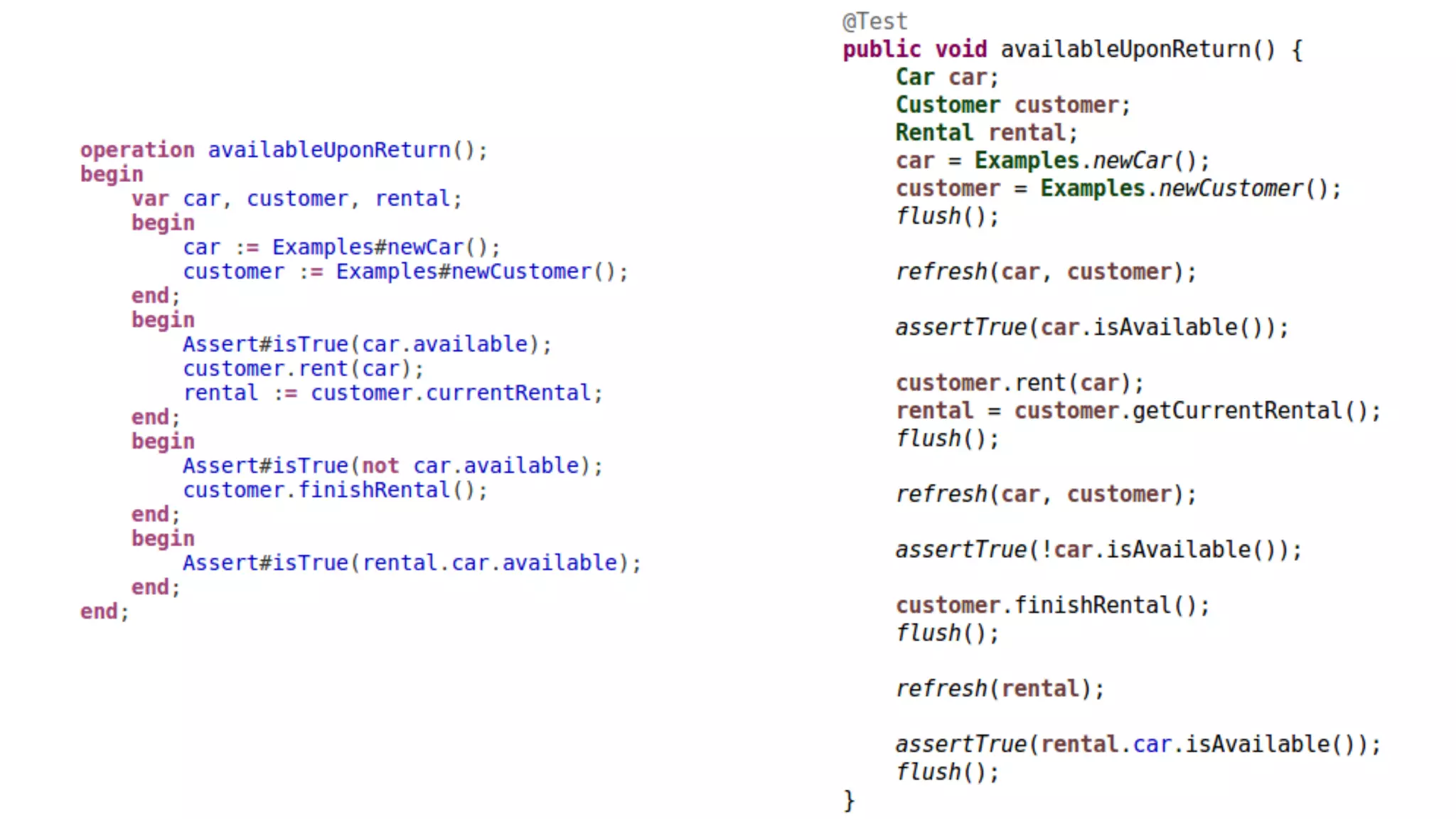
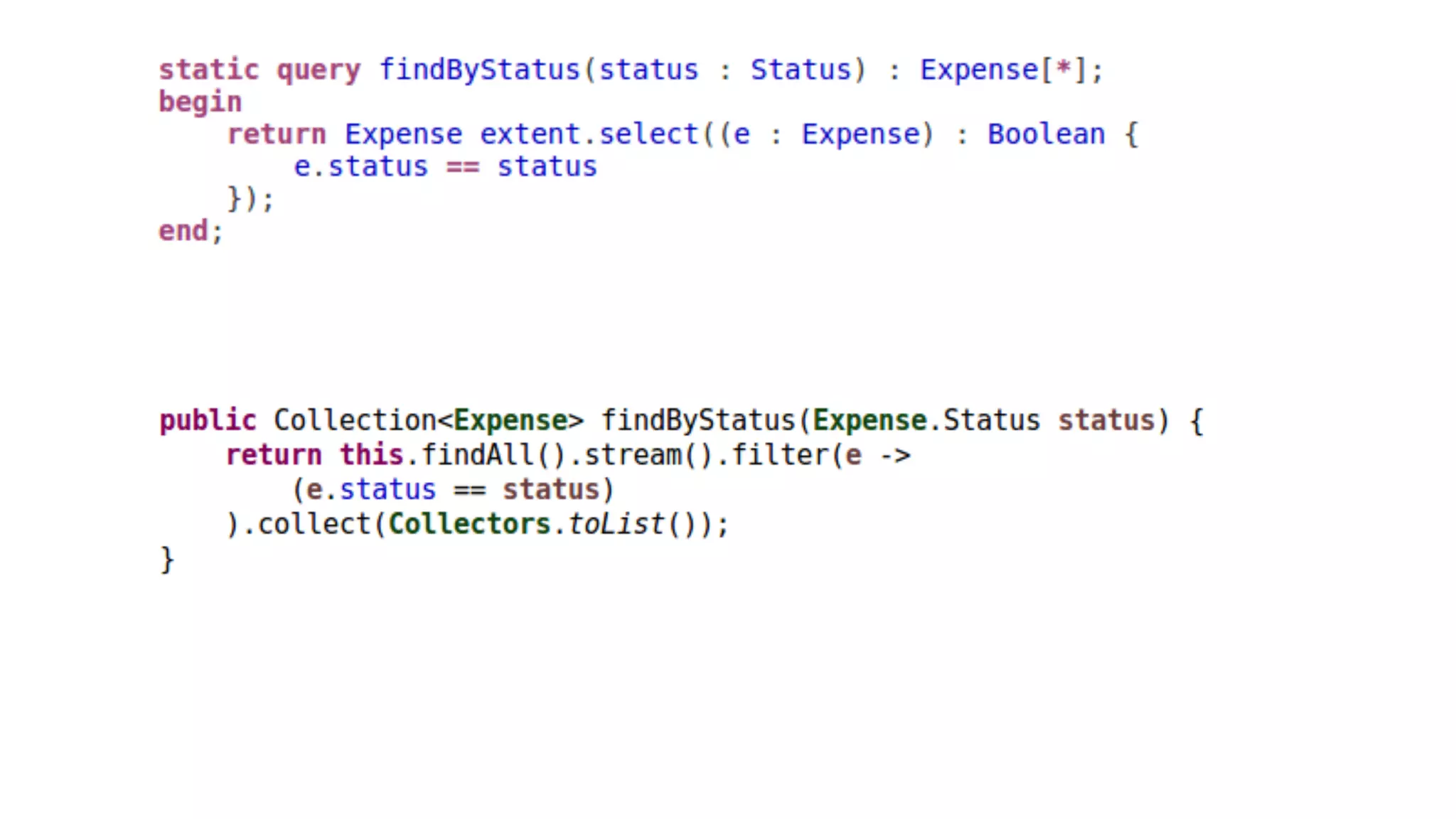
The document discusses generating business applications through executable models that separate business logic from technological choices. It highlights the importance of understanding the target platform and selecting the appropriate generator language, along with testing and reusing generators effectively. Additionally, it mentions ongoing development of a Java EE generator and the Alpha status of the Cloudfier tool.