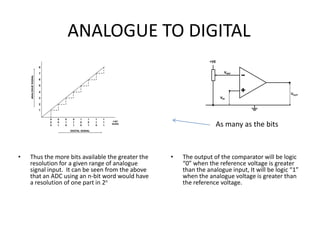
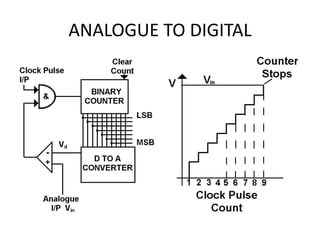
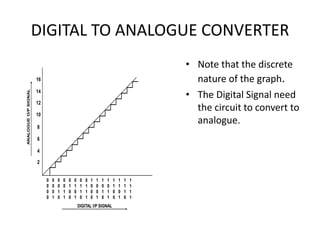
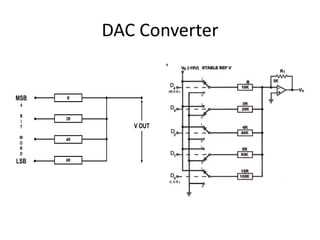
The document discusses data conversion between analogue and digital signals, defining key concepts such as analogue data (variable values) and digital data (discrete values). It explains the functions and limitations of analogue to digital and digital to analogue converters, emphasizing accuracy and resolution. Additionally, it highlights the significance of bit depth in enhancing the resolution of digital representations of analogue signals.