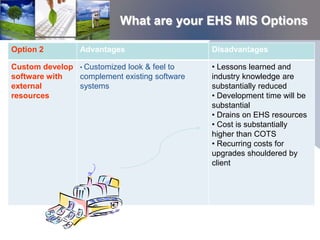
1. E2 ManageTech proposes a 5-task scope of work to design an EHS management information system for the client. The tasks include defining requirements, screening software vendors, analyzing costs and benefits, facilitating vendor demonstrations, and producing a design summary.
2. E2 would conduct workshops to identify functional and technical requirements from various stakeholders. They would use templates of common requirements from other clients to accelerate the process.
3. E2 has experience implementing over 150 EHS software systems and would evaluate the client's existing systems and commercially available options. They would facilitate demonstrations of shortlisted software vendors.
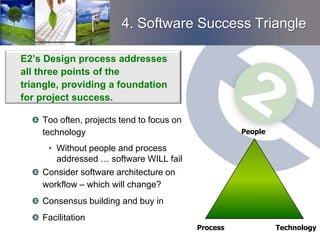
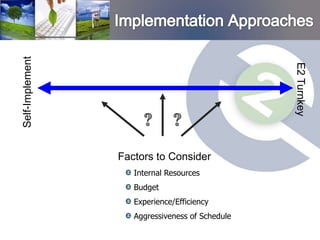
4. E2's design process aims to optimize project scope and budget based on financial considerations like return