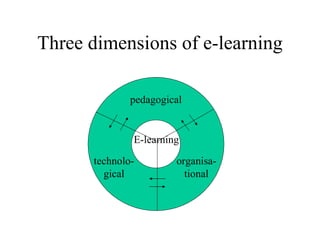
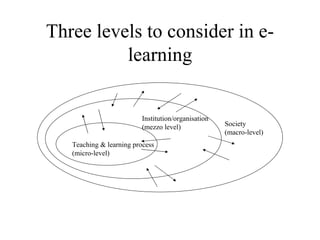
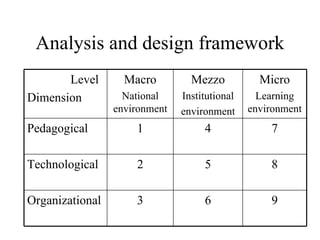
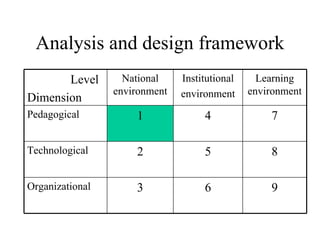
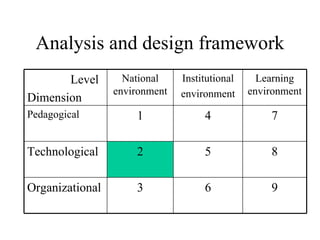
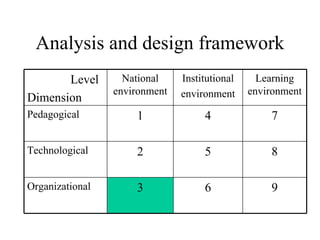
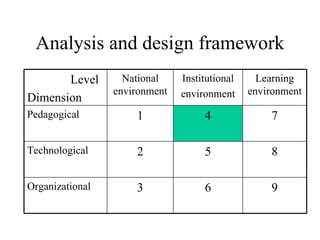
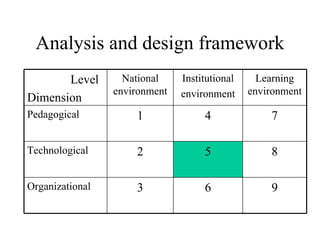
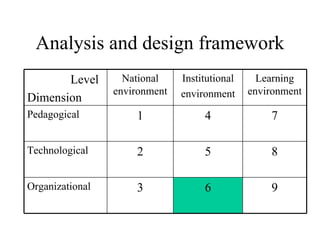
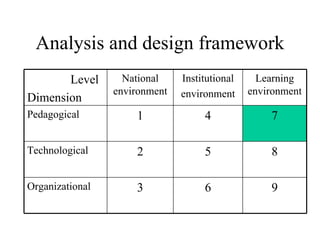
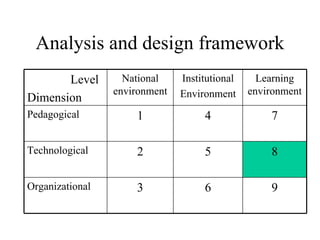
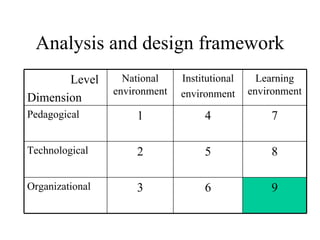
The document outlines an e-learning analysis and design framework developed by Eric Kluijfhout for the Institute for Community Participation at Bethlehem University. It details three dimensions of e-learning—pedagogical, technological, and organizational—across macro (national), mezzo (institutional), and micro (learning) levels. Additionally, it identifies various prerequisites and influences that impact e-learning effectiveness, including curriculum, technology access, and institutional strategies.