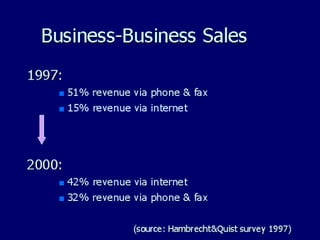
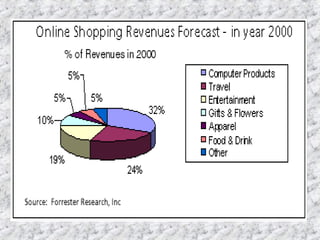
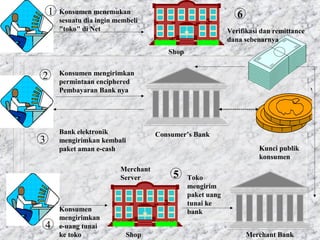
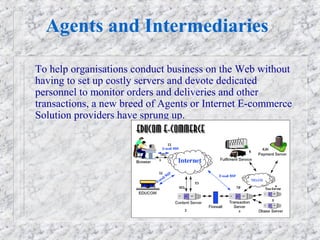
Electronic commerce has evolved from using private electronic data interchange networks to now utilizing the public Internet. The Internet allows smaller businesses and customers to access electronic networks at a lower cost. While private networks traditionally charged per transaction, the Internet allows real-time transactions with fixed connection fees. Examples are provided of how electronic commerce transactions take place, including ordering, payment, order fulfillment, and shipping notification. Key players like banks and payment providers help facilitate online payments between customers, merchants, and banks.