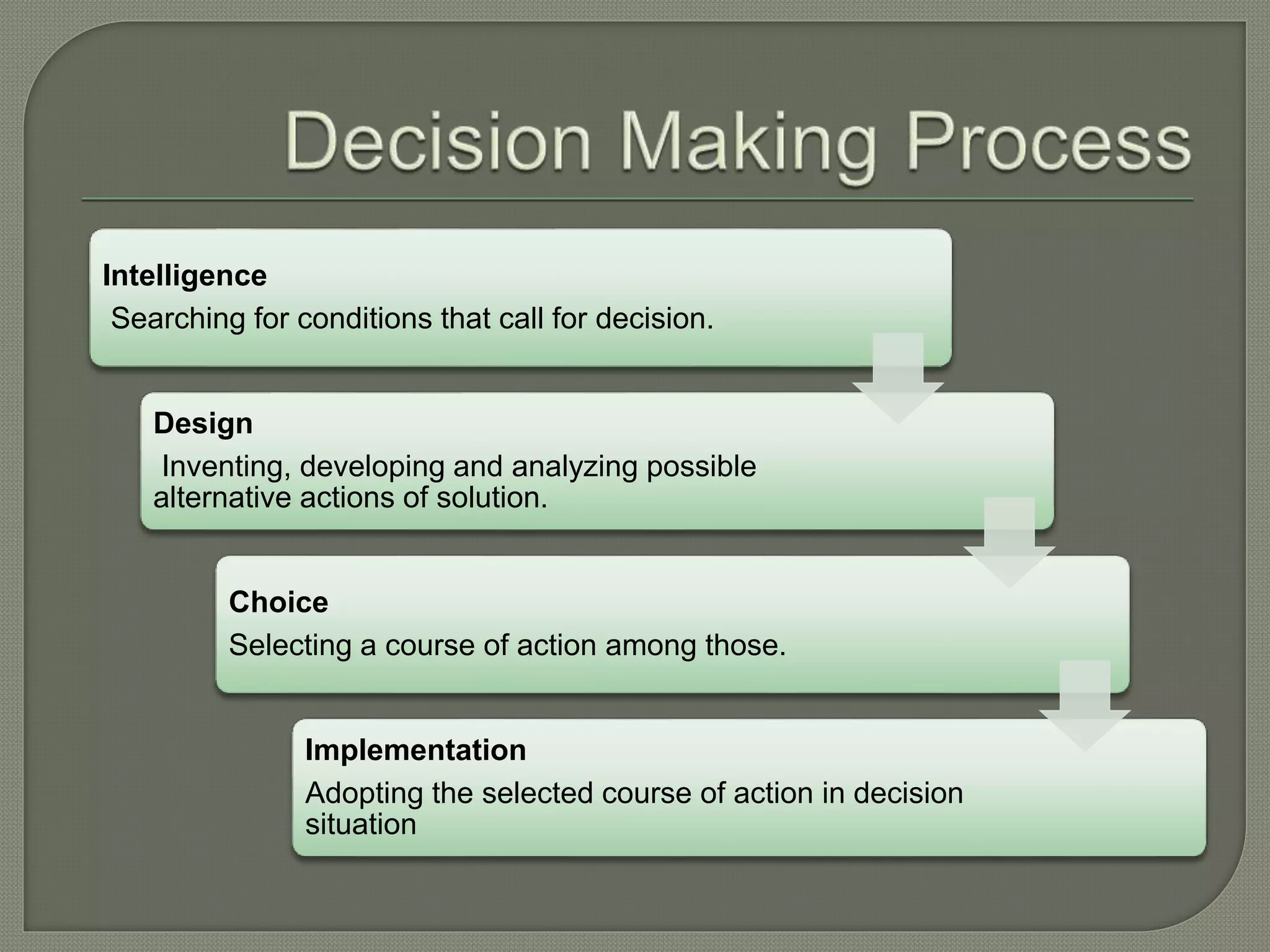
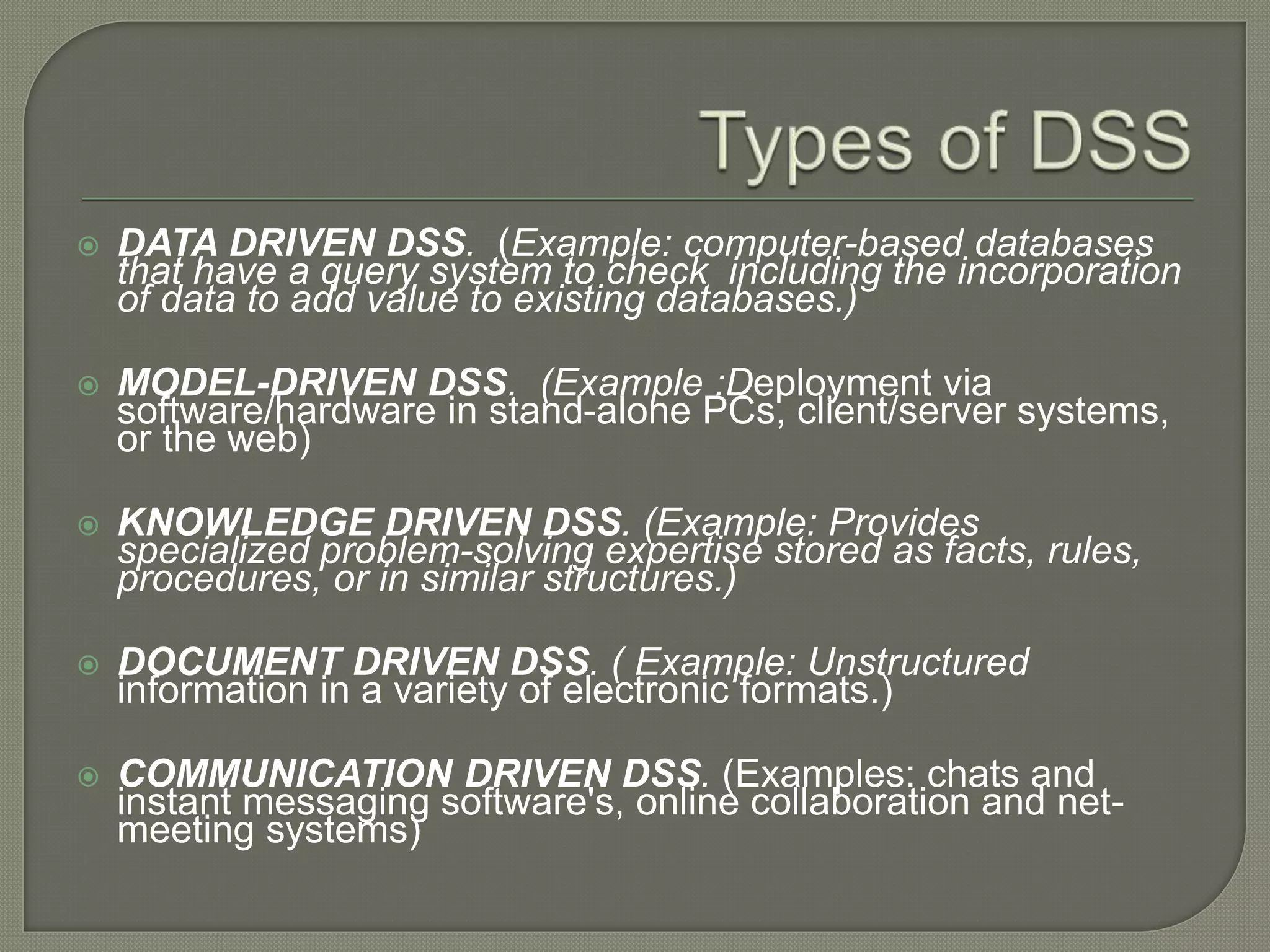
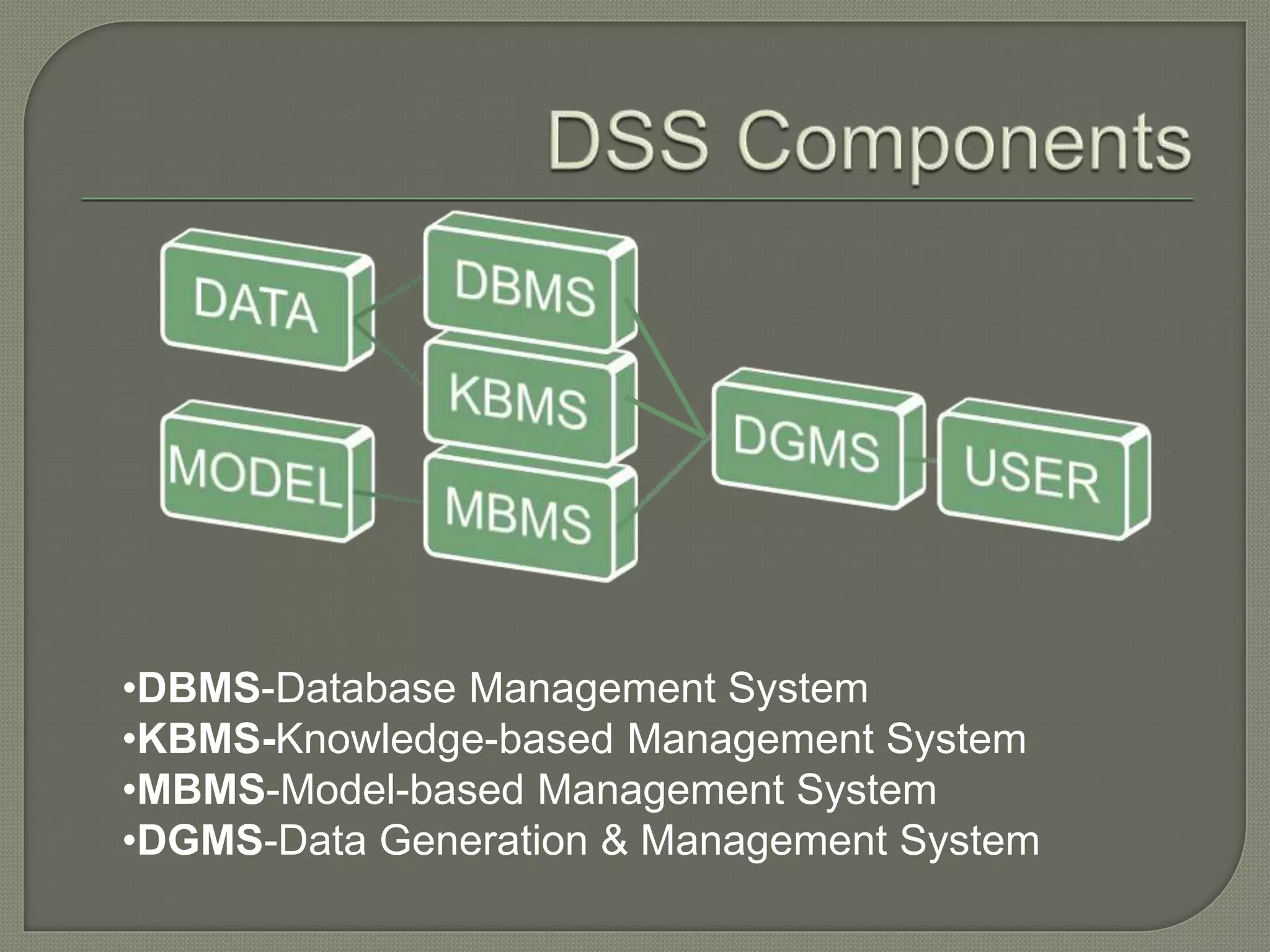
The document defines decision support systems (DSS) as interactive computer systems that help decision-makers use data and models to solve structured, unstructured, or semi-structured problems. It discusses how DSS can aid in decision-making by integrating information and supporting alternatives. The document also outlines the key stages of decision-making - intelligence, design, choice, and implementation - and describes different types of DSS like data-driven, model-driven, and knowledge-driven systems. Examples are provided of how DSS are used in domains like airline reservations and loan approval.