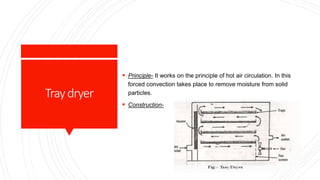
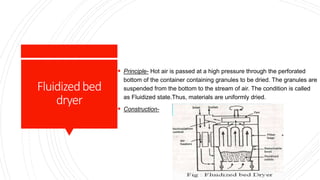
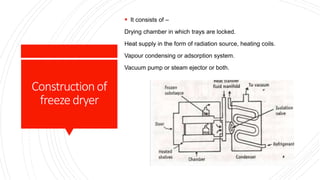
The document discusses different drying techniques used in the pharmaceutical industry. It describes tray drying, fluidized bed drying, vacuum drying, and freeze drying. Tray drying involves circulating hot air over solid materials placed on trays to remove moisture. Fluidized bed drying suspends materials in a stream of hot air to dry them uniformly. Vacuum drying uses reduced pressure to lower the boiling point of water for faster evaporation. Freeze drying works by freezing materials, reducing pressure, and allowing ice to sublimate directly to water vapor for drying thermolabile substances. Each method has advantages like speed, uniformity, or suitability for certain materials as well as disadvantages like cost or potential for degradation.