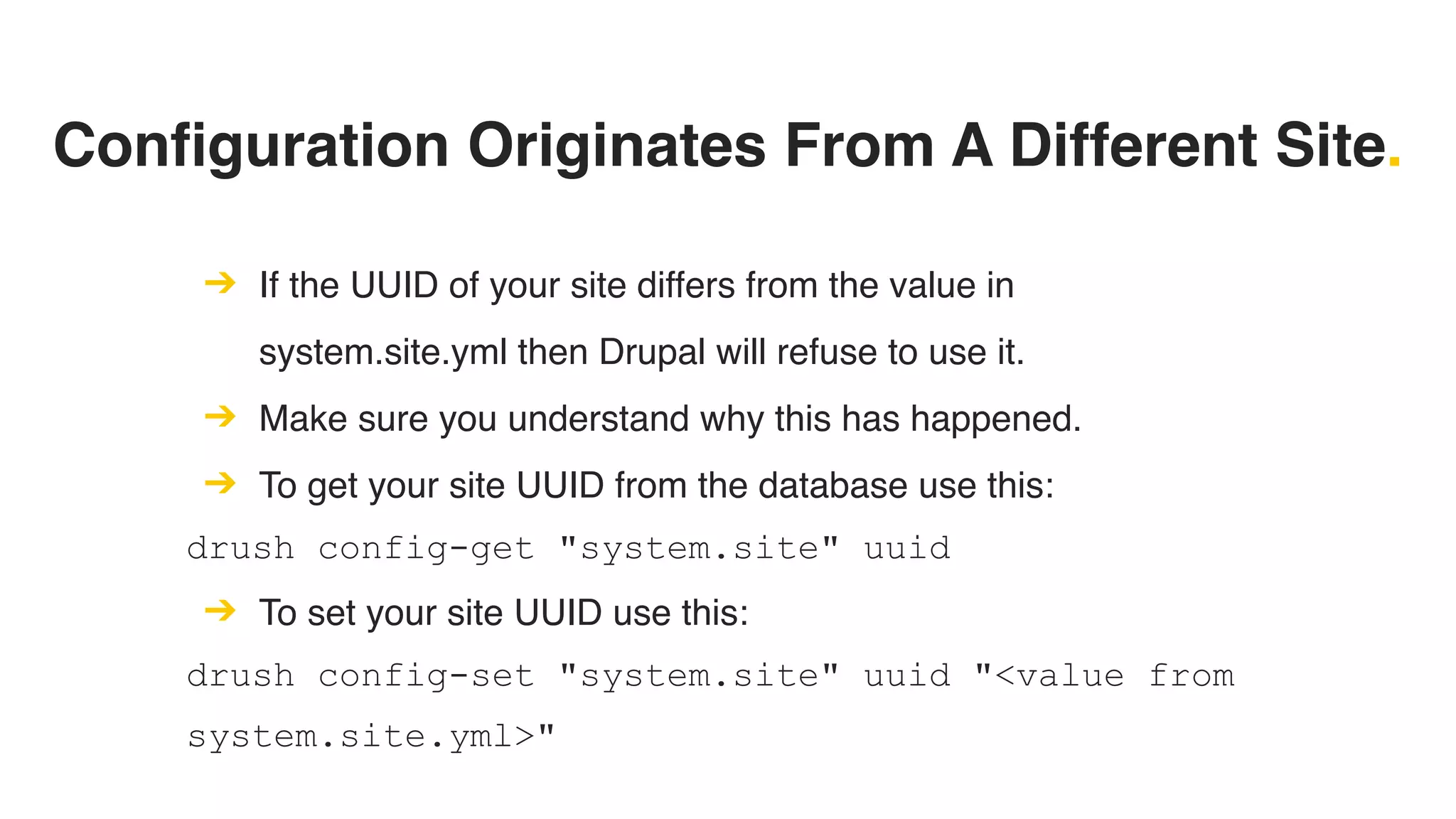
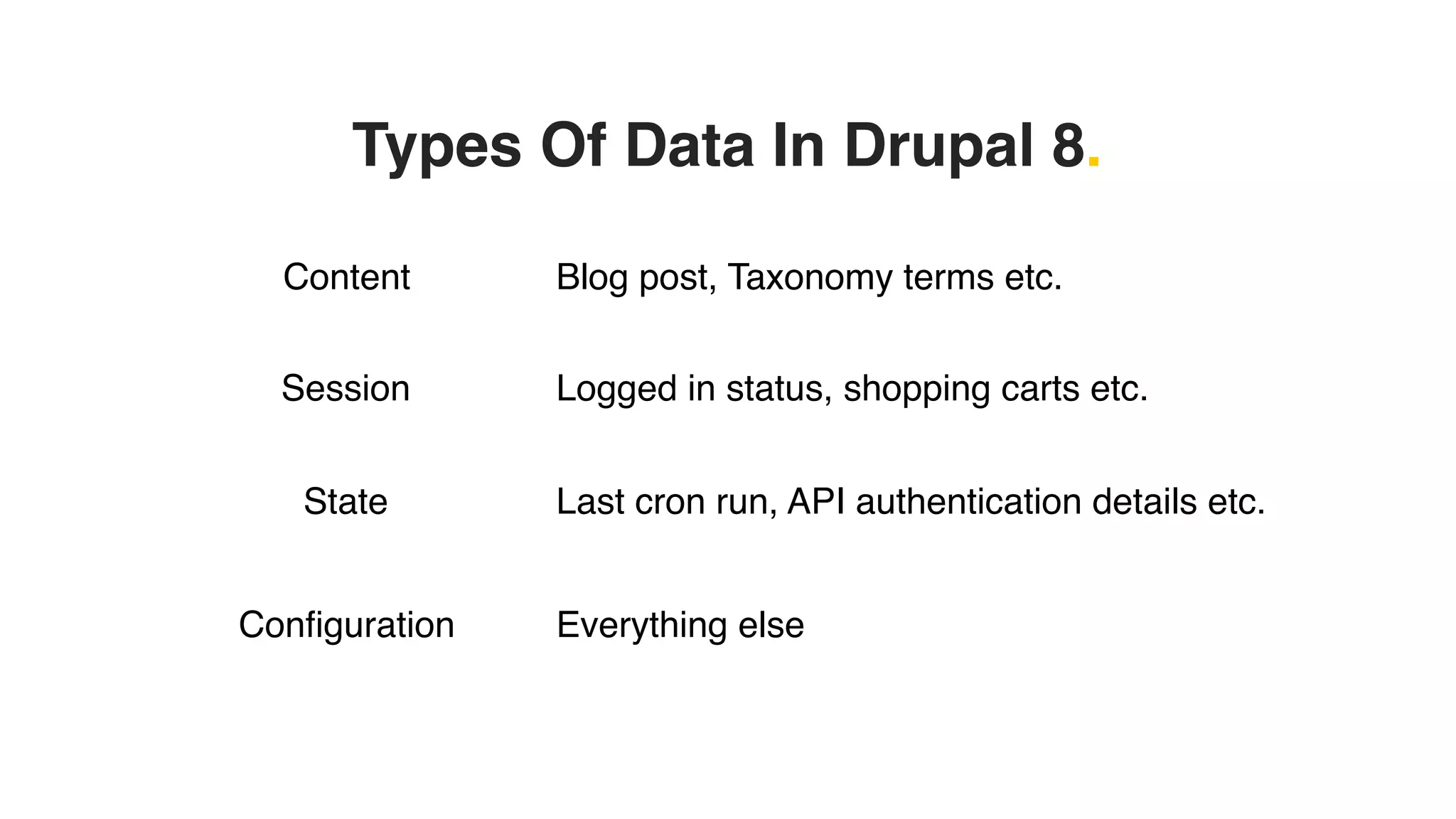
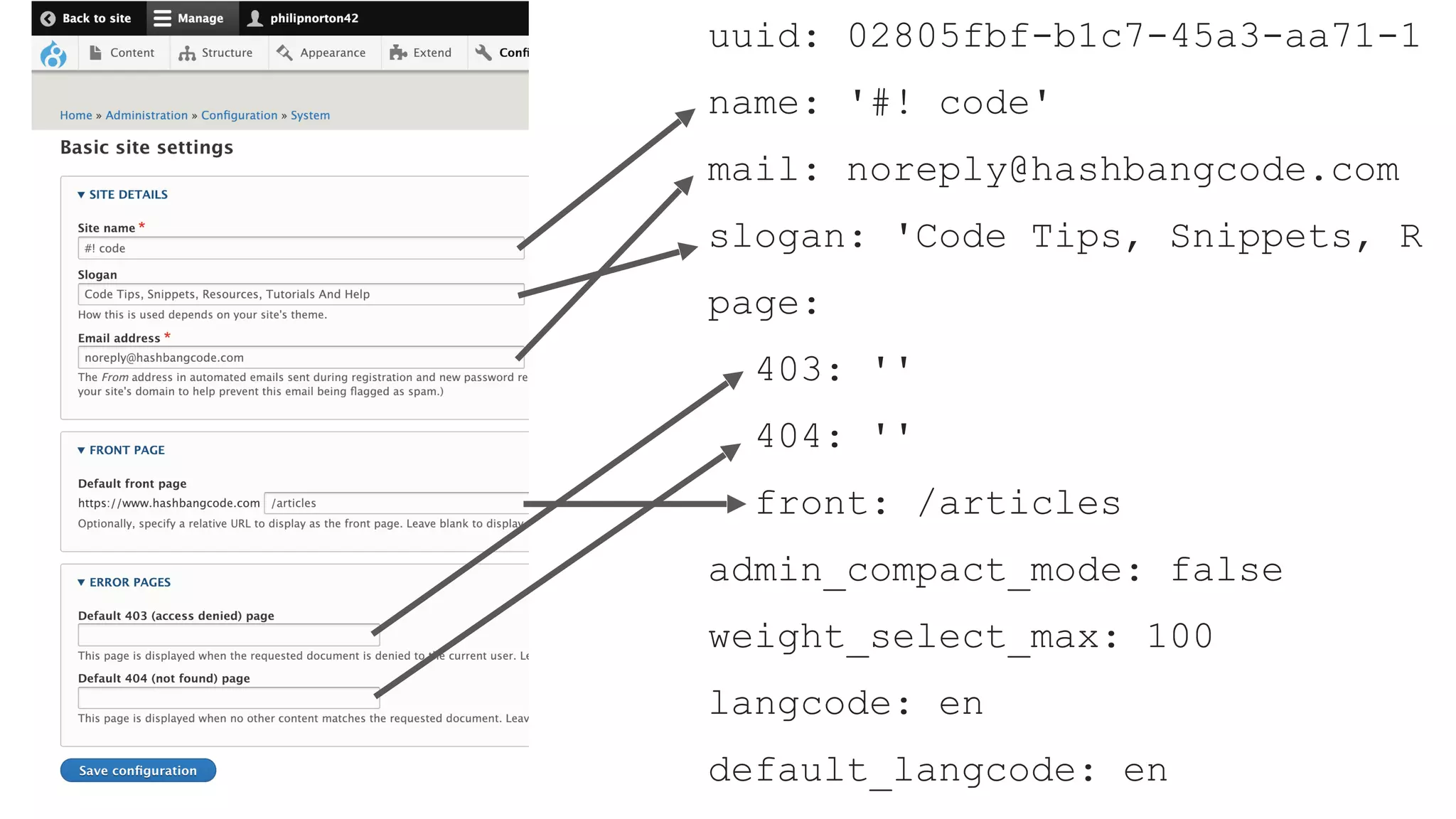
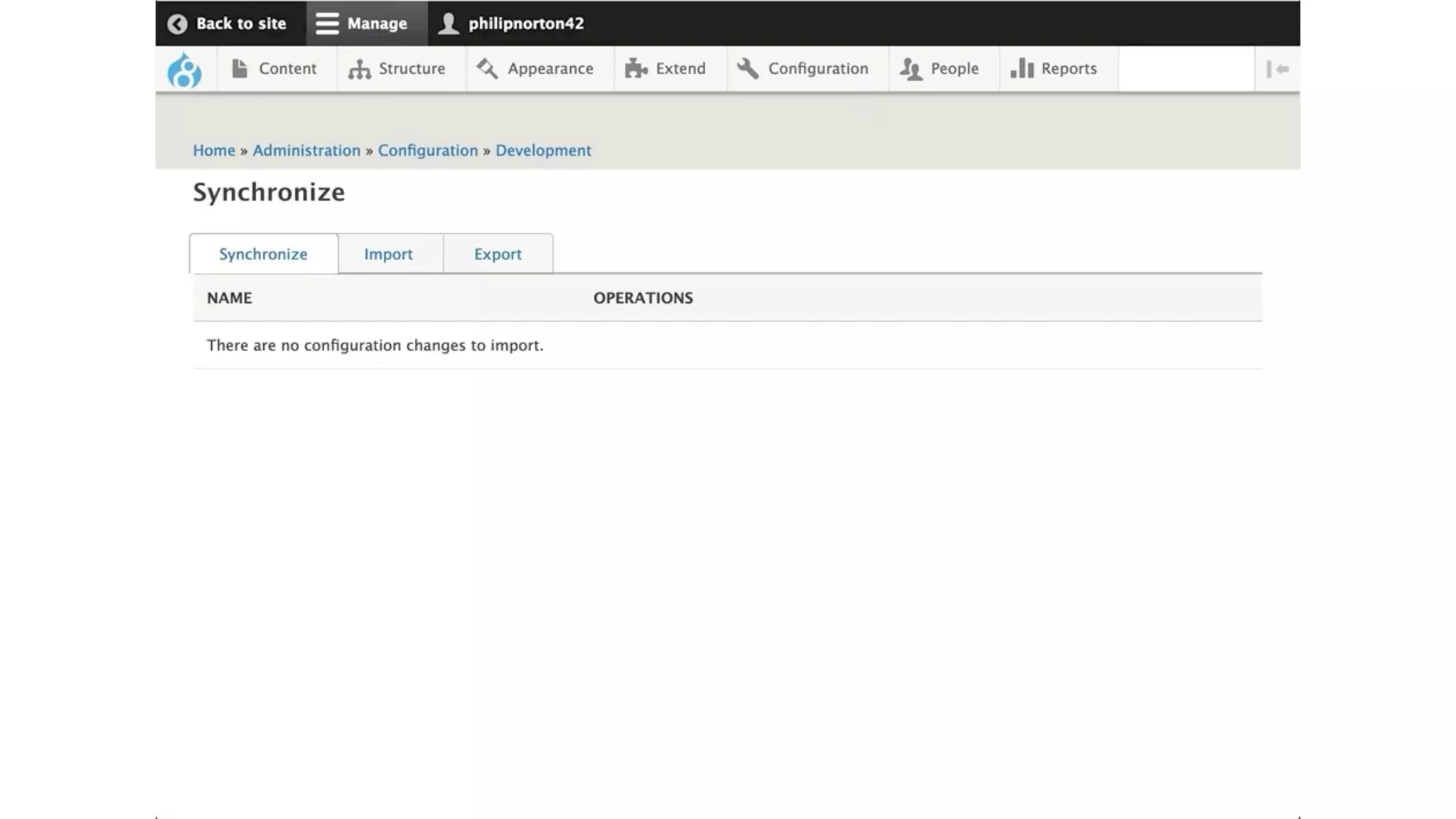
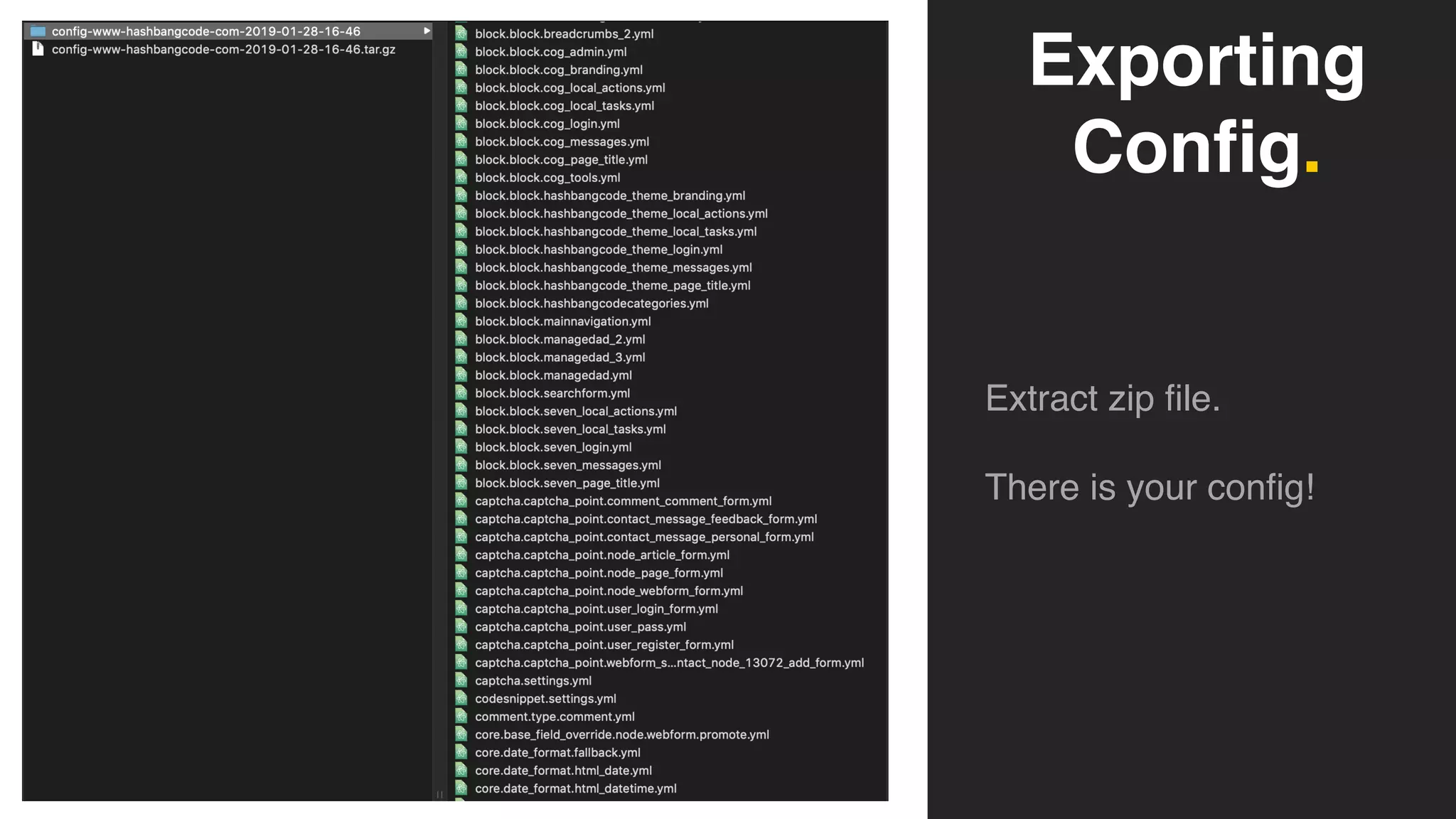
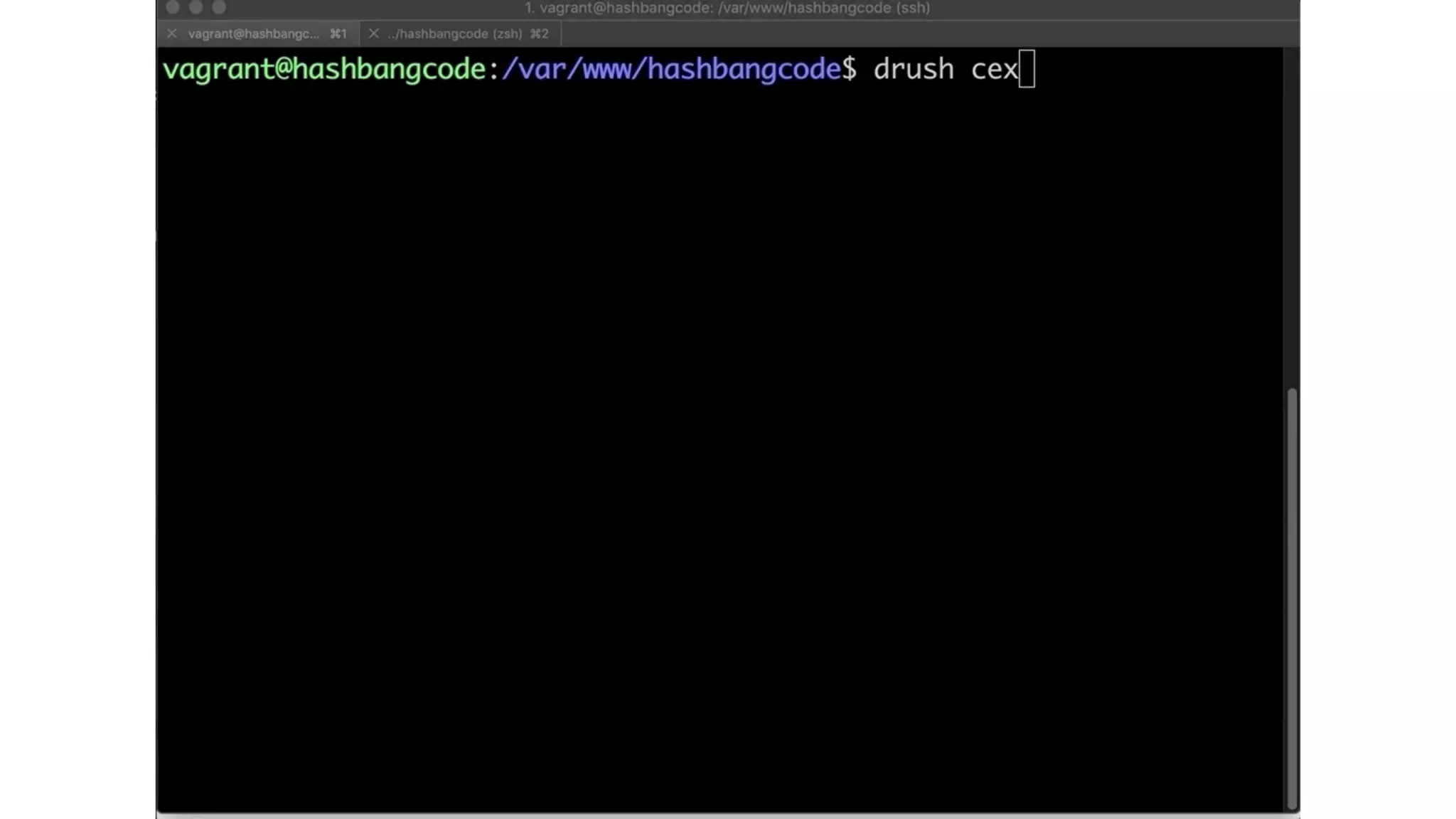
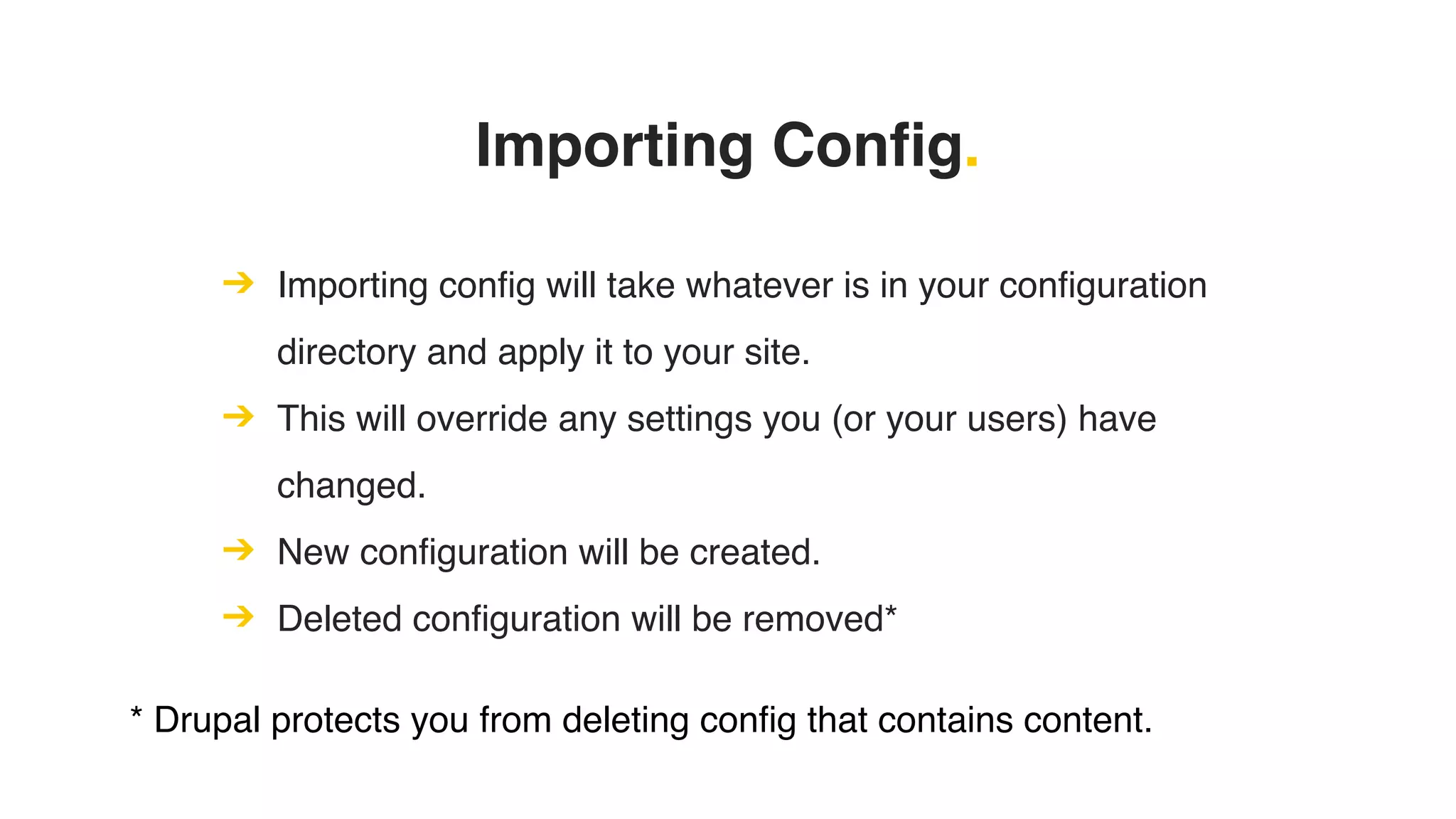
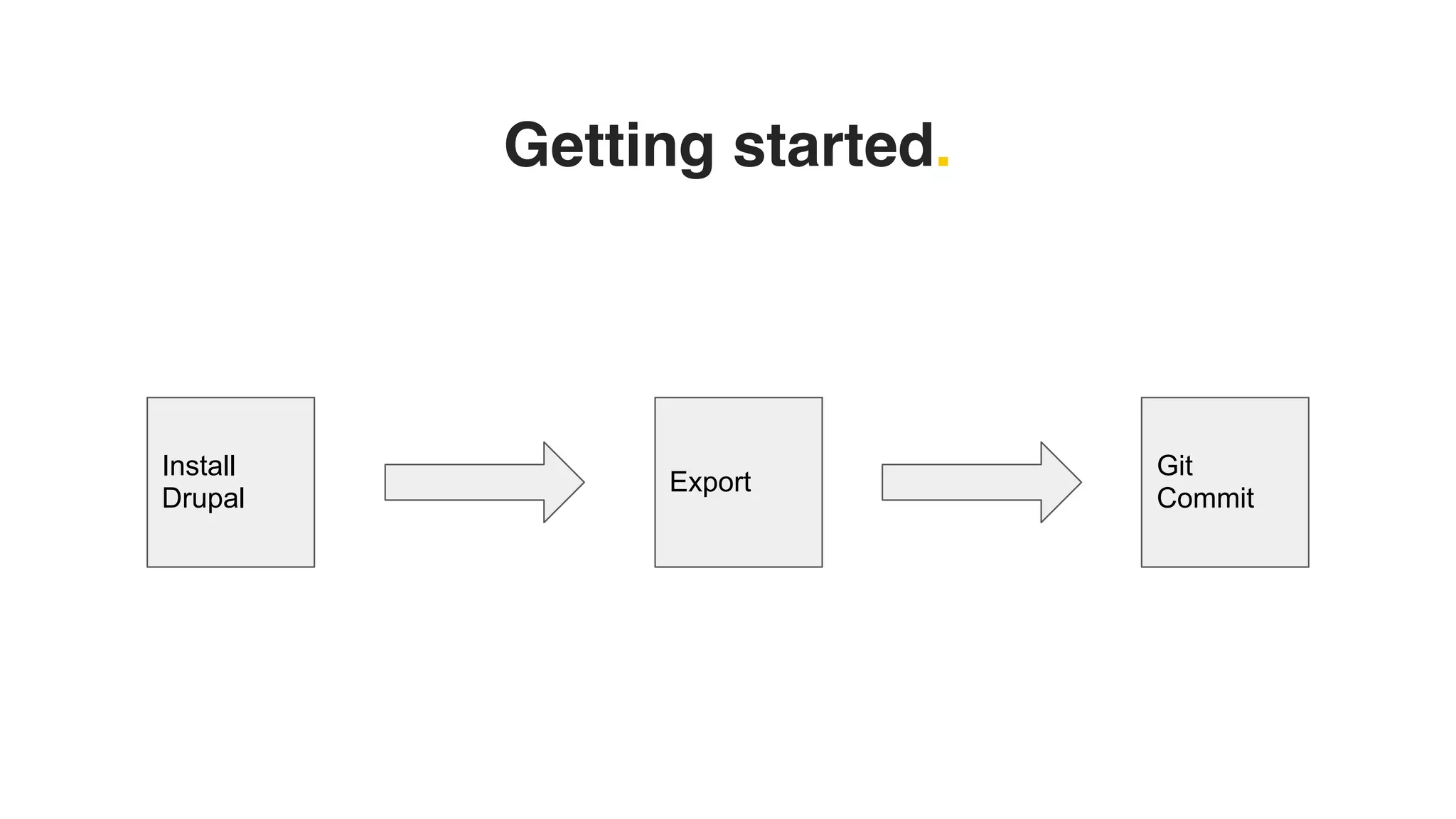
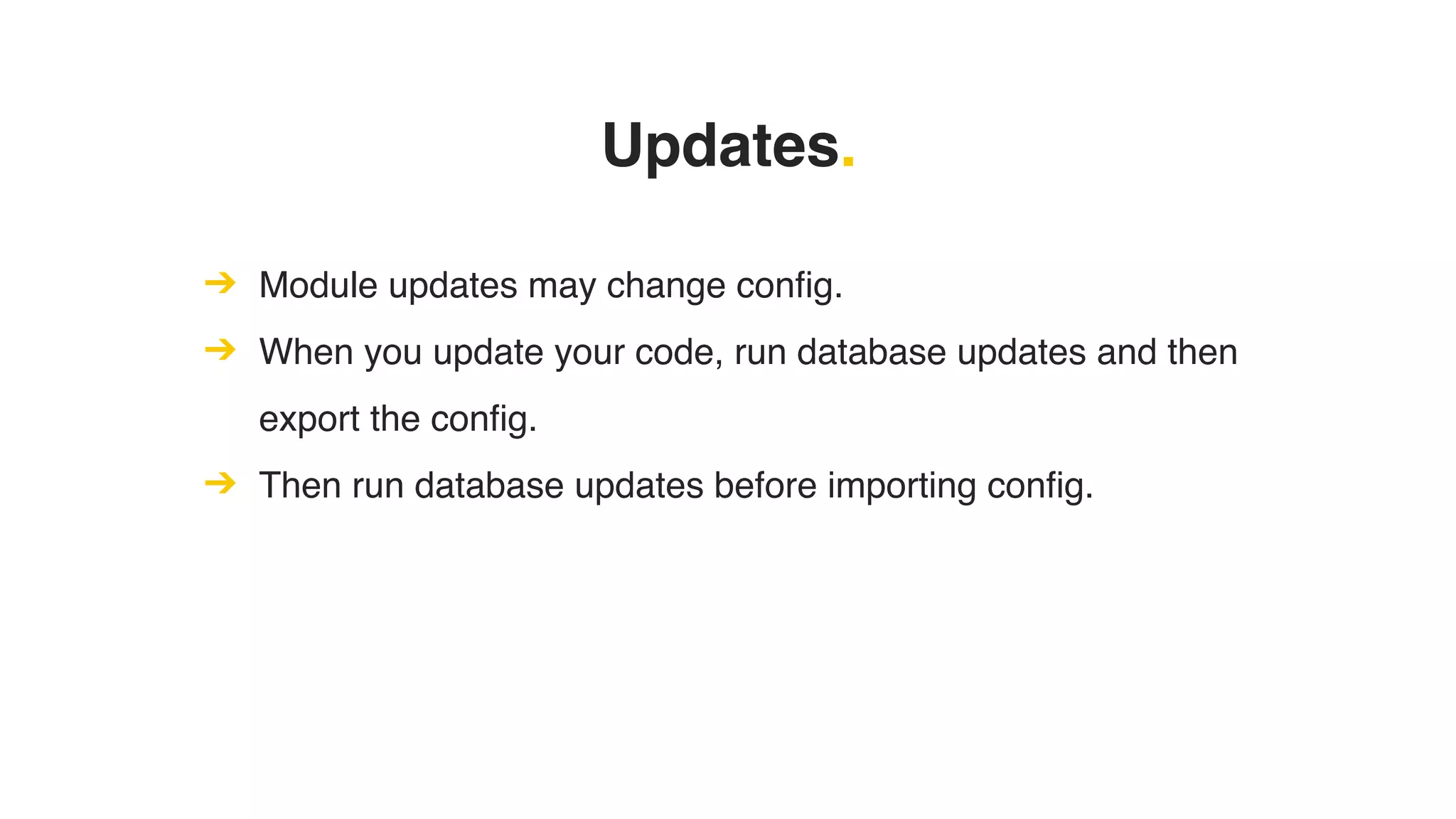
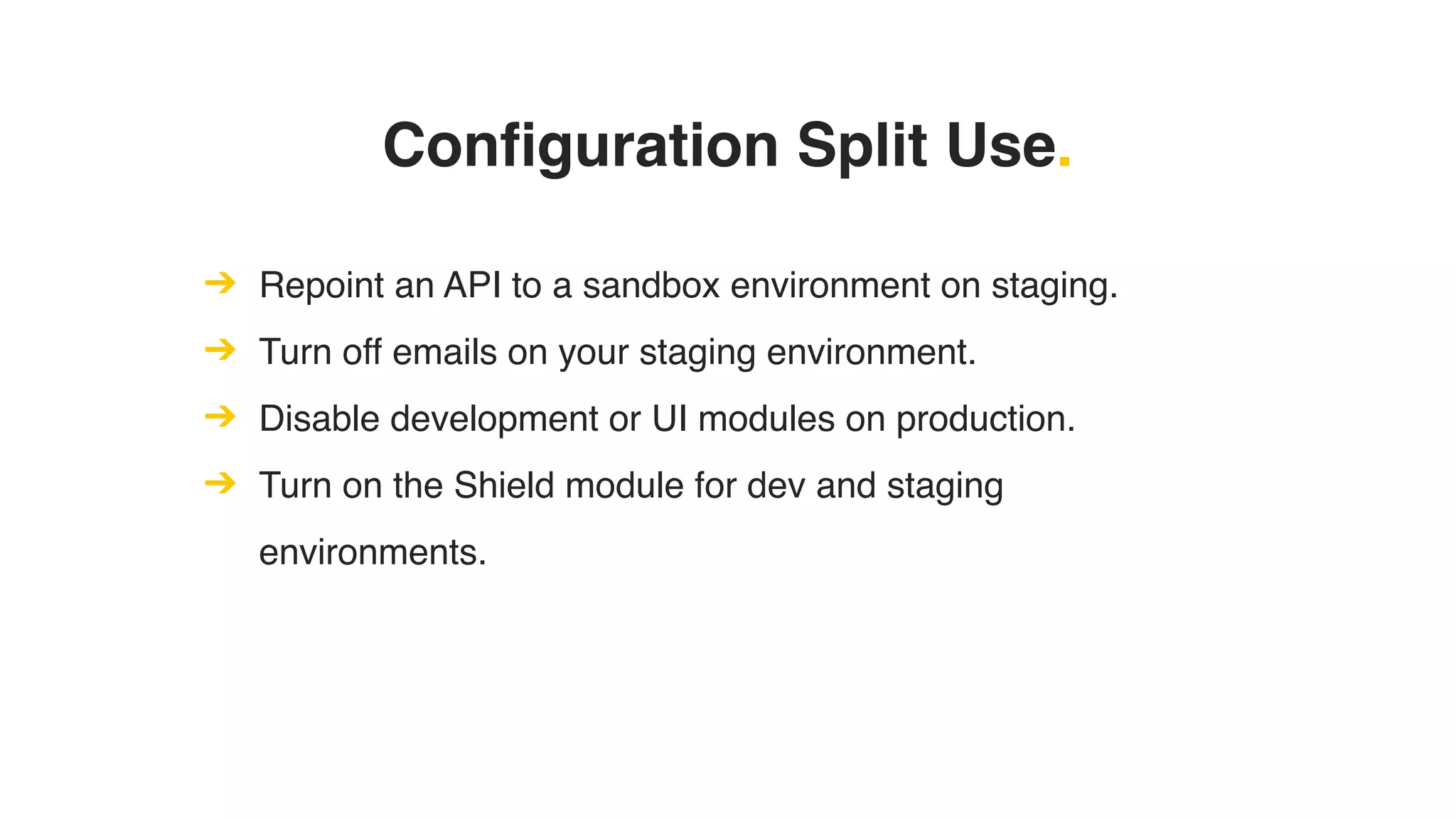
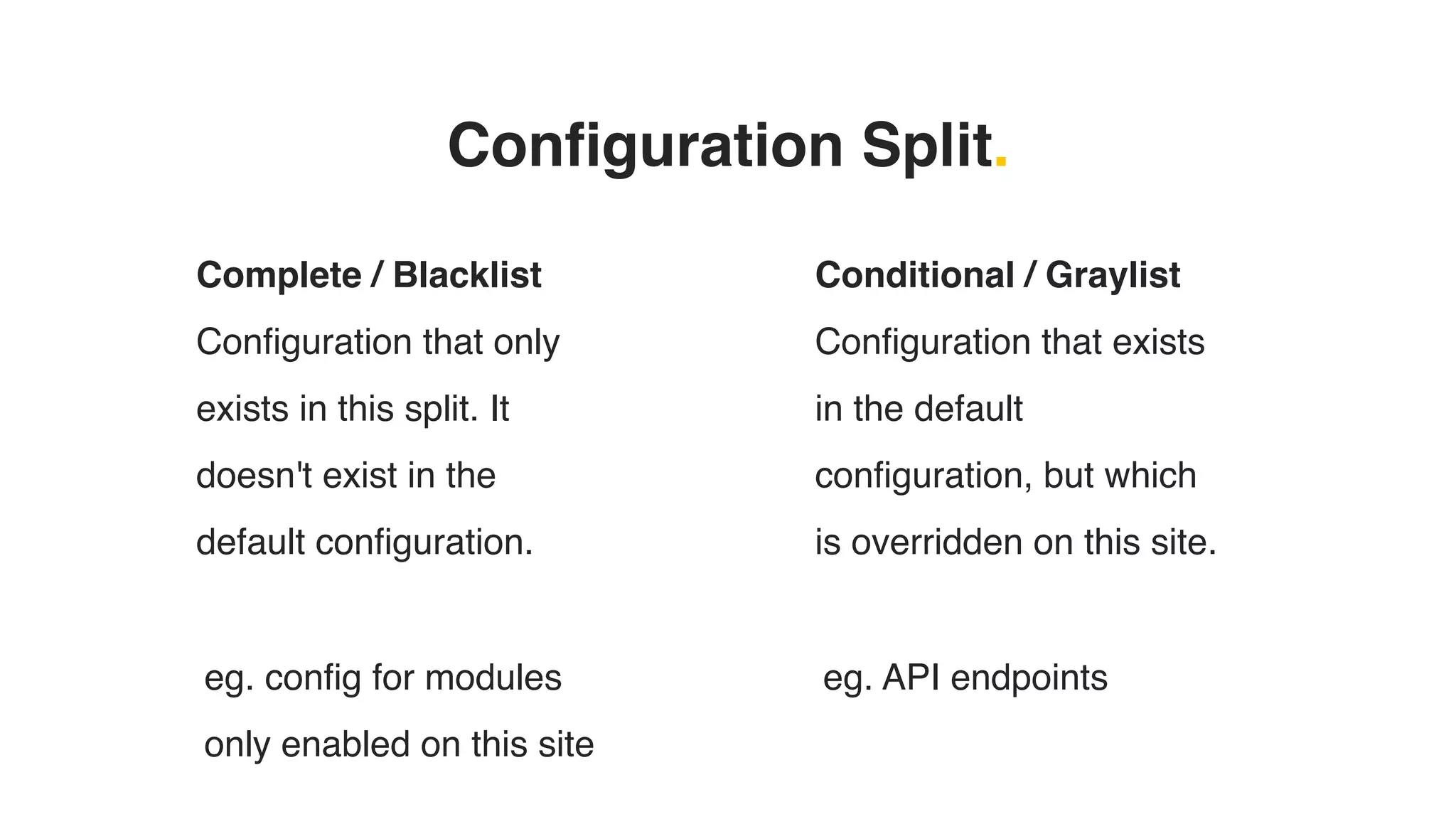
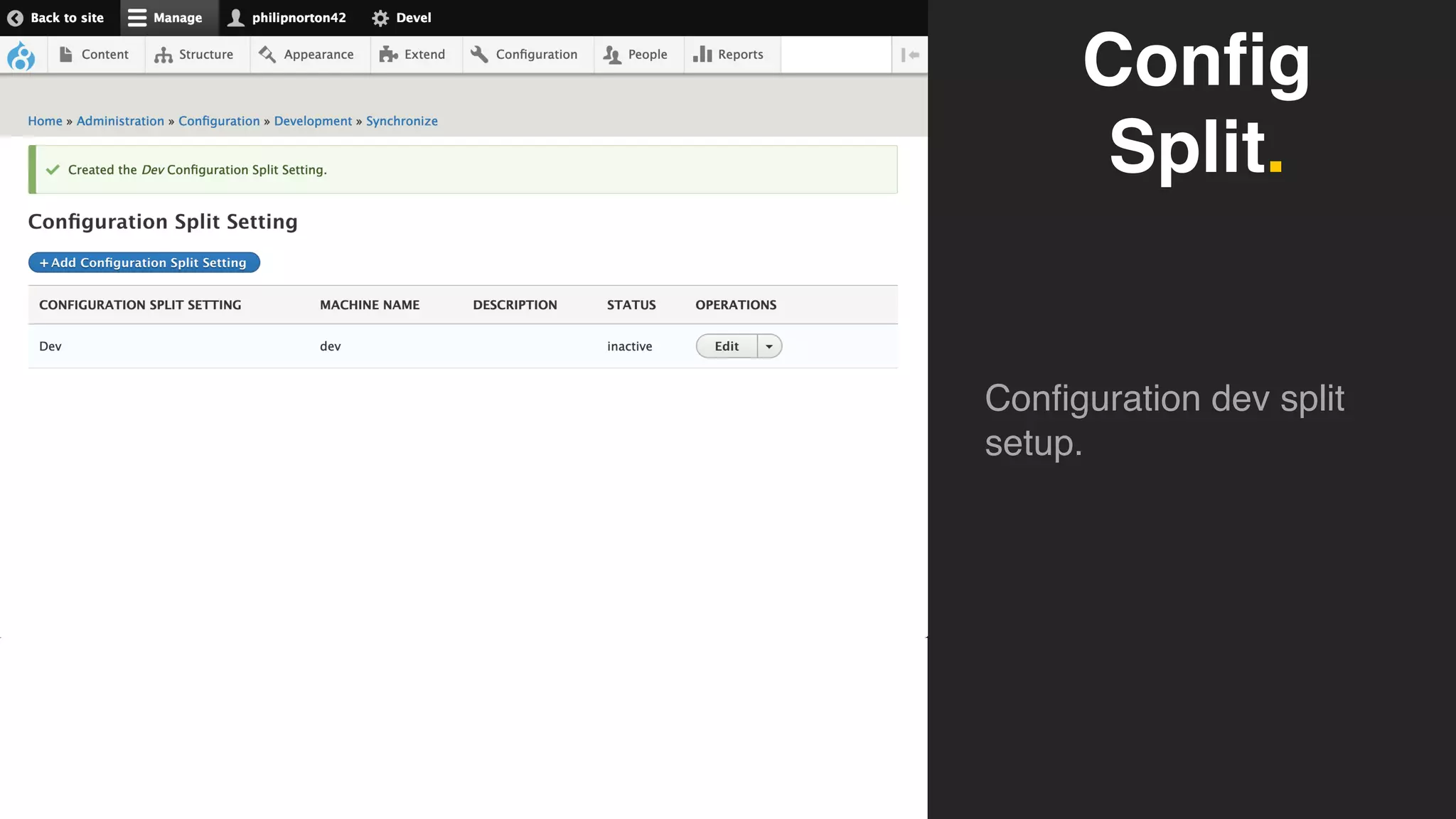
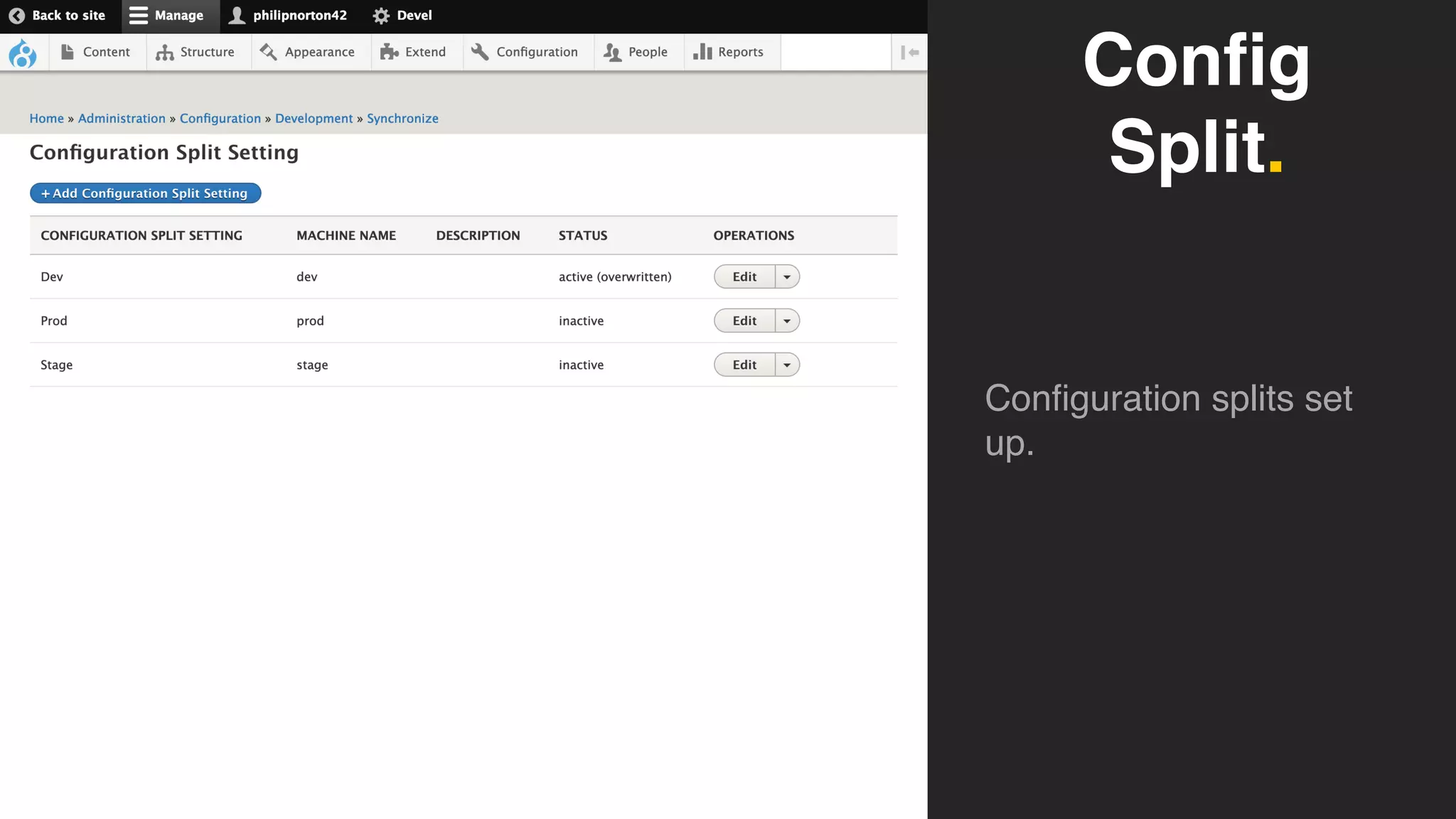
Phil Norton's talk at DrupalCamp London 2019 covers best practices in managing configuration in Drupal. He discusses the challenges of configuration, how to export and import it effectively, and the importance of version control using Git. Additionally, he explains advanced techniques such as configuration splits for different environments and preventing configuration changes on production sites.



























![$config_directories[CONFIG_SYNC_DIRECTORY] = '../config/sync';
Put this in settings.php](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-34-2048.jpg)





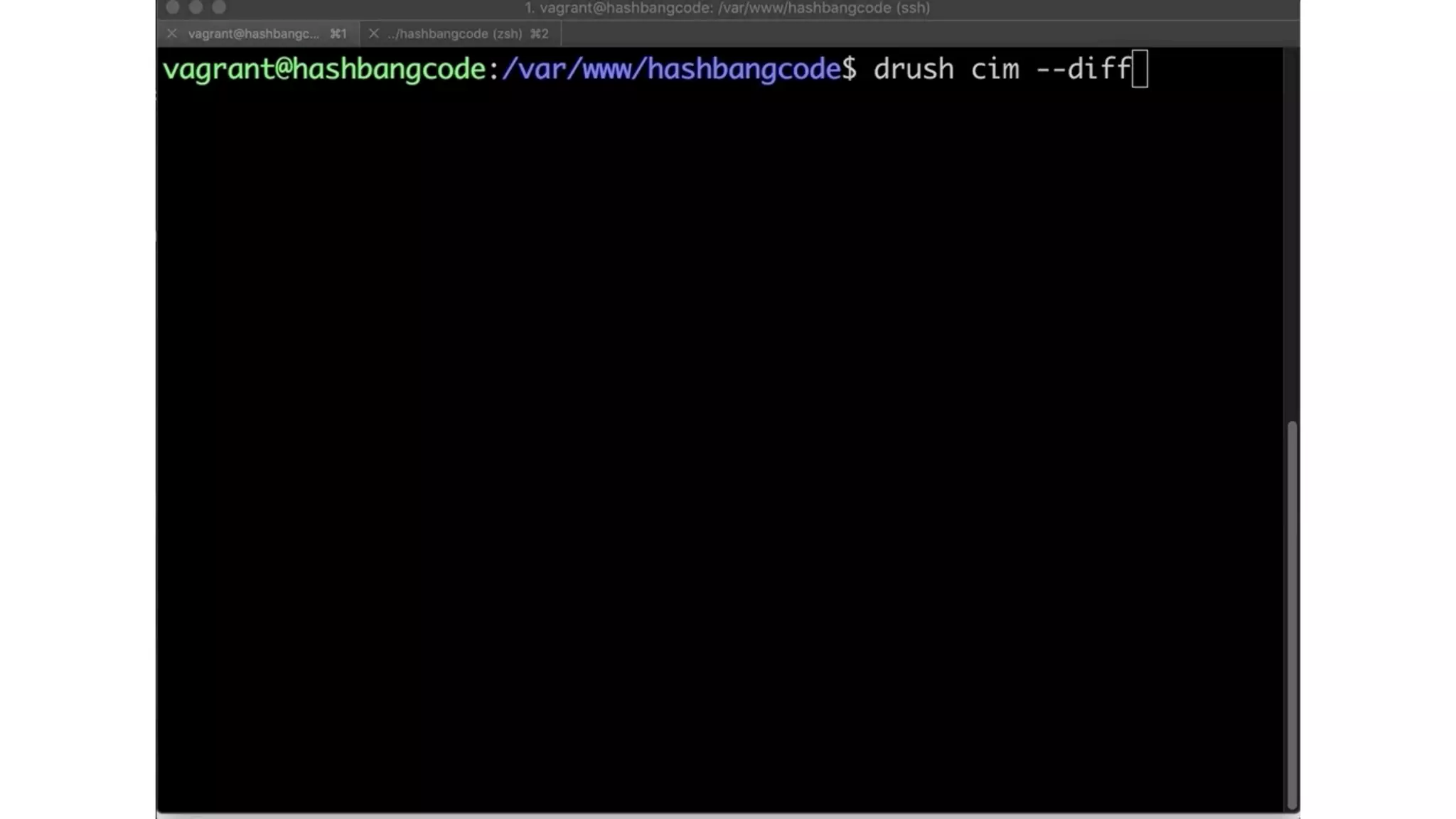





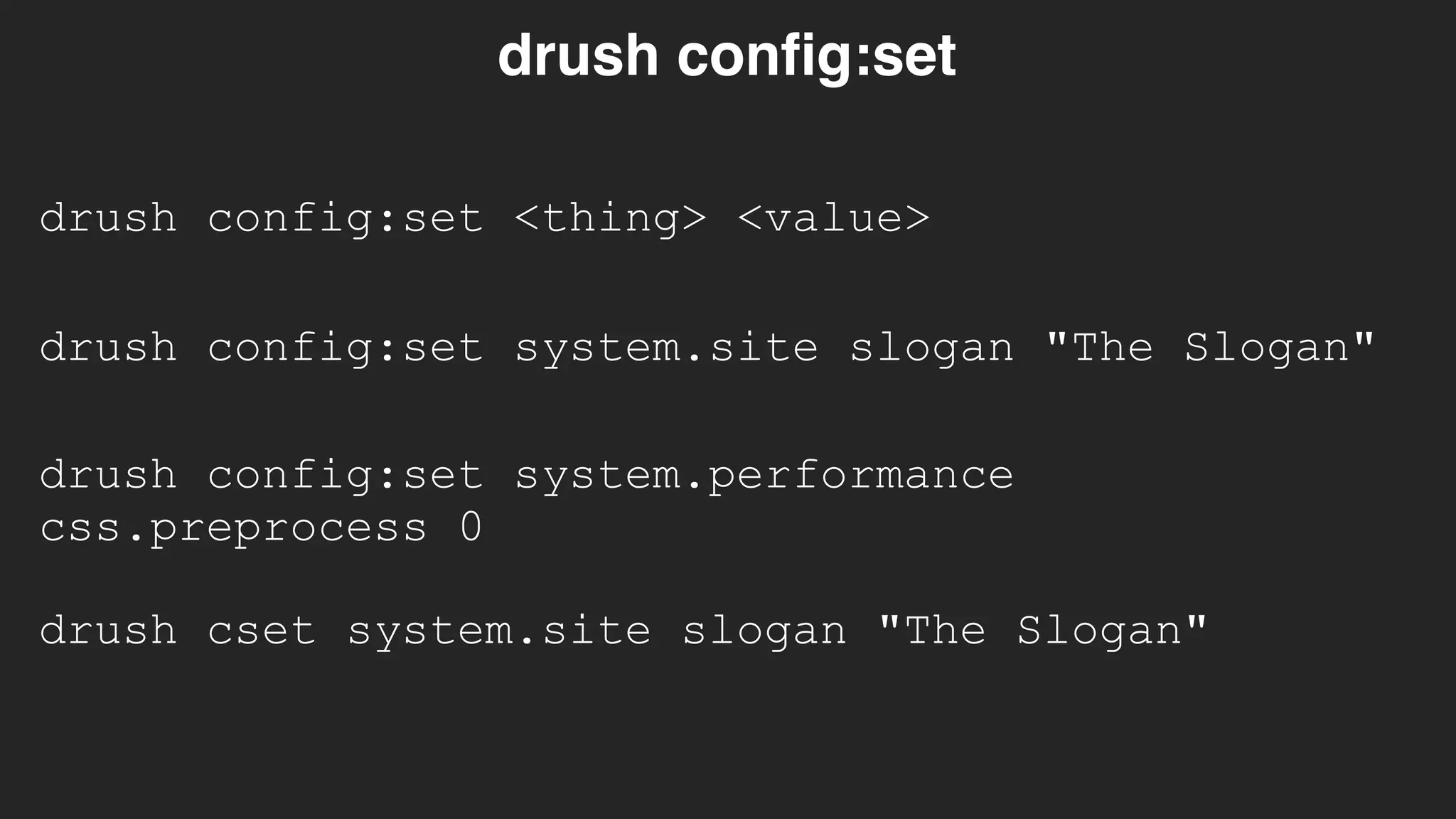
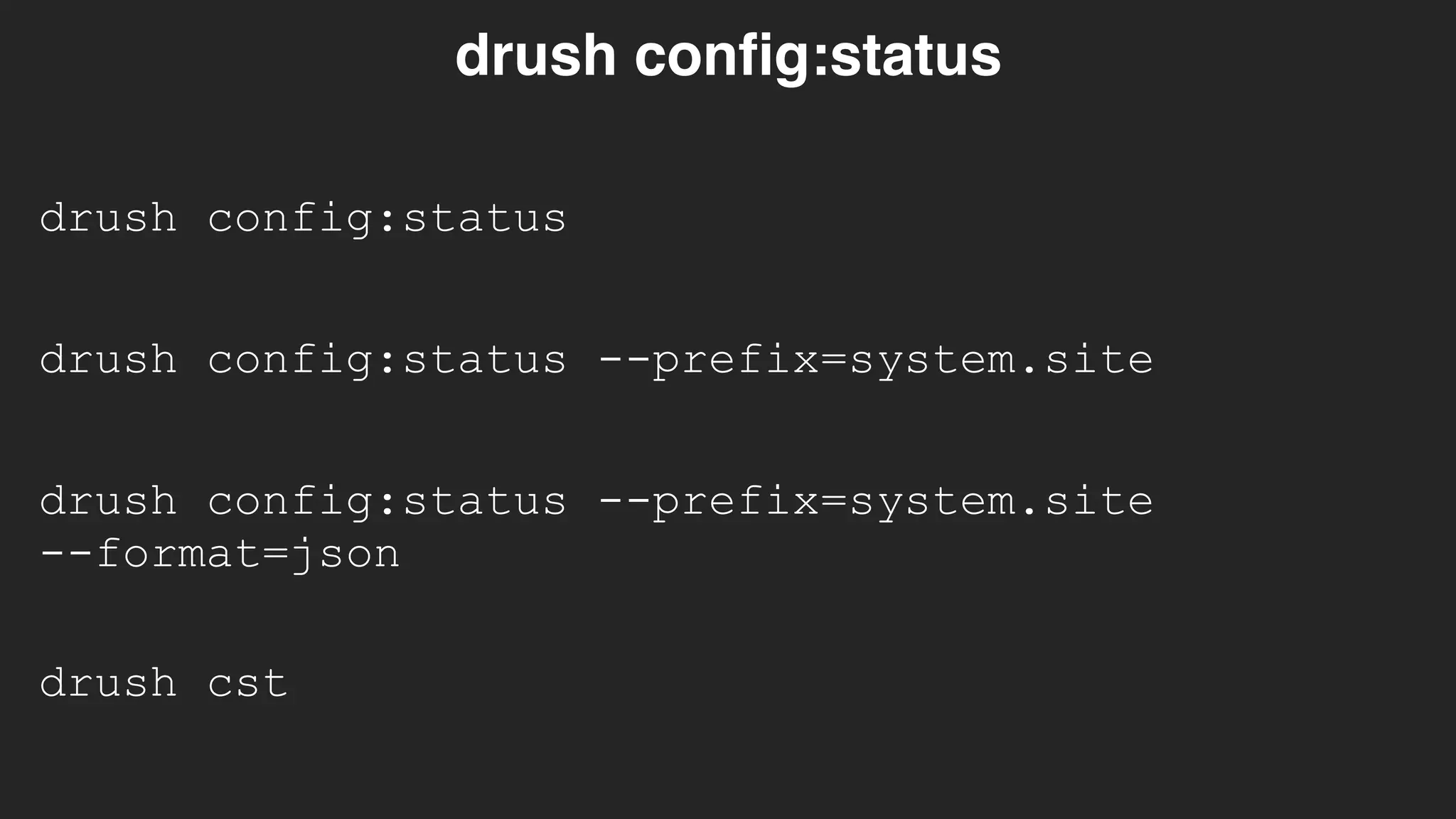
















![$config['config_split.config_split.dev']['status'] = TRUE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-84-2048.jpg)








![if ($sitename == 'site1' && $environment == 'dev') {
$config['config_split.config_split.site1_dev']['status'] = TRUE;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-93-2048.jpg)


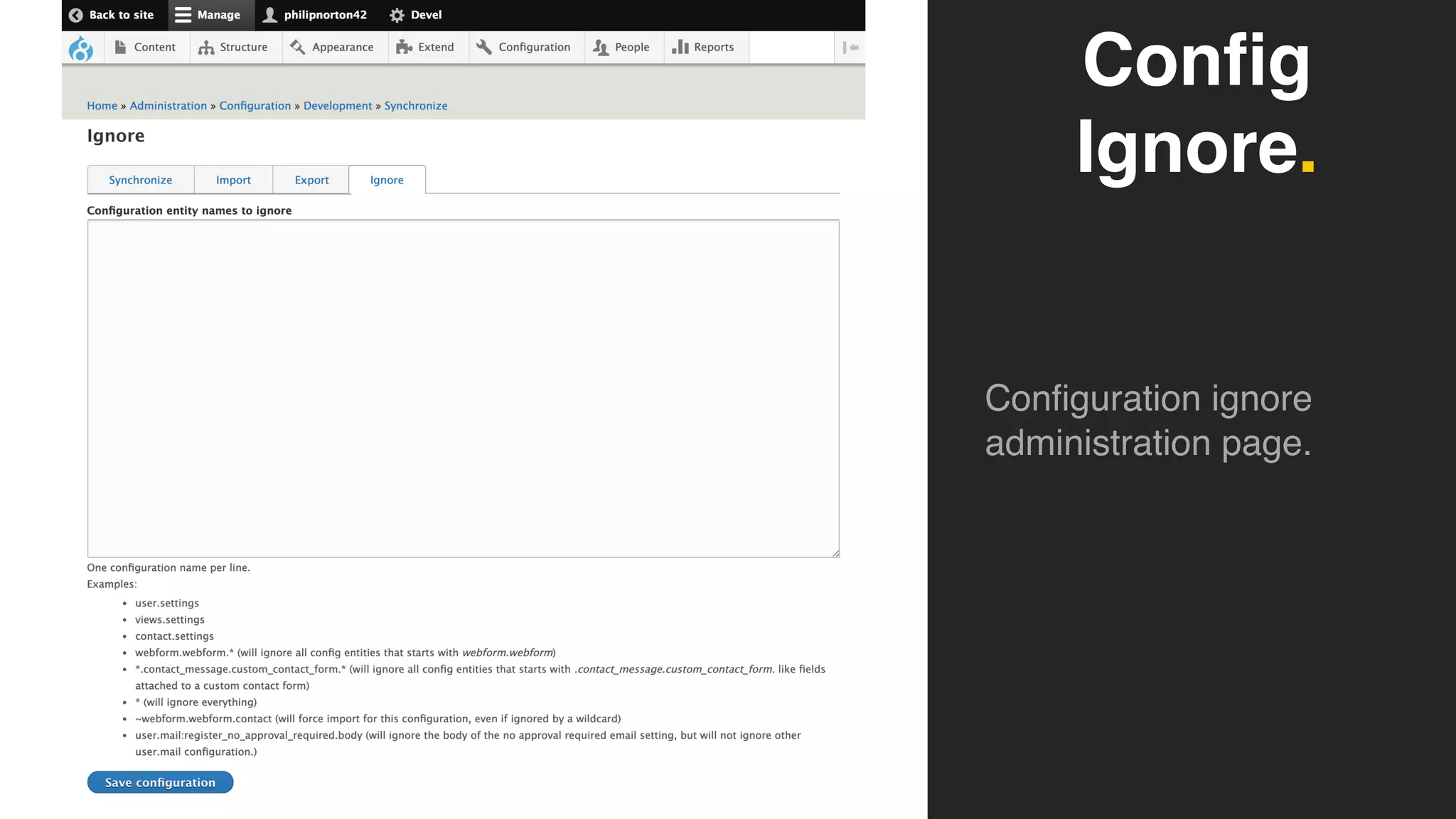



![$settings['config_readonly'] = TRUE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-101-2048.jpg)
![if (PHP_SAPI !== 'cli') {
$settings['config_readonly'] = TRUE;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-102-2048.jpg)


![$settings['config_readonly_whitelist_patterns'] =
[
'config_name.to.ignore',
'wildcards*allowed',
];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal8config-190313105742/75/Getting-Into-Drupal-8-Configuration-105-2048.jpg)