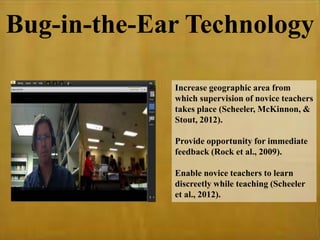
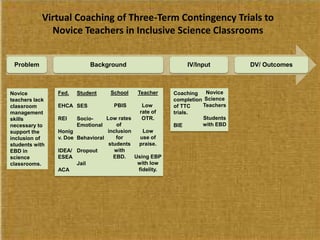
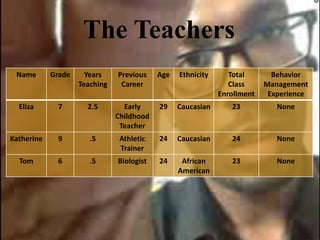
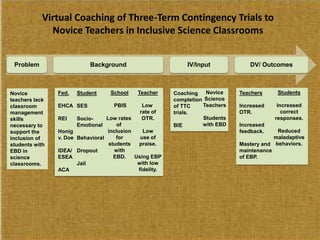
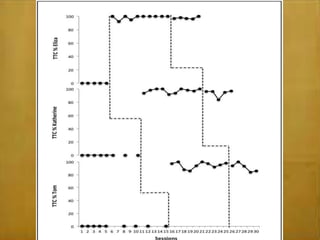
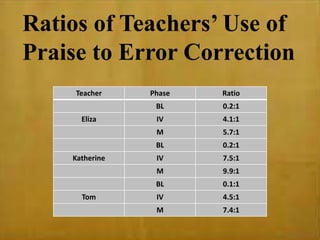
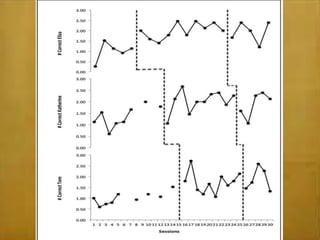
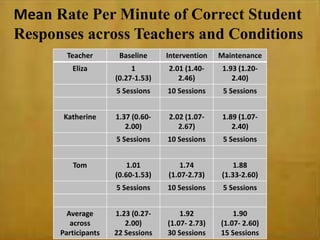
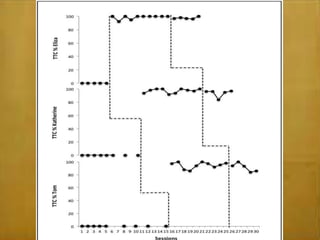
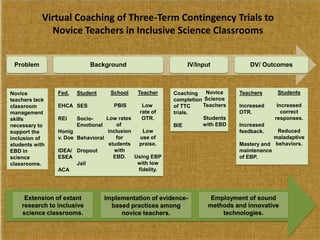
This study examined the effects of virtual coaching on novice science teachers' use of three-term contingency trials with students with emotional and behavioral disorders. Three novice teachers received immediate feedback via Bluetooth earpieces to complete contingency trials with students. Results showed the intervention increased teachers' use of praise, feedback, and mastery of evidence-based practices. It also increased students' correct responses and reduced problem behaviors. Teachers maintained these behaviors after coaching ended. The study employed valid methods and extended research on virtual coaching to inclusive science classrooms.