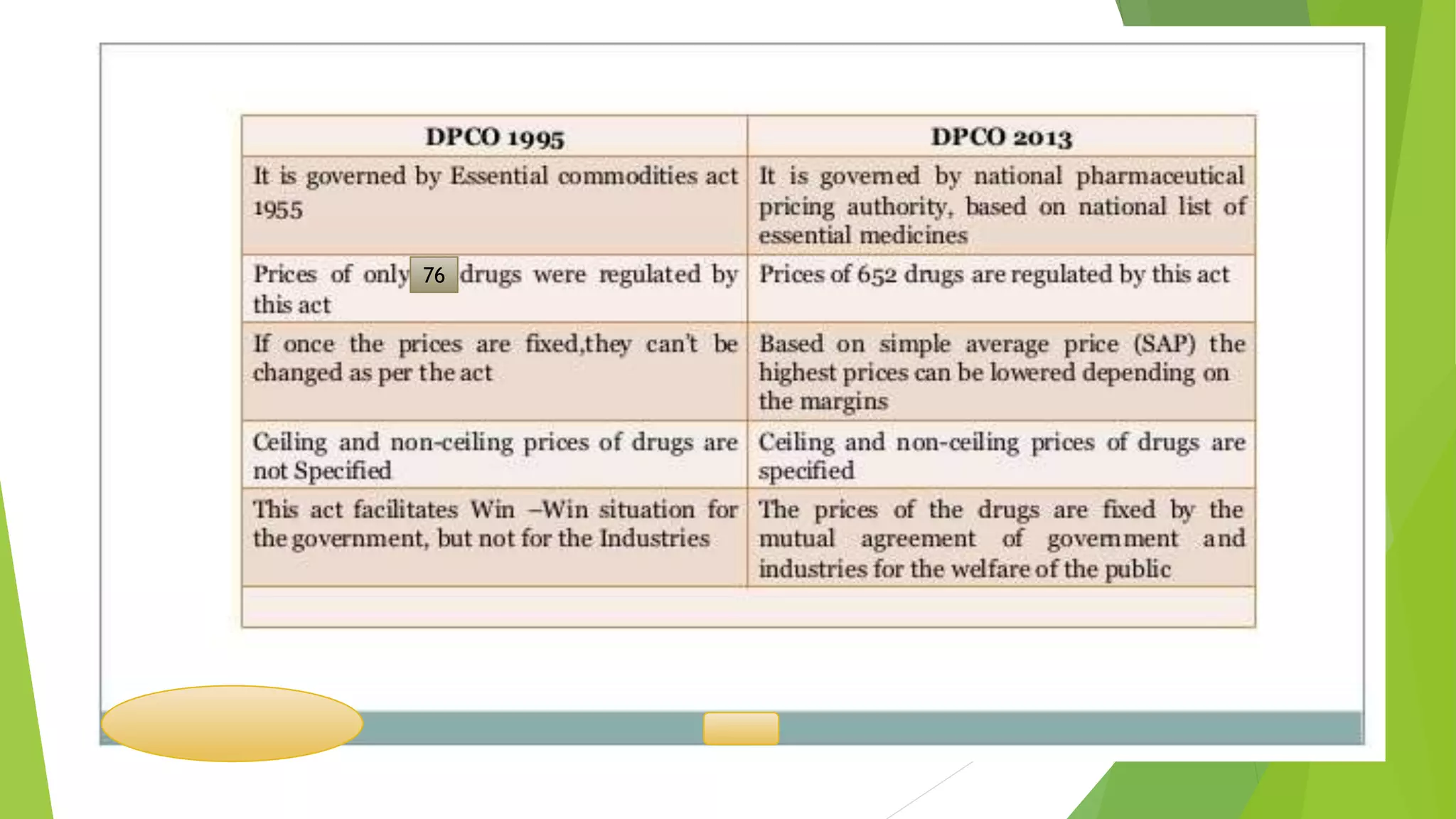
This document summarizes the Drug (Price Control) Order of 1995 in India. It establishes schedules that list bulk drugs and formulations subject to price controls. The order's objectives are to ensure adequate production and equitable distribution of drugs, maintain drug supplies, and make drugs available at fair prices. It defines key terms and establishes the formula used to calculate the retail price of scheduled formulations based on material and manufacturing costs. The government has the power to exempt manufacturers from price controls after considering factors like number of employees, capital invested, products made, sales, and production of new drugs. Penalties are established for non-compliance.