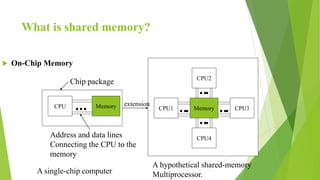
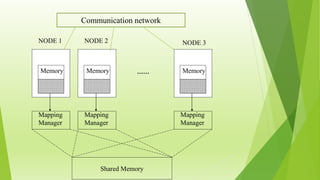
Distributed shared memory (DSM) is a memory architecture where physically separate memories can be addressed as a single logical address space. In a DSM system, data moves between nodes' main and secondary memories when a process accesses shared data. Each node has a memory mapping manager that maps the shared virtual memory to local physical memory. DSM provides advantages like shielding programmers from message passing, lower cost than multiprocessors, and large virtual address spaces, but disadvantages include potential performance penalties from remote data access and lack of programmer control over messaging.