This document discusses registers, register transfer, and binary logic in digital systems. It contains the following key points:
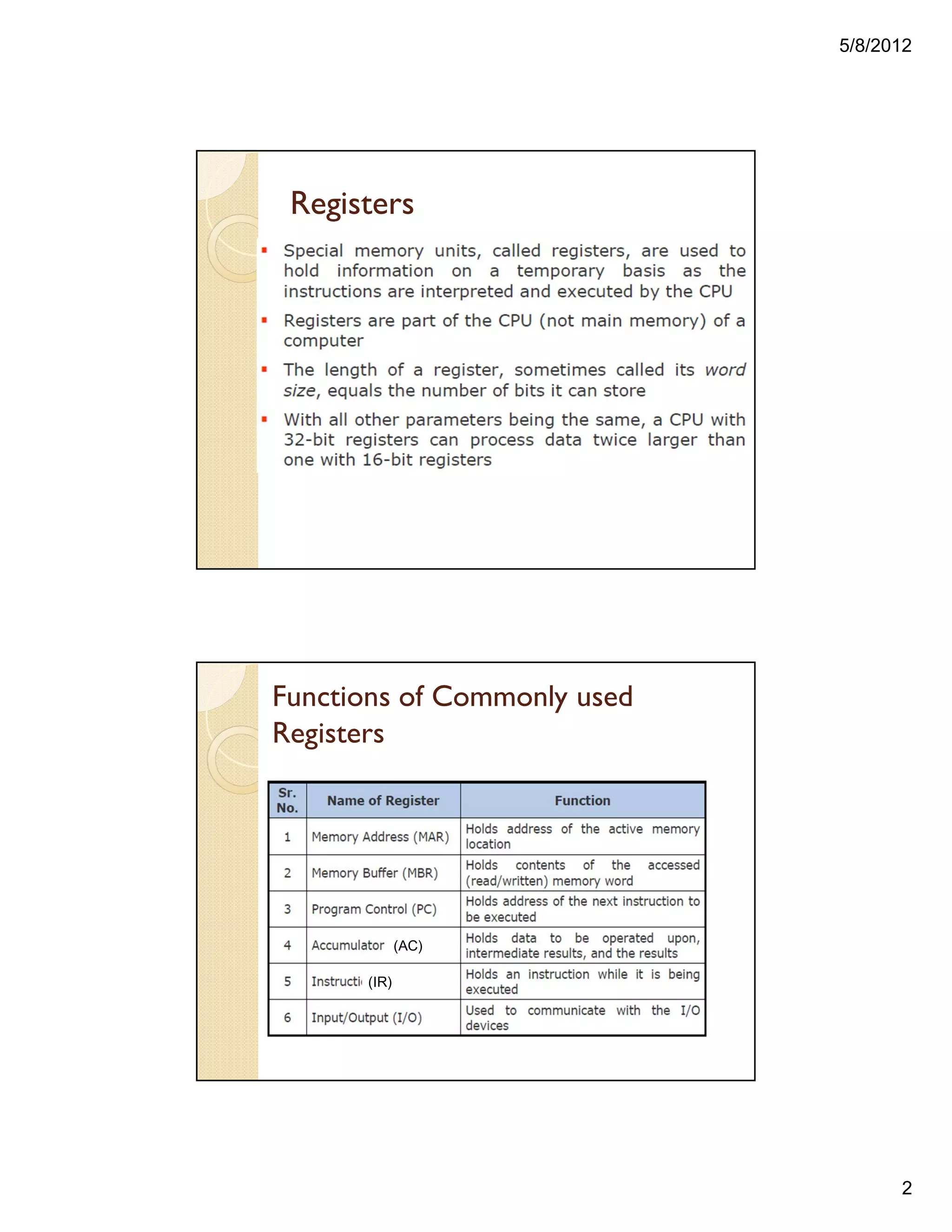
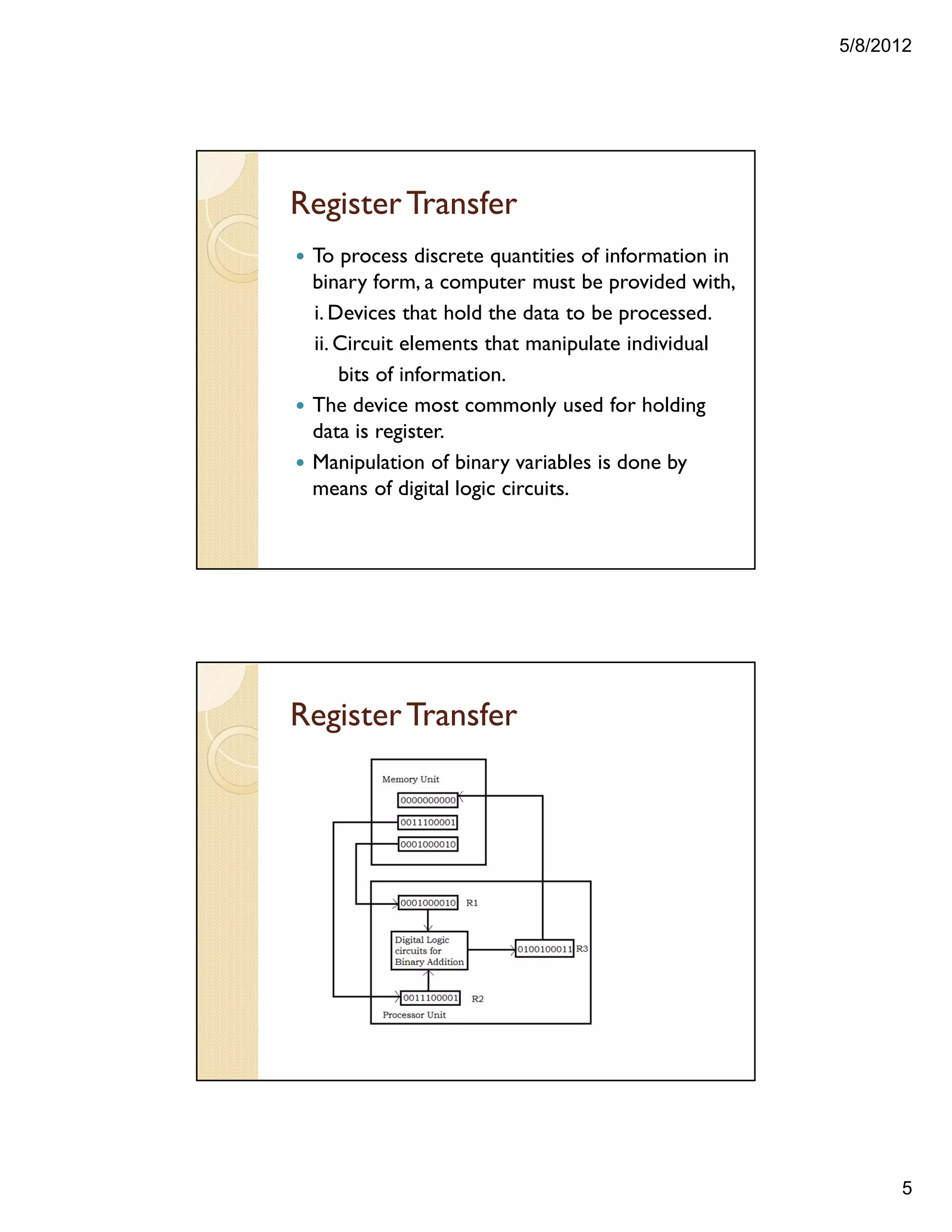
1. Registers are used to store and hold binary information in a computer system. Register transfer involves moving data between registers, such as from an input register to a processor register.
2. The control unit uses registers to track computer sequences. Data must be stored in a register when transferred to or from an input/output device.
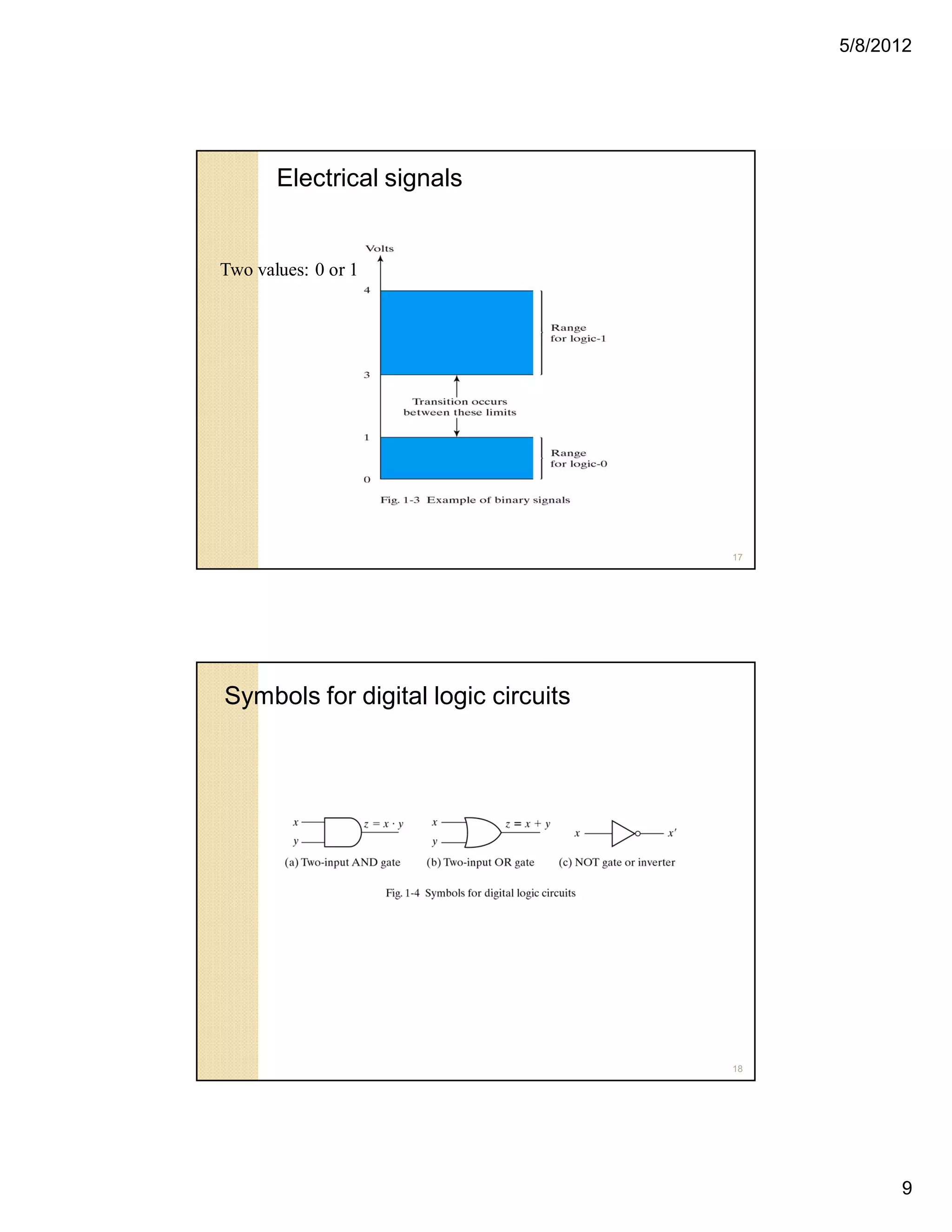
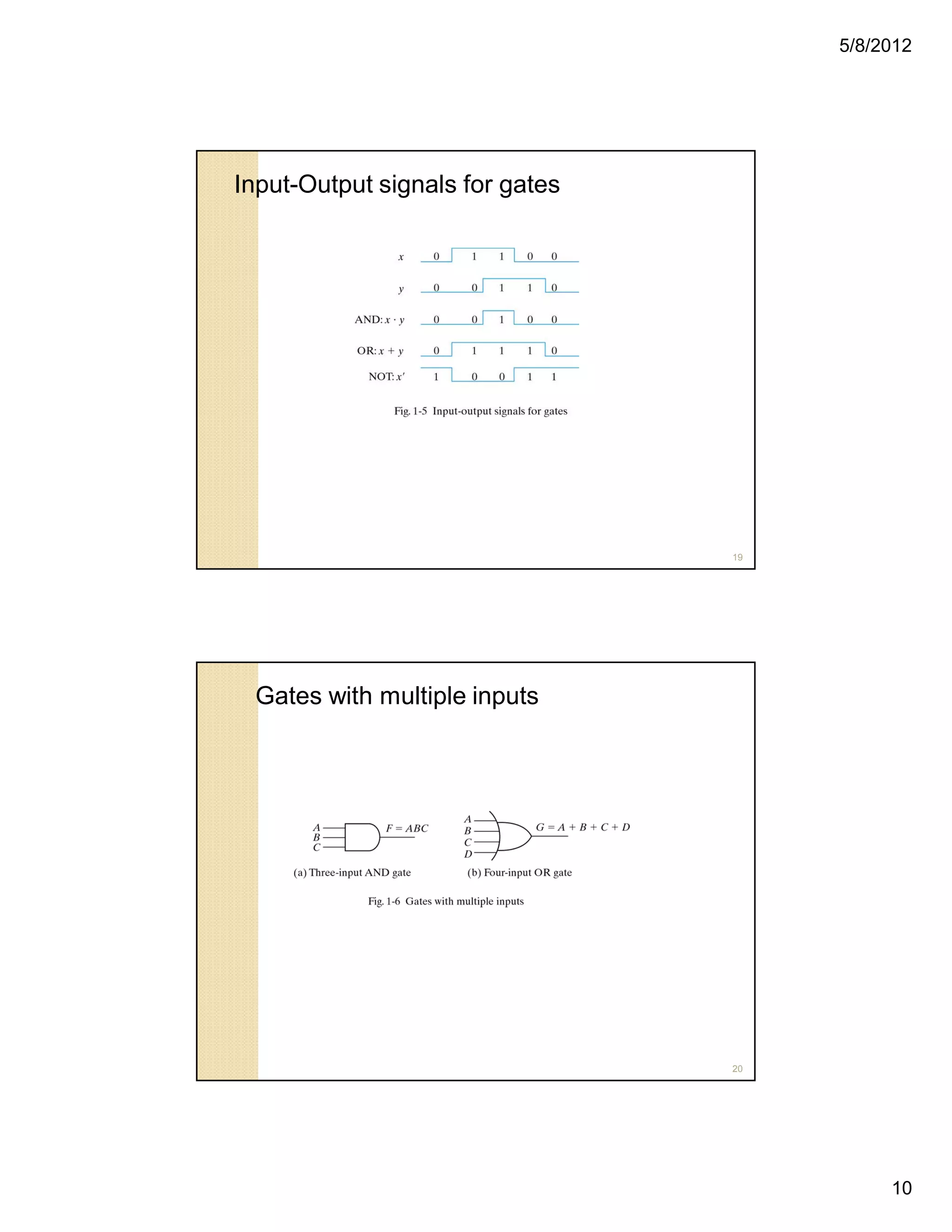
3. Binary logic deals with variables that can take on two values (0 or 1) and logical operations on these values. Logic gates are used to manipulate bits.