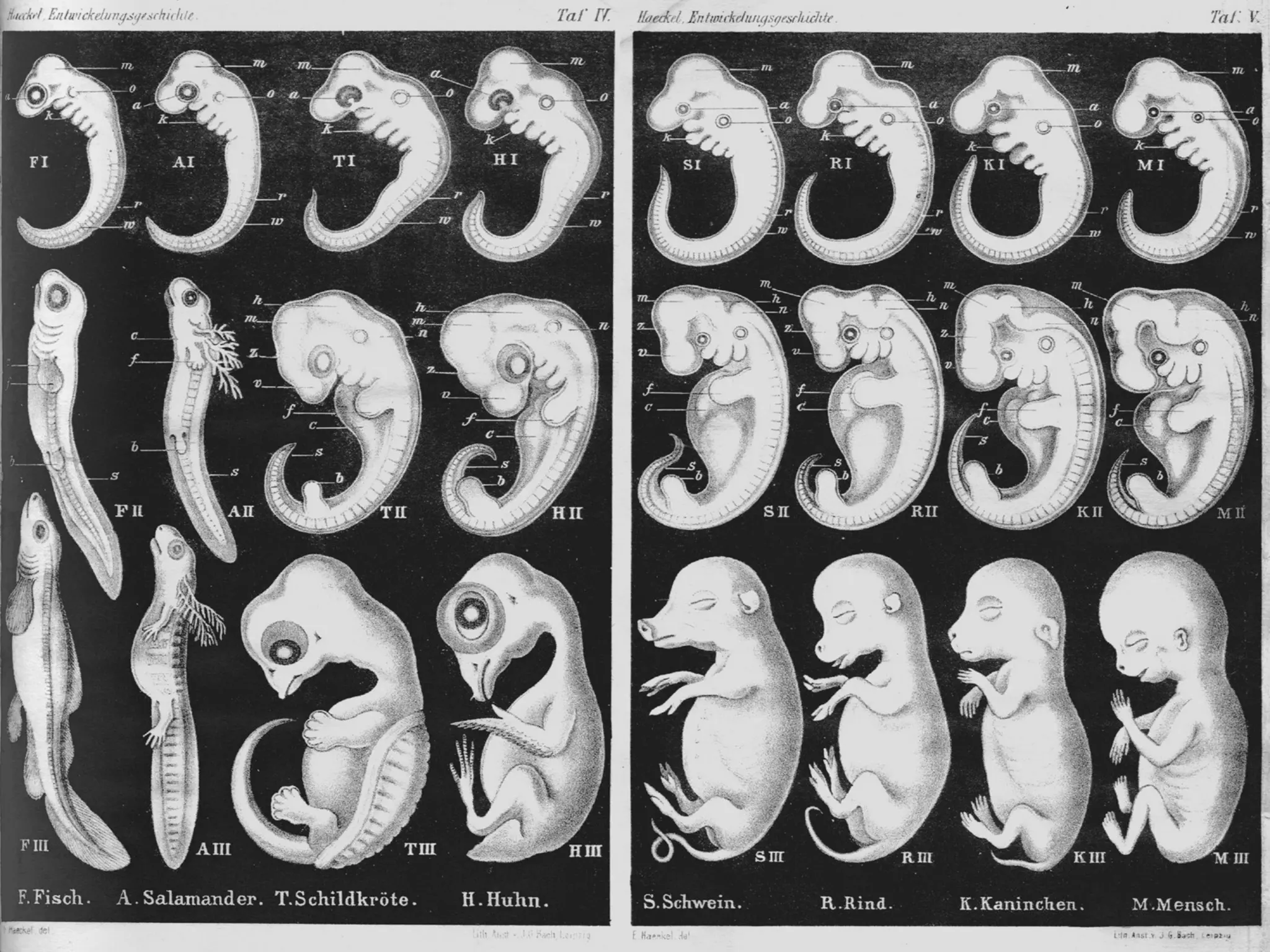
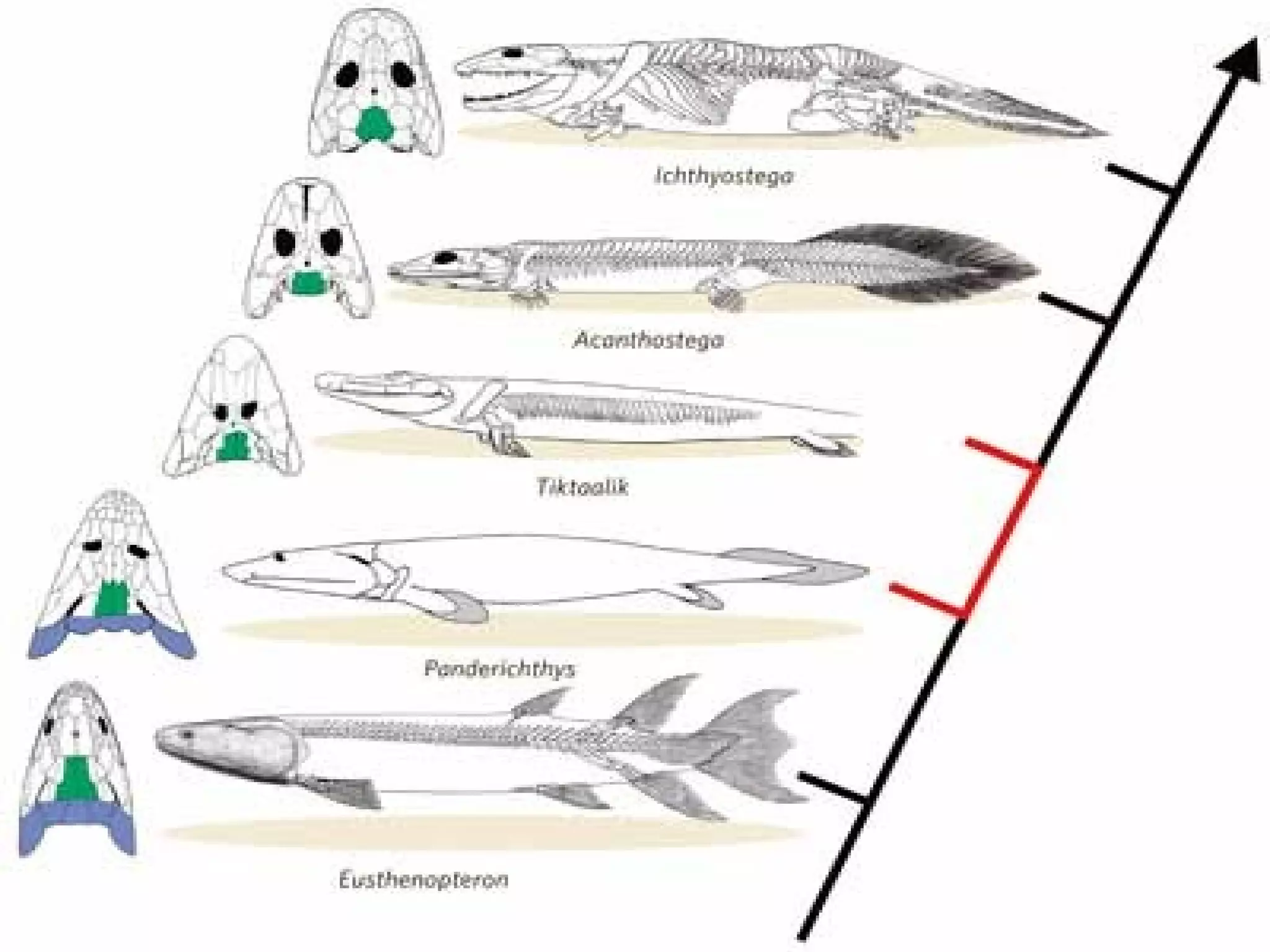
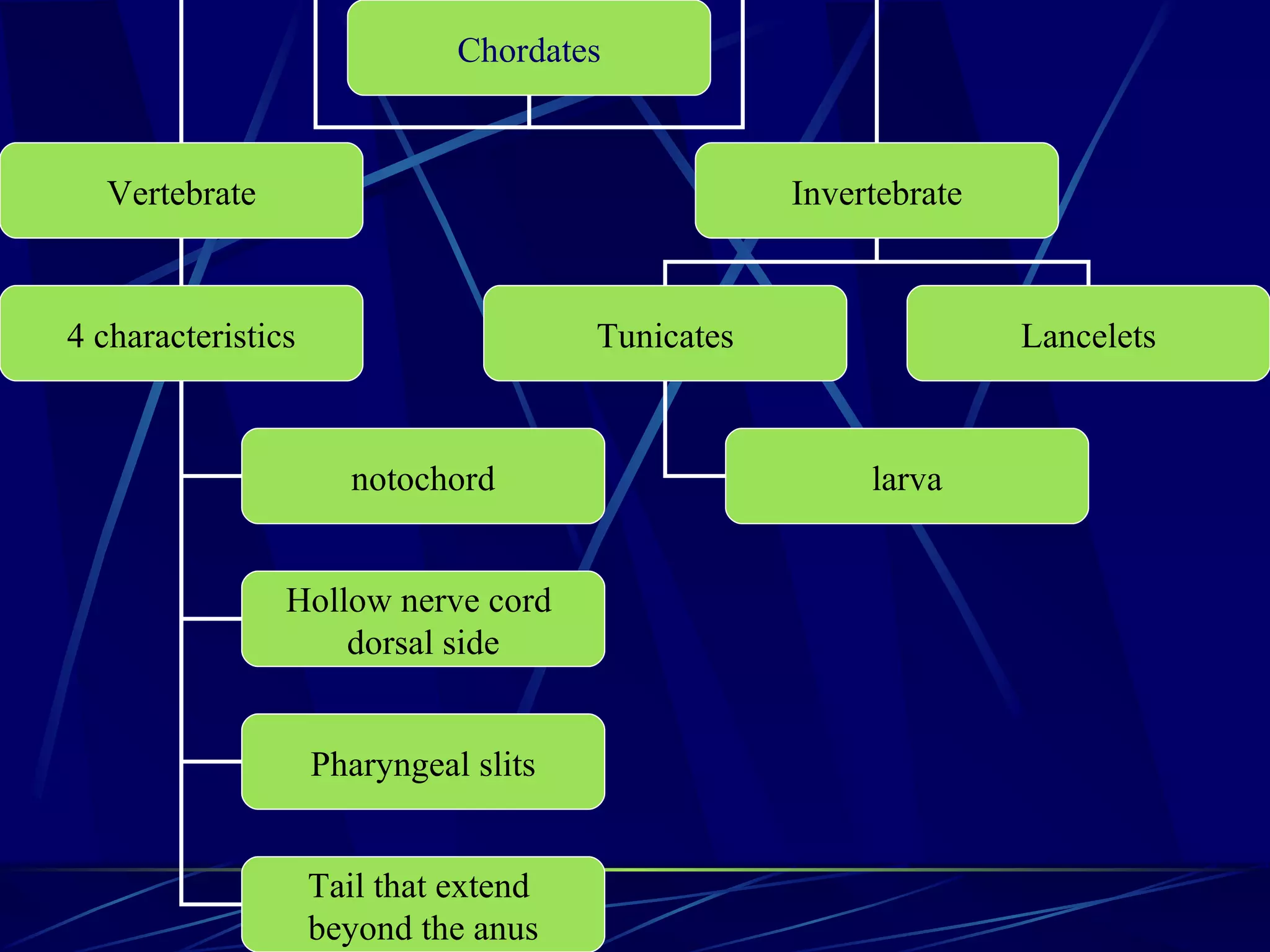
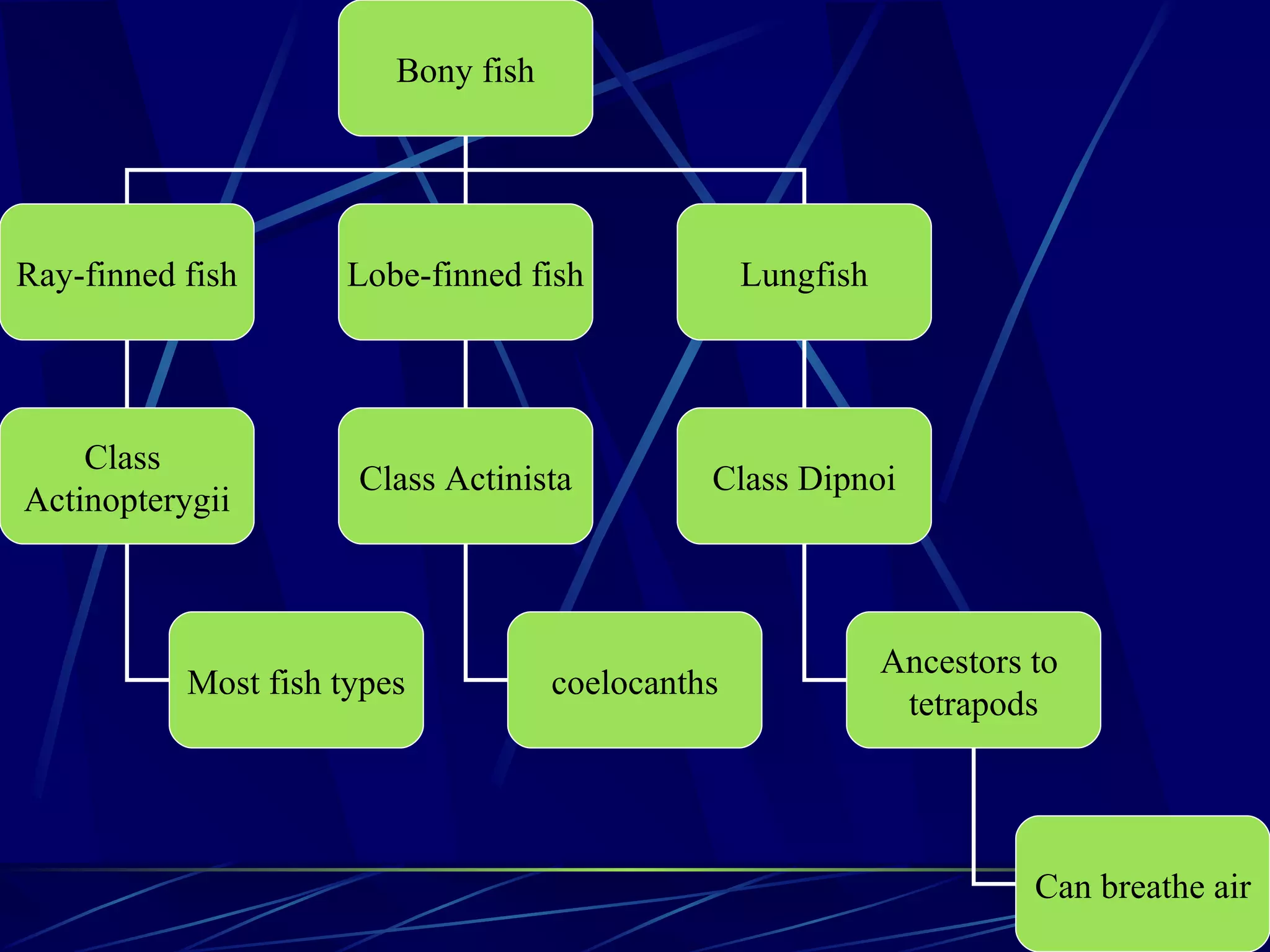
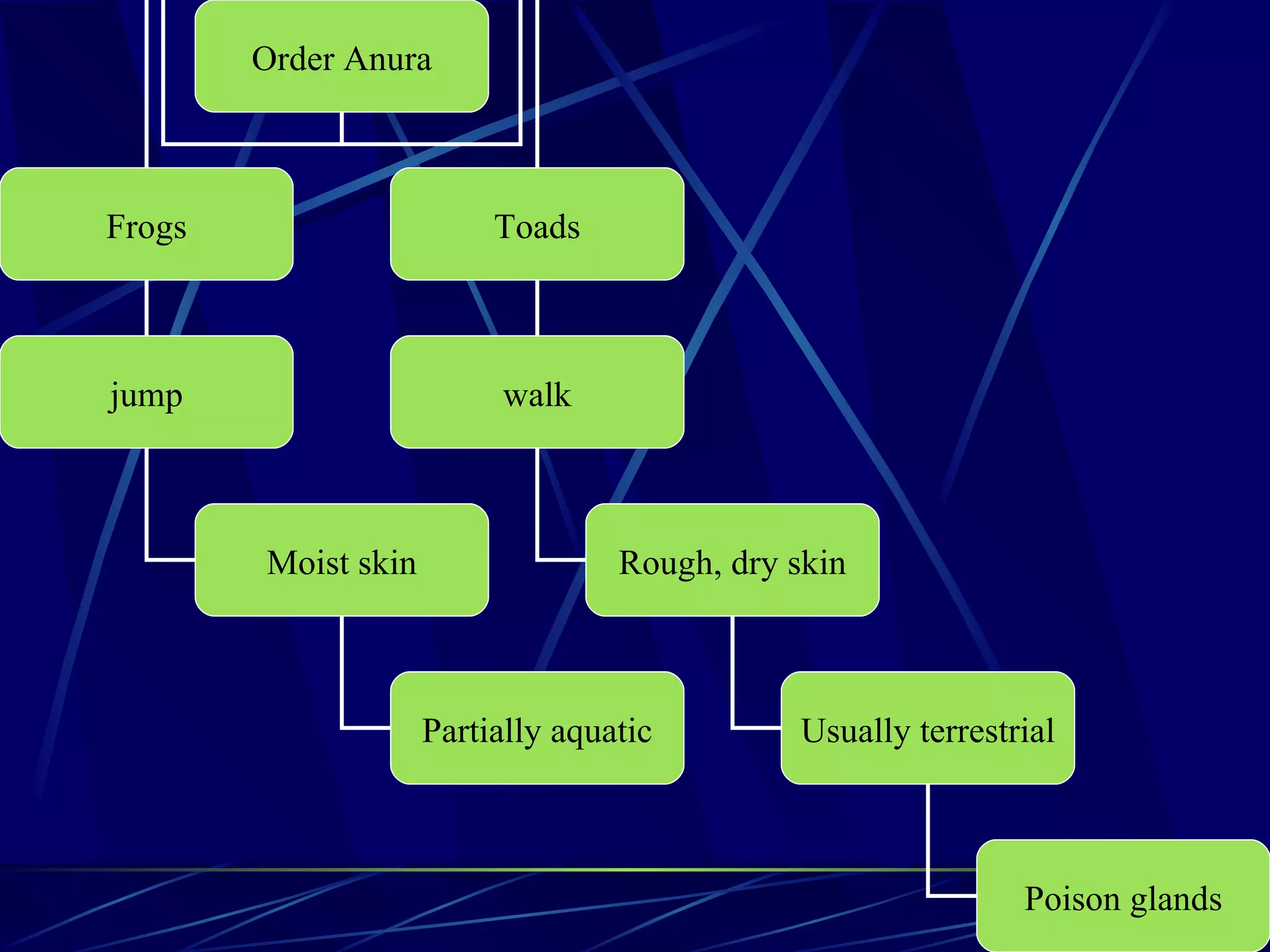
The document discusses the diversity of chordates and vertebrates. It covers the four key characteristics of vertebrates, including having a notochord, hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a tail that extends beyond the anus. It then describes the major groups of fish, including sharks, rays, bony fish, lobe-finned fish, and lungfish. Finally, it discusses the three orders of amphibians: frogs and toads, salamanders and newts, and caecilians.