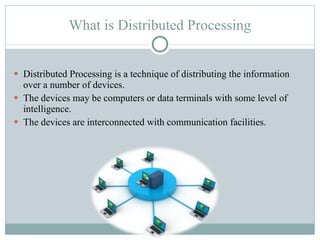
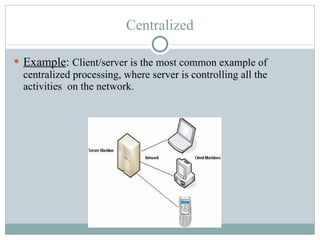
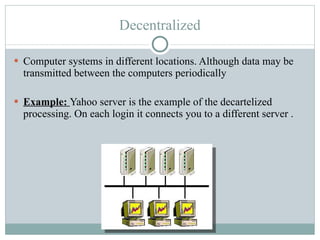
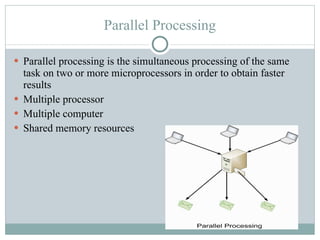
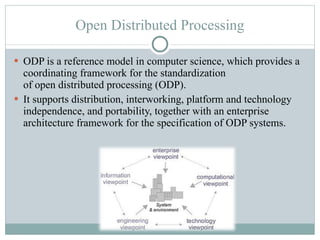
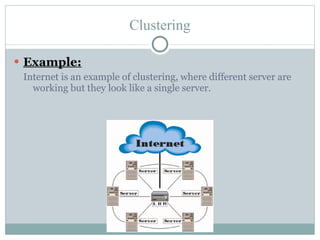
Distributed processing is a technique where computing tasks and data are distributed across multiple computers or devices that are connected through communication facilities. A distributed system is one where components located at networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages. Some key forms of distributed processing include centralized, decentralized, parallel, open distributed processing, and clustering. Distributed processing provides advantages like quicker response times, lower costs, improved data integrity, and resource sharing, but also poses challenges like heterogeneity, security, scalability, and failure handling.