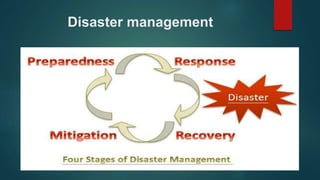
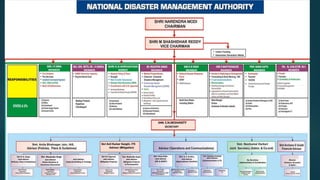
The document discusses disaster management and provides a case study on the Uttarakhand tragedy in India. It defines a disaster and outlines the different types. The disaster management process and emergency management approaches are described, including preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation. The case study then examines the 2013 floods in Uttarakhand that were caused by cloud bursts during monsoon season, leaving thousands stranded or swept away. It concludes that the Indian government needs new ideas and technology to better prevent natural disasters and educate people on preparedness.