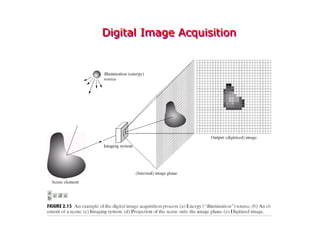
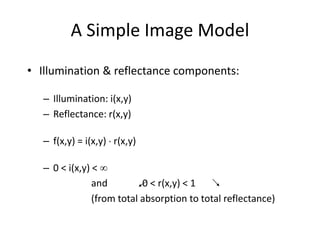
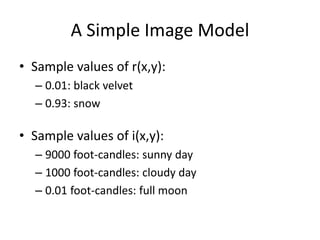
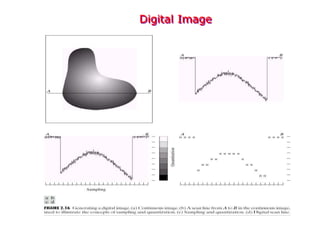
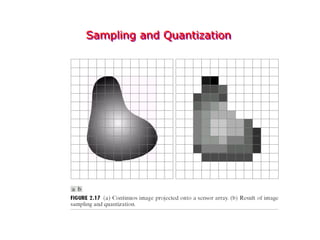
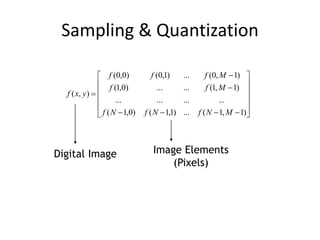
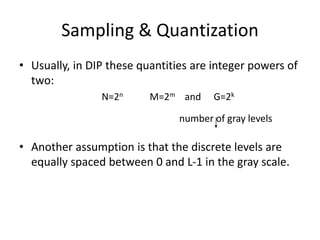
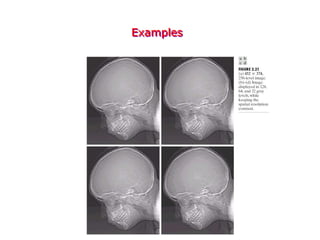
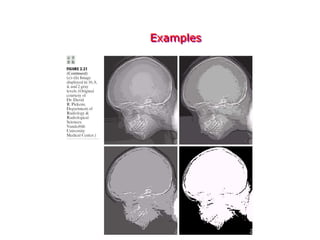
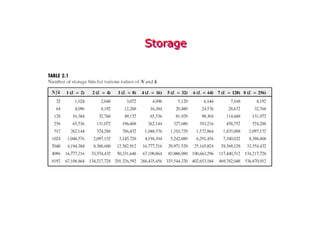
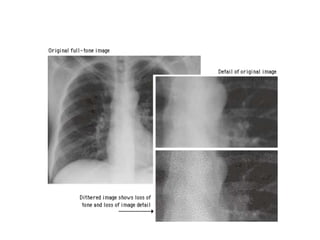
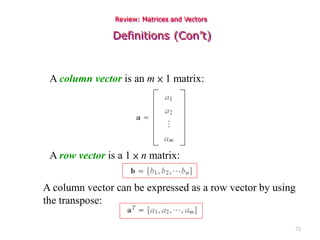
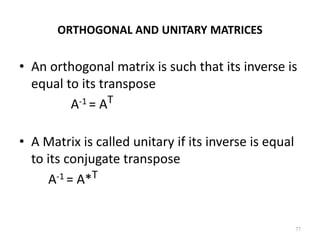
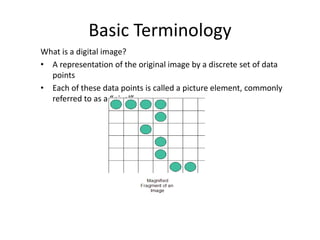
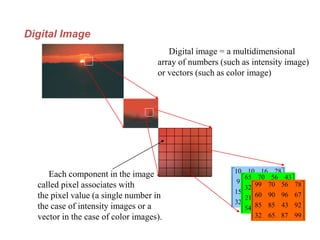
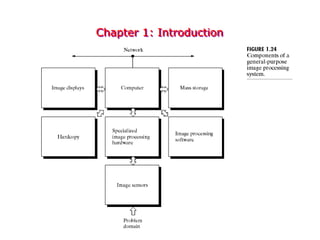
Digital images can be represented as multidimensional arrays of numbers or vectors. Each component in the image, called a pixel, associates with a pixel value such as intensity or color. To create a digital image, an analog image is sampled and quantized by converting the continuously sensed data into discrete numeric values. Sampling involves assigning numeric coordinates to pixels according to a grid, while quantization assigns numeric values to represent the brightness or color at each pixel location. The number of samples and quantization levels can impact the quality and file size of the digital image.



























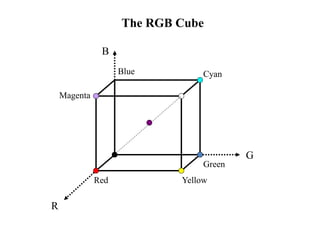
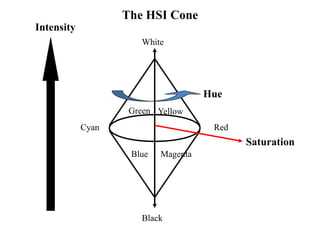
![The HSI Model (an alternative to RGB)
• Hue, H, specifies the dominant pure colour perceived
by the observer (e.g. red, yellow, blue)
[i.e. a representation of the frequency/wavelength]
• Saturation, S, specifies the degree to which a pure
colour has been diluted by white light to produce
observed colour.
• Intensity, I, is related to the perceived brightness of
the colour.
N.B. Decoupling (separating) intensity from colour is
very useful in image manipulation and analysis as
increased/decreased lighting in a scene (more or less)
only effect this parameter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalimagefundamentals-240129192103-73084391/85/digitalimagefundamentals-ppt-43-320.jpg)