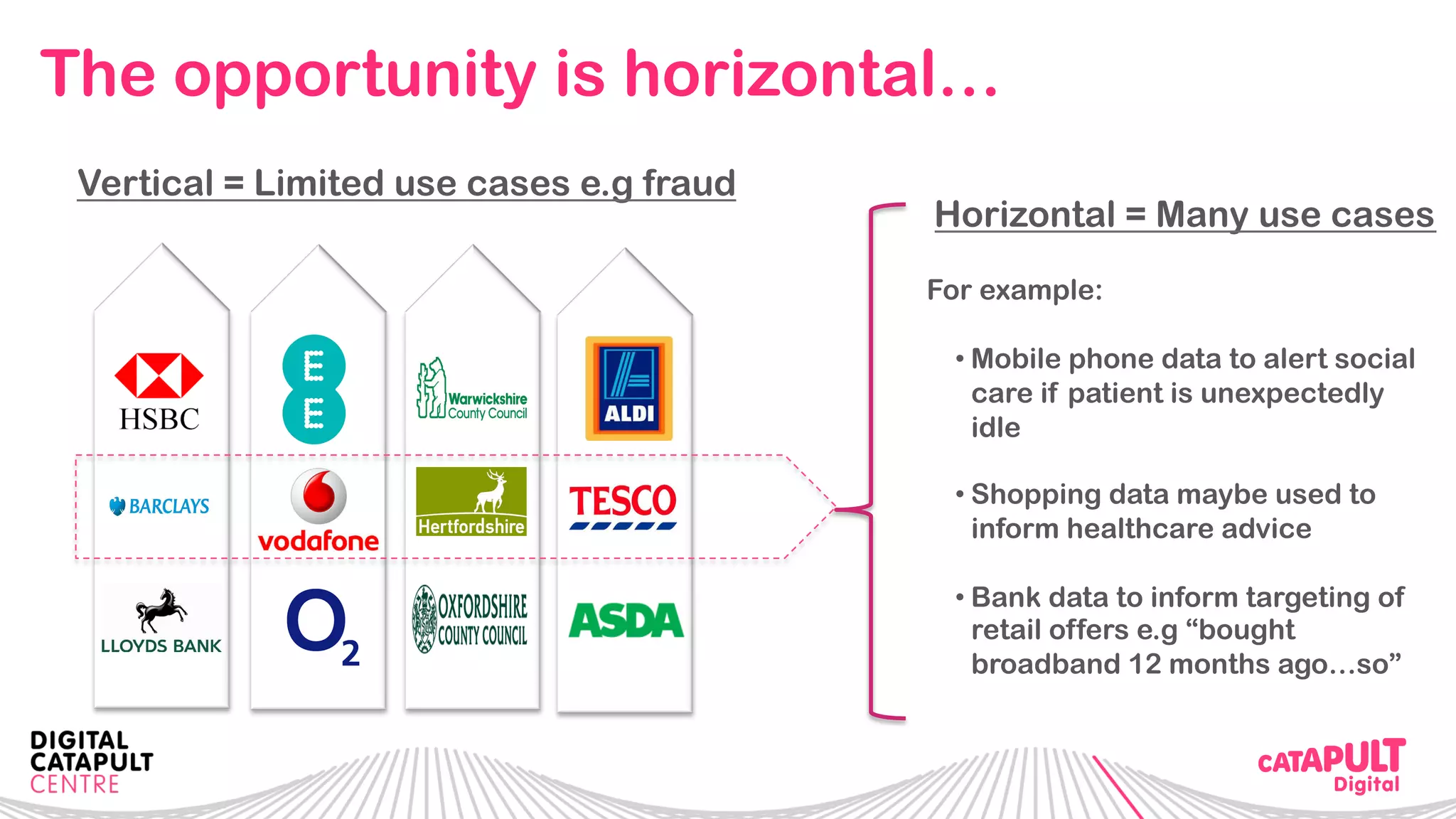
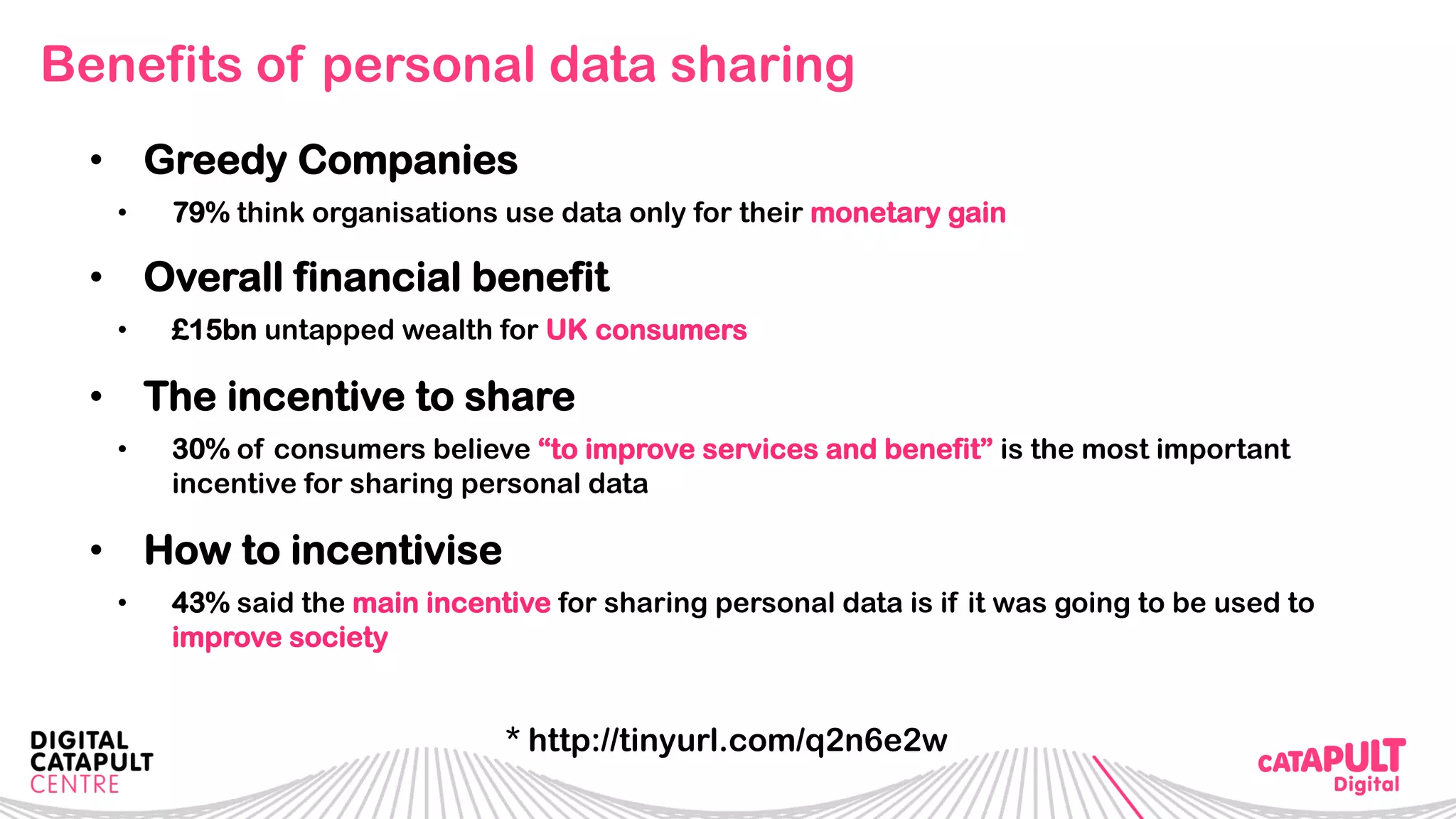
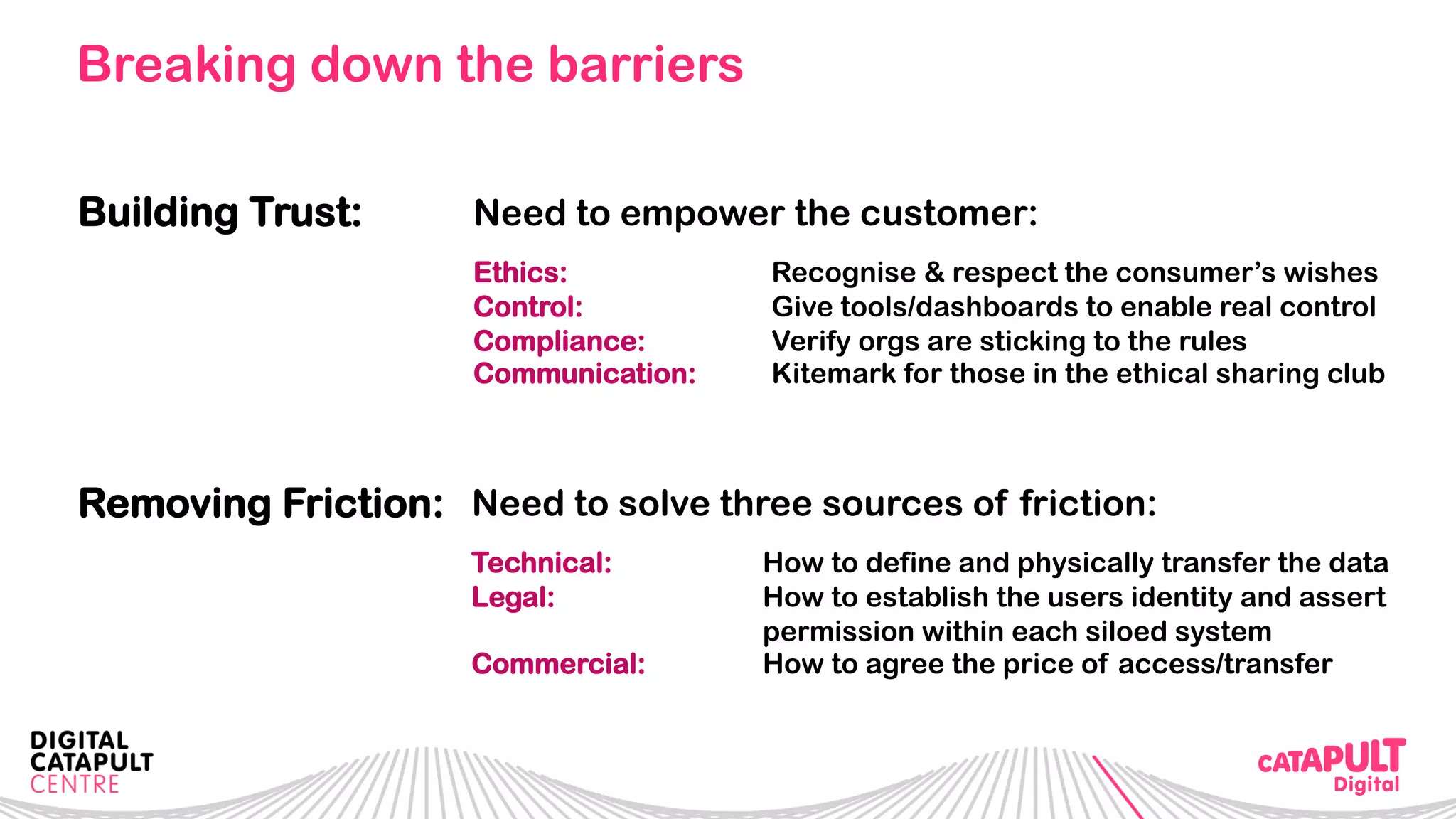
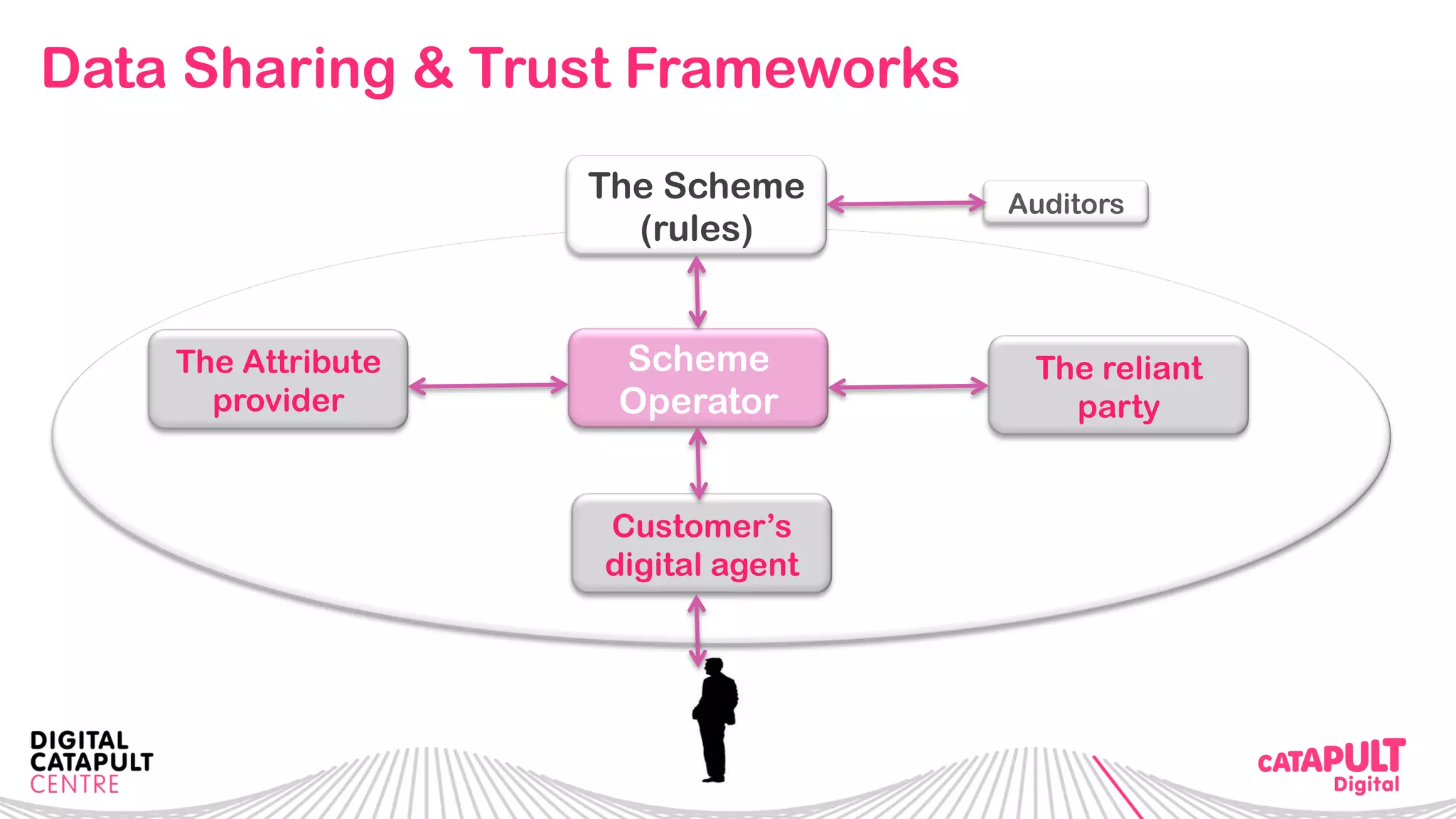
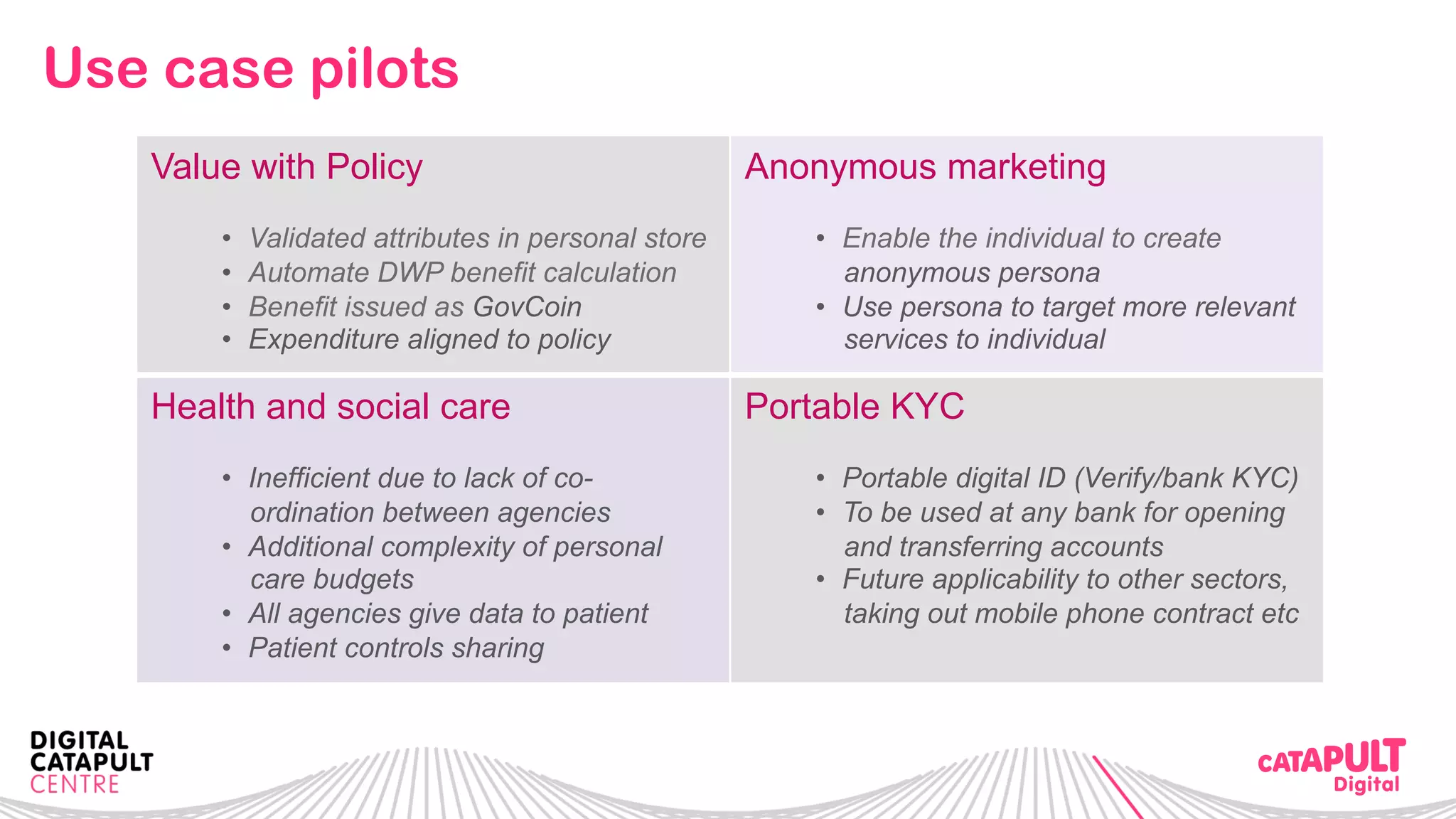
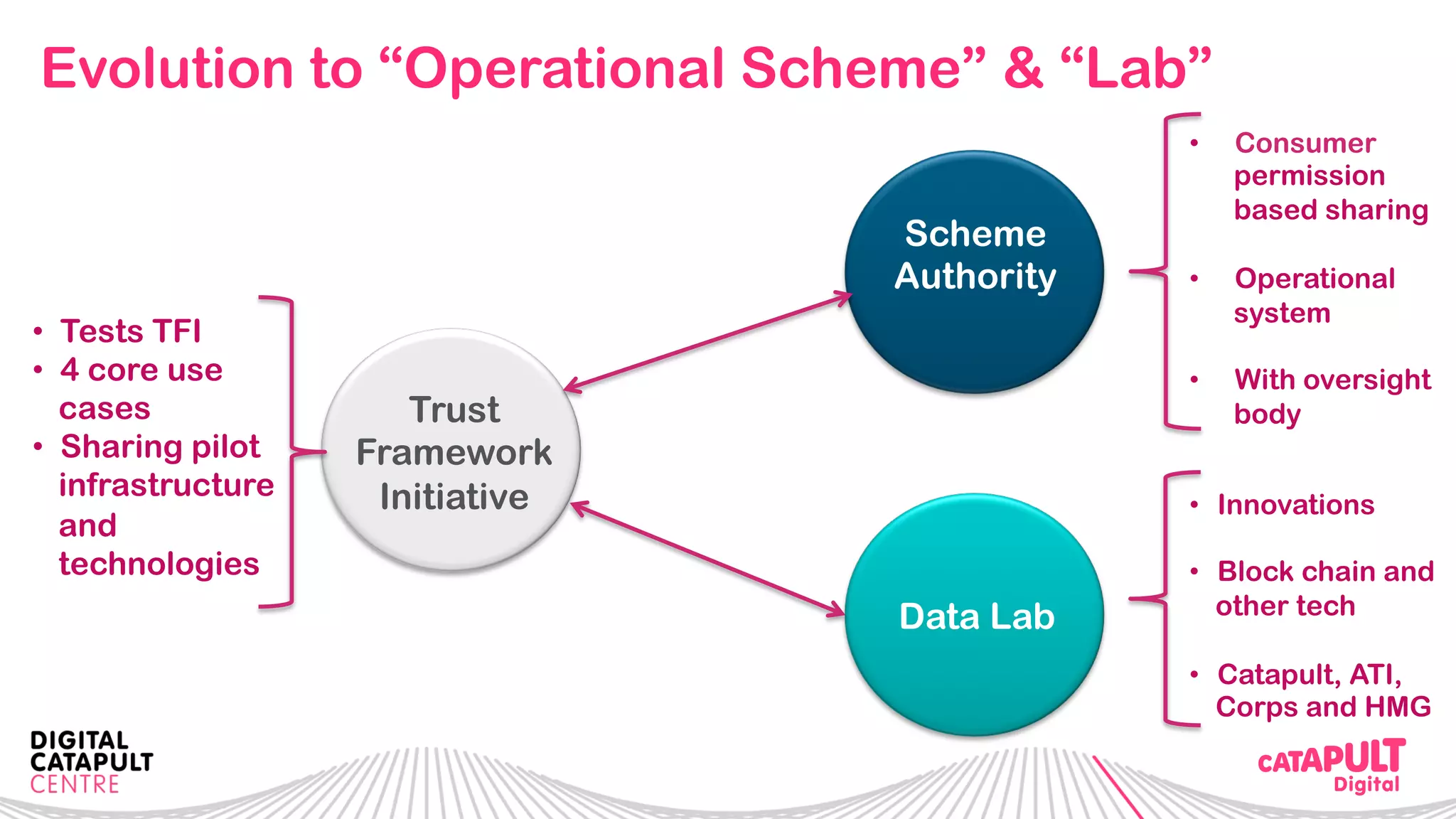
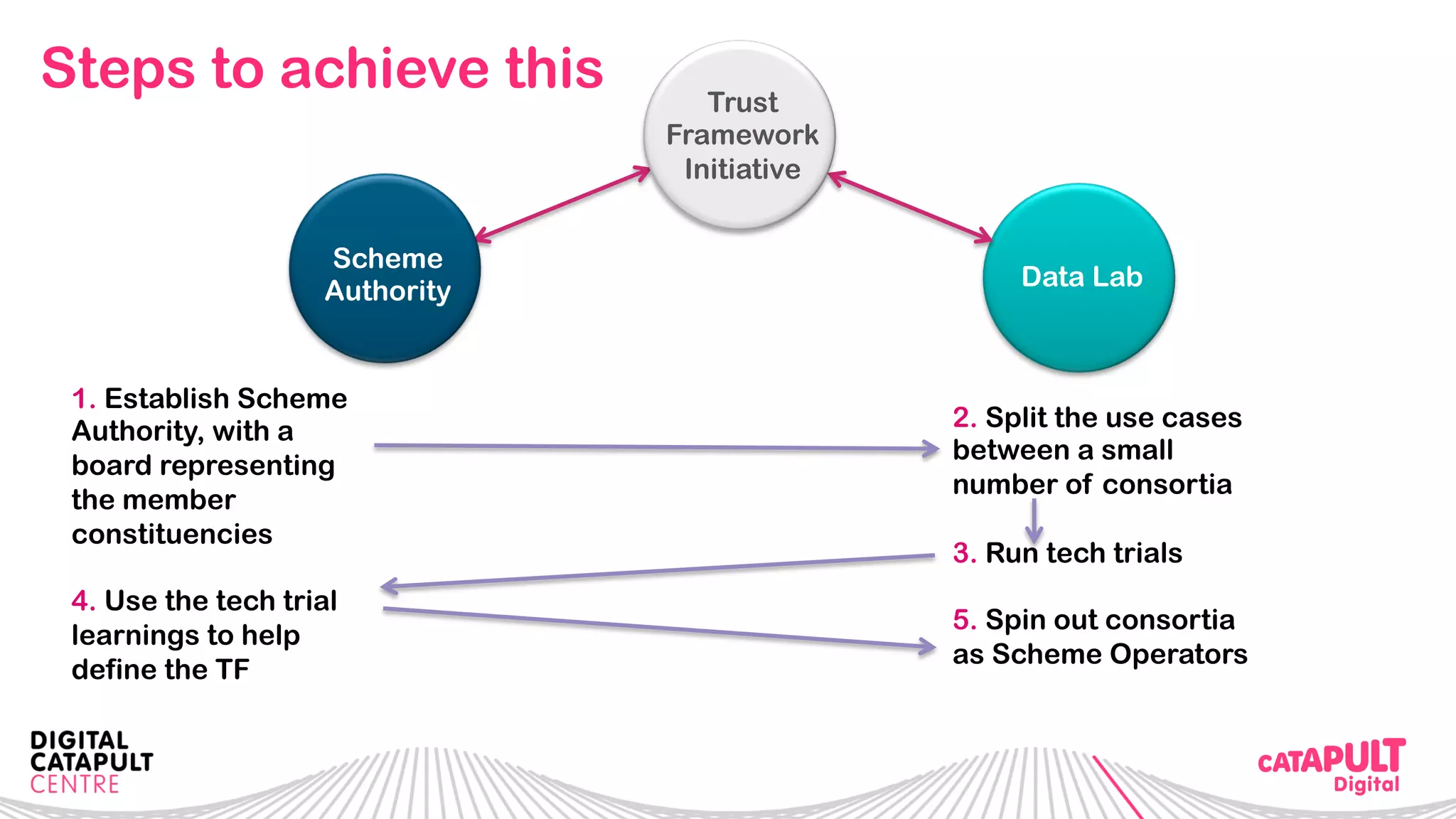
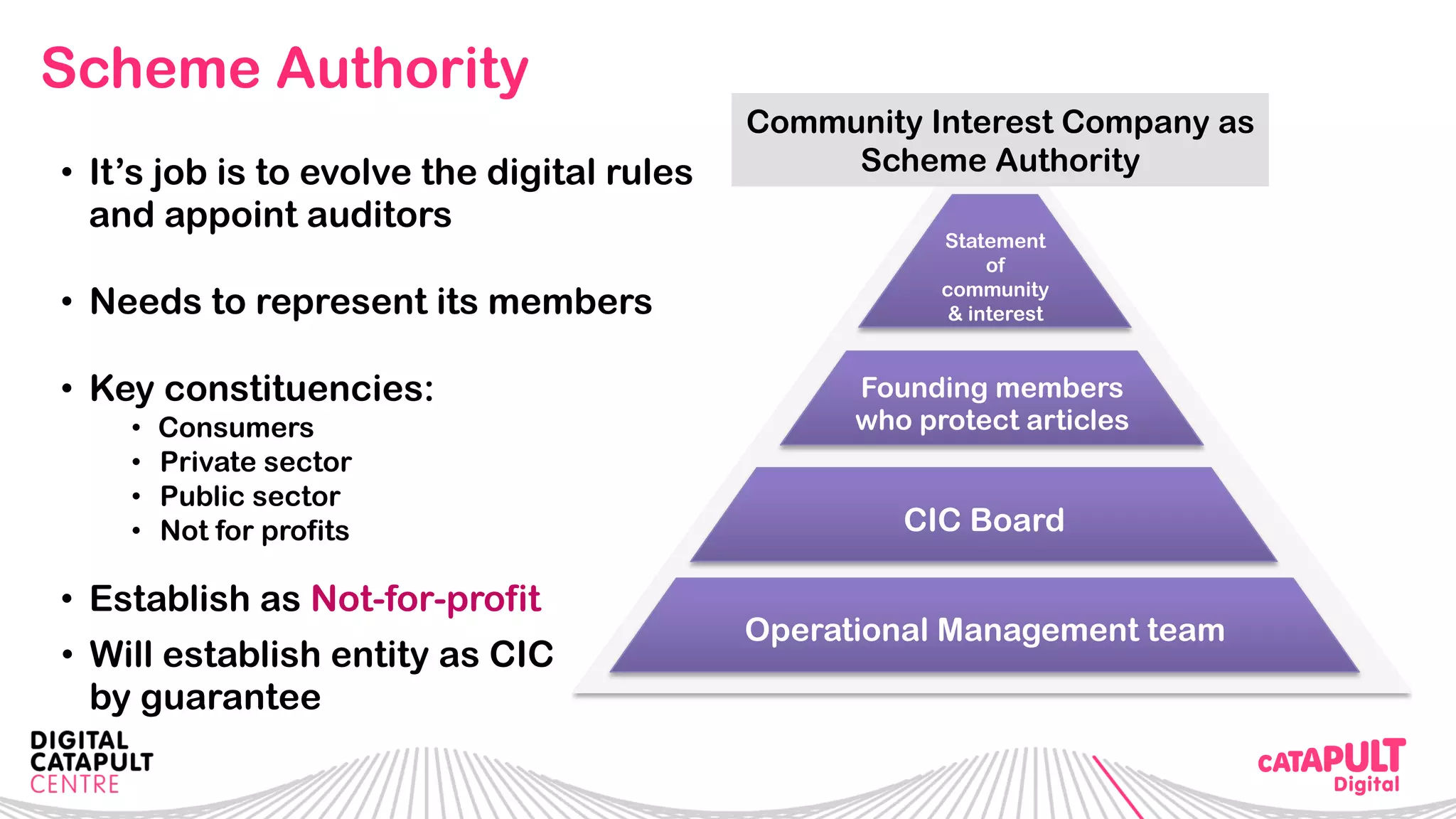
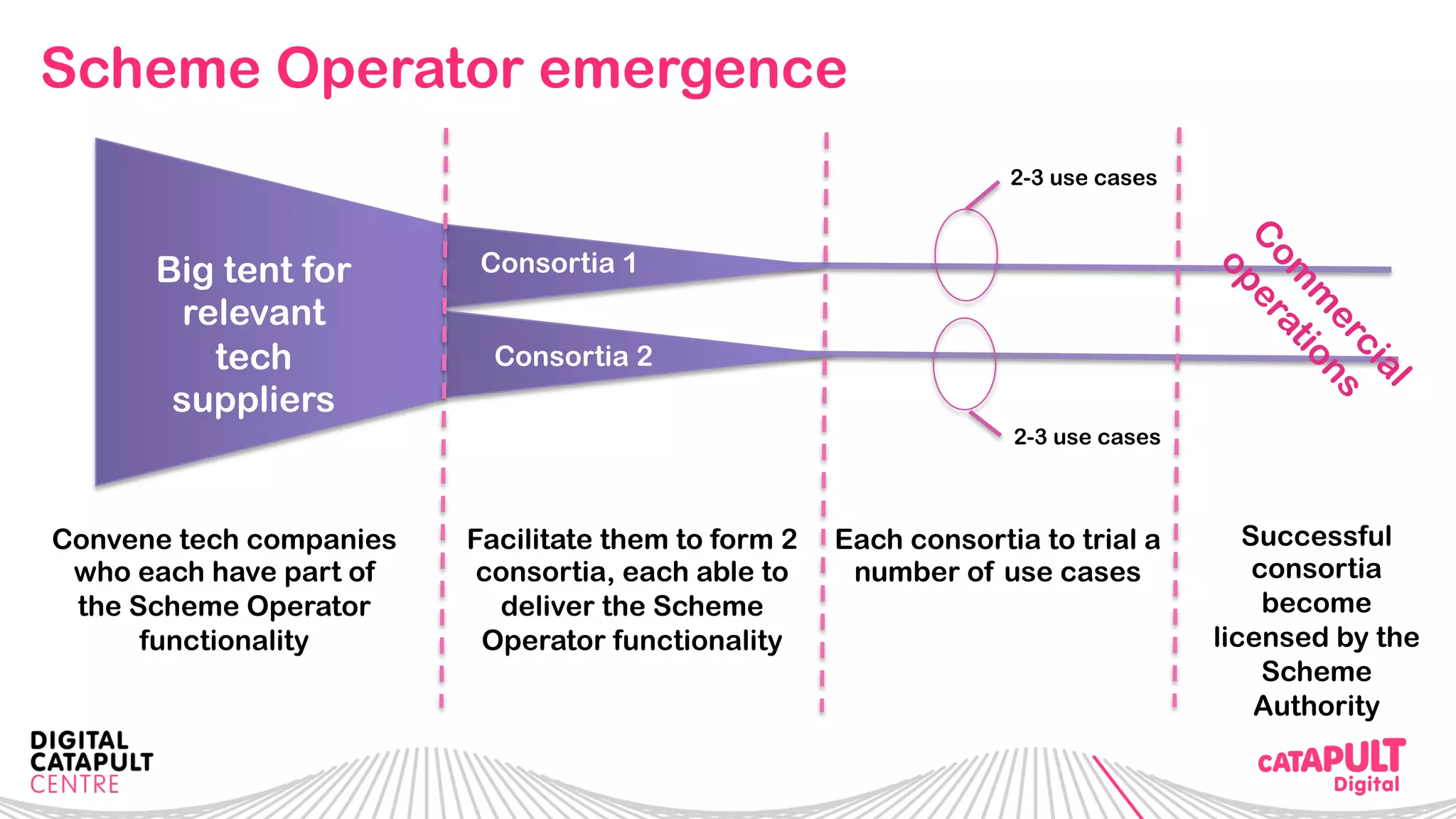
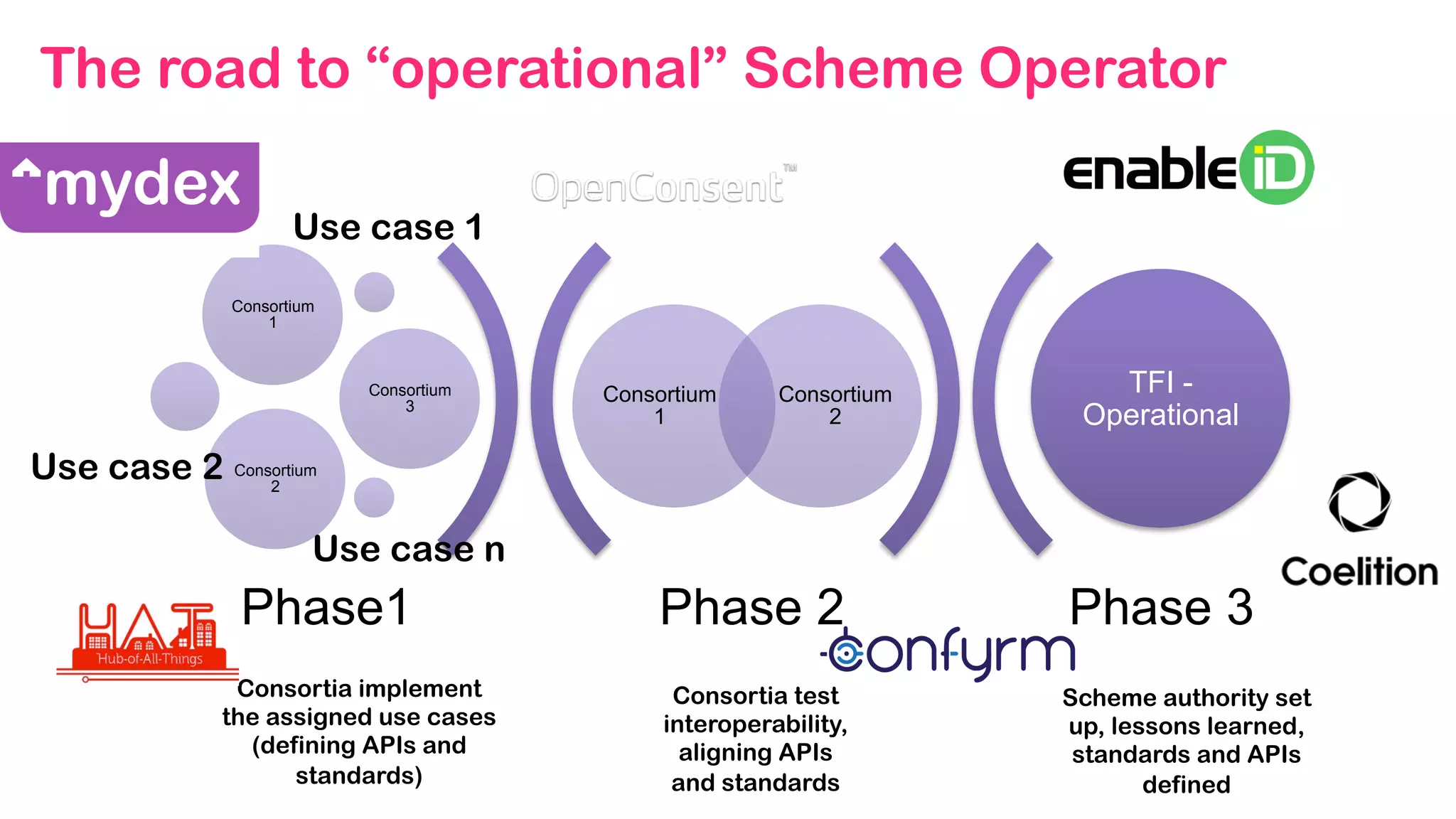
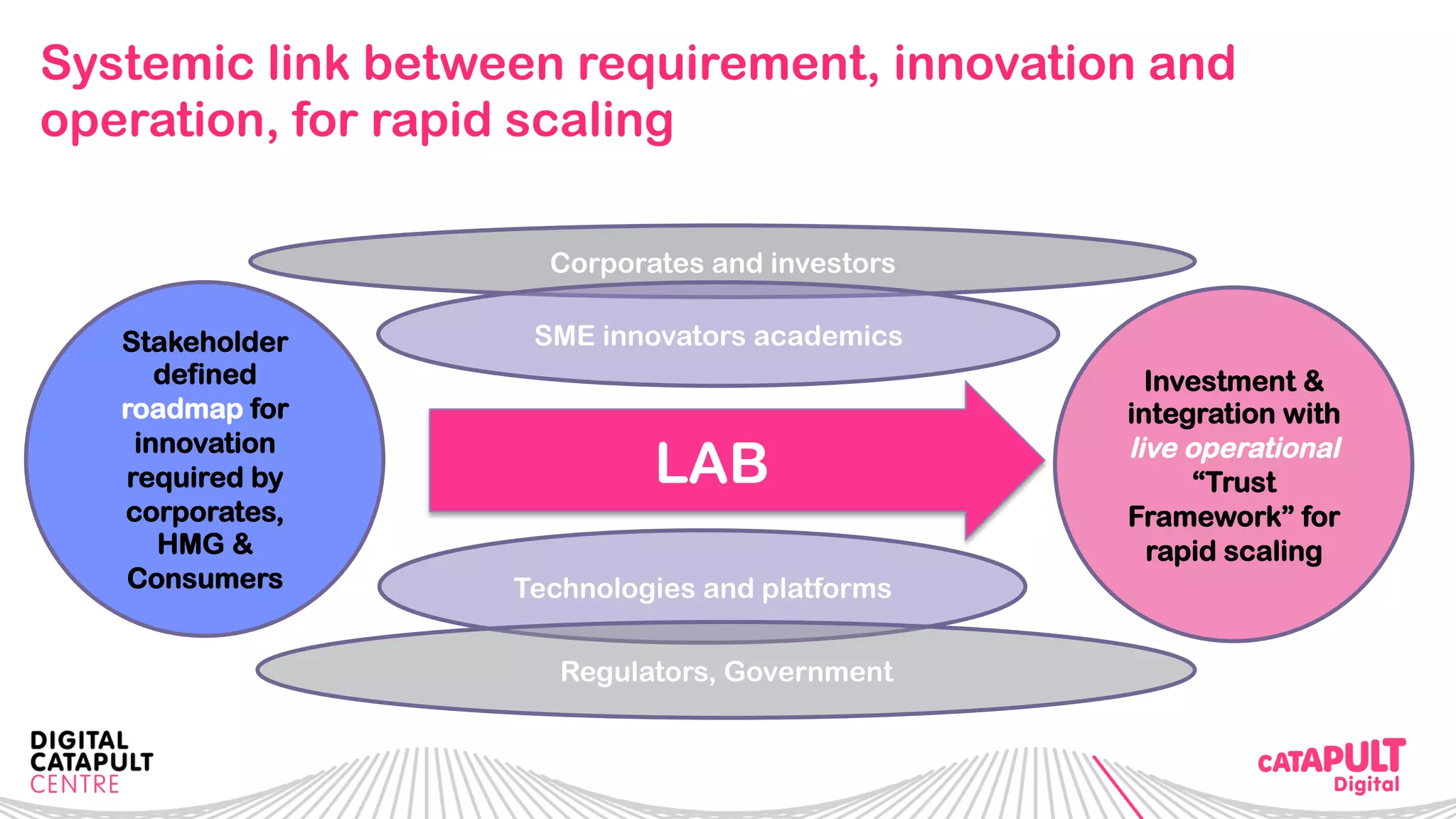
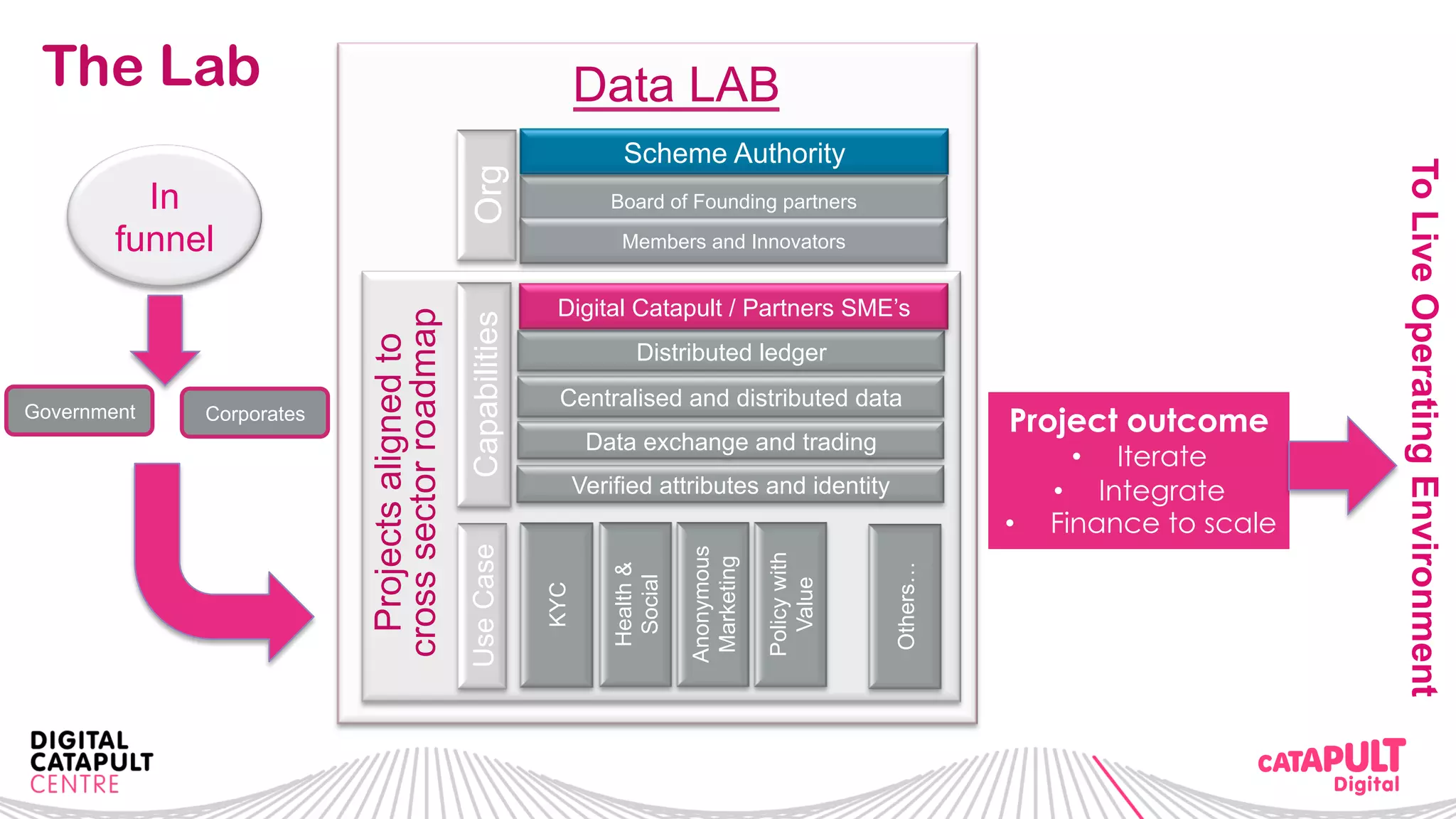
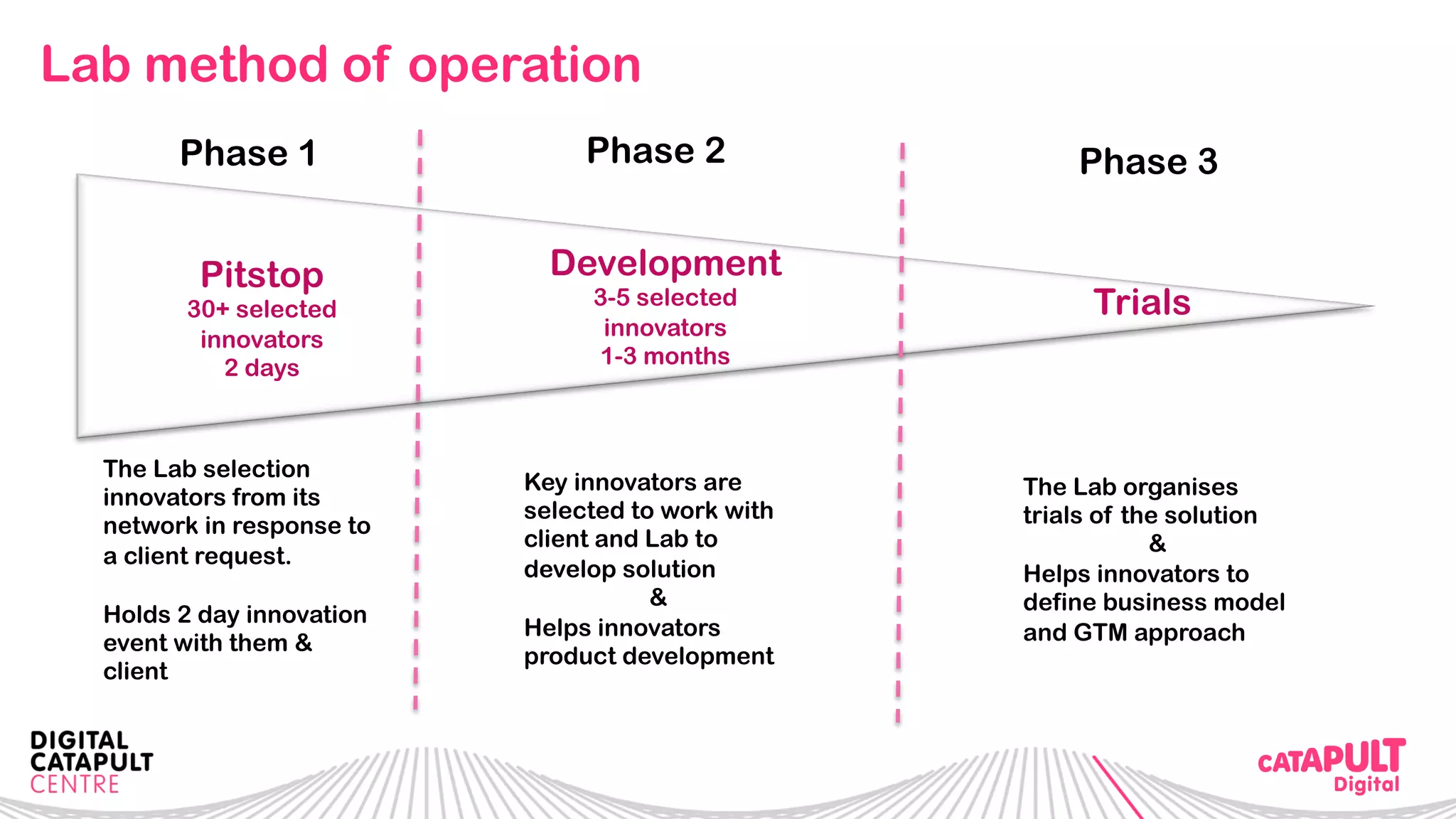
The document outlines the Digital Transformation & Open Innovation Trust Framework Initiative led by Michele Nati, focusing on enhancing the use of personal data through improved trust and sharing mechanisms in the UK. It highlights the importance of data as a crucial resource for consumer-facing businesses, explores consumer attitudes towards personal data sharing, and discusses strategies for building trust among stakeholders. The initiative aims to facilitate collaboration among tech suppliers, academics, and the public sector to create a user-centric data sharing lab that promotes innovation and addresses data privacy concerns.