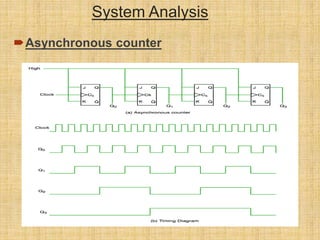
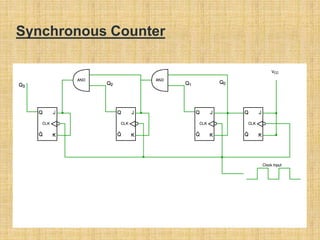
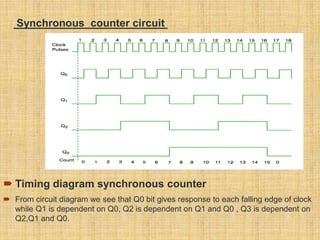
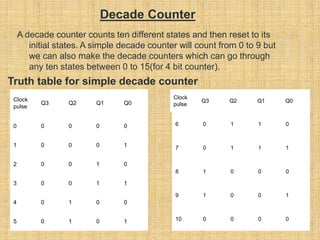
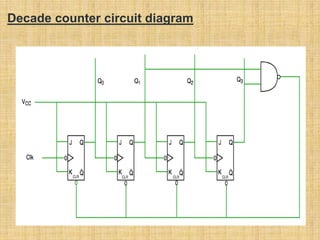
This document summarizes a student project on digital logic counters. It introduces counters and classifies them as either asynchronous or synchronous. Asynchronous counters use a ripple effect where each subsequent flip-flop is clocked by the previous one's output, while synchronous counters use a single global clock. It then discusses decade counters specifically, which count from 0 to 9 and reset, and provides the circuit diagram for a decade counter that uses NAND gates to clear the counter when the binary state reaches 10.