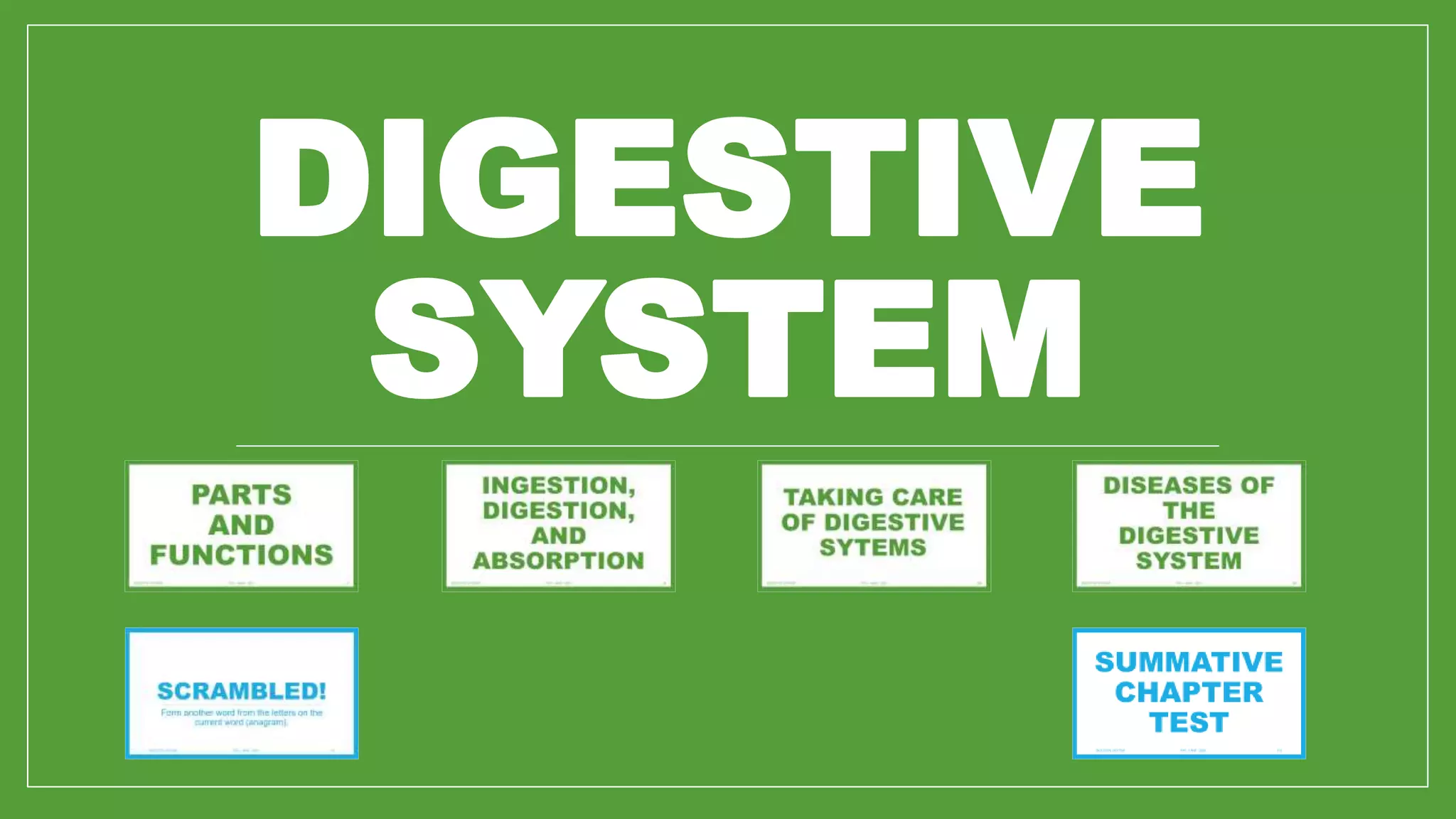
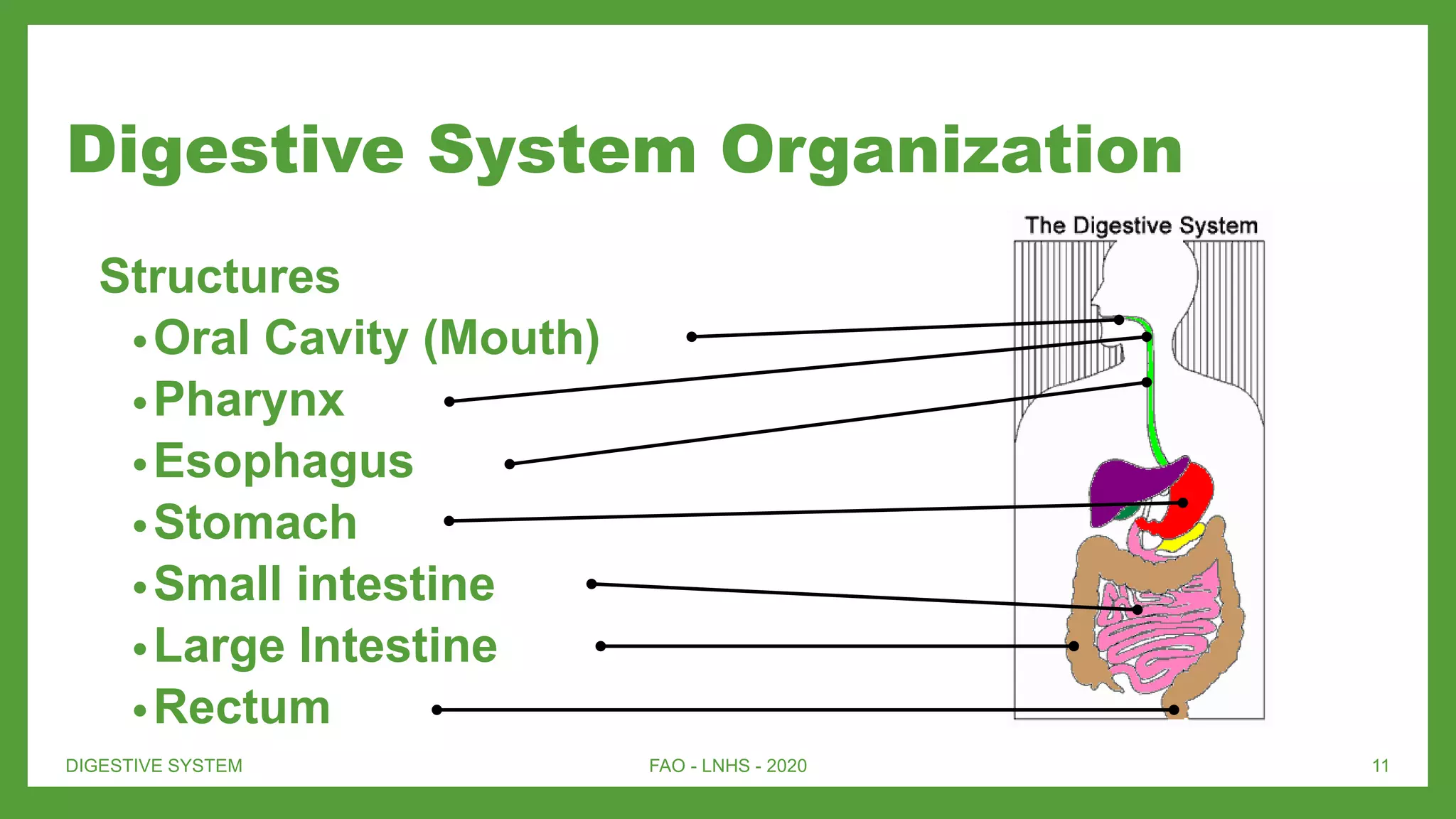
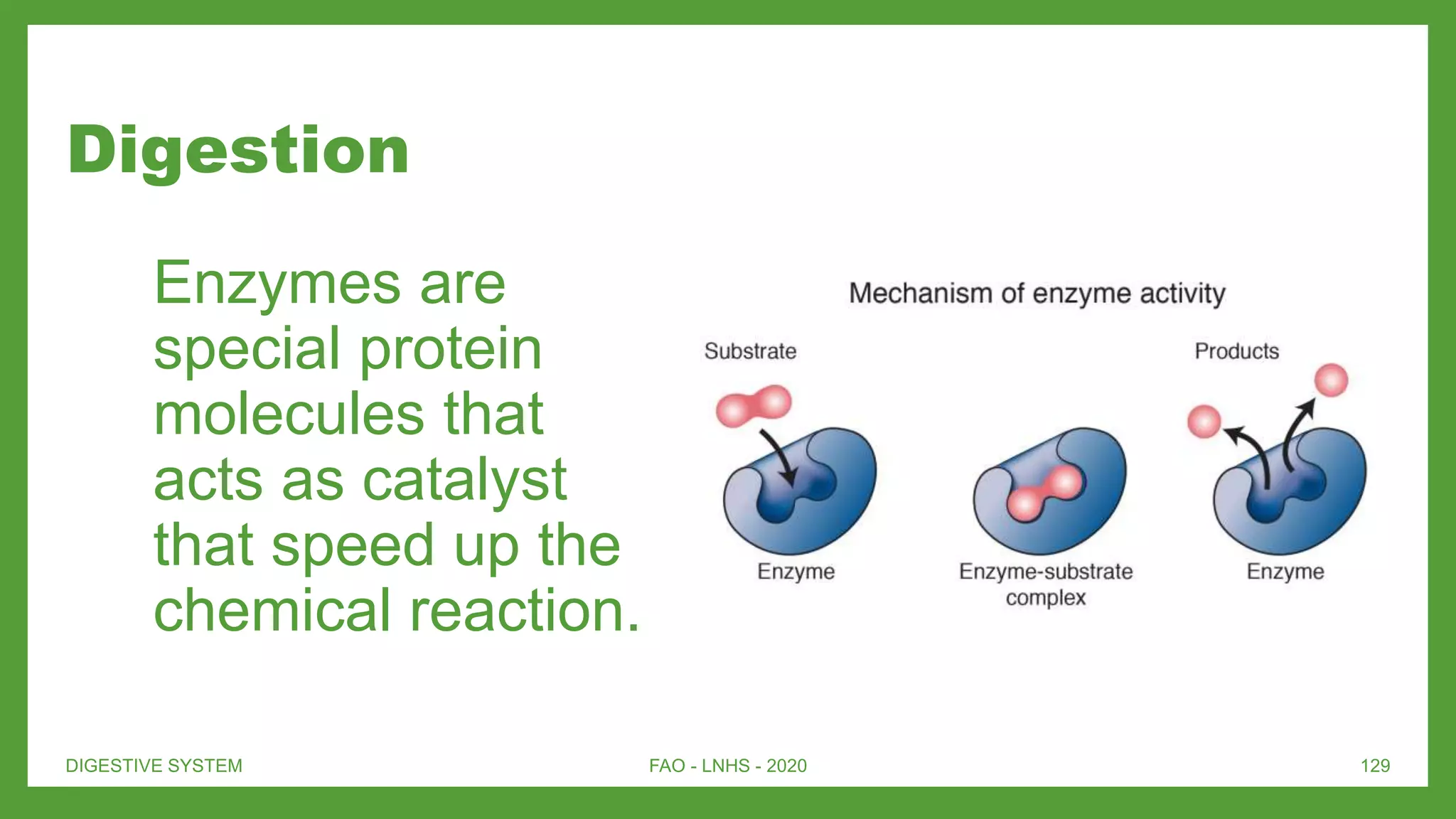
The document provides an overview of the digestive system, targeting seventh-grade biology lessons. It covers the path of food, the roles of various organs, the importance of enzymes in digestion, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases. Key components include the oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, along with their functions and interactions with accessory organs like the liver and pancreas.






















![Under the Star[ch]
Bring crackers in class and have
them tested for the precense of
starch using an iodine test.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM FAO - LNHS - 2020 25
QUICK-TIVITY!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g8-sci-q4c1-digestivesystem-200202103038/75/Digestive-System-Grade-8-Quarter-4-25-2048.jpg)















































































































































![Under the Star[ch] Part 2
Cut a thin slice of cucumber and
potato. Add a drop of iodine
solution. Observe and compare
what happens.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM FAO - LNHS - 2020 170
QUICK-TIVITY!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g8-sci-q4c1-digestivesystem-200202103038/75/Digestive-System-Grade-8-Quarter-4-170-2048.jpg)

















































































