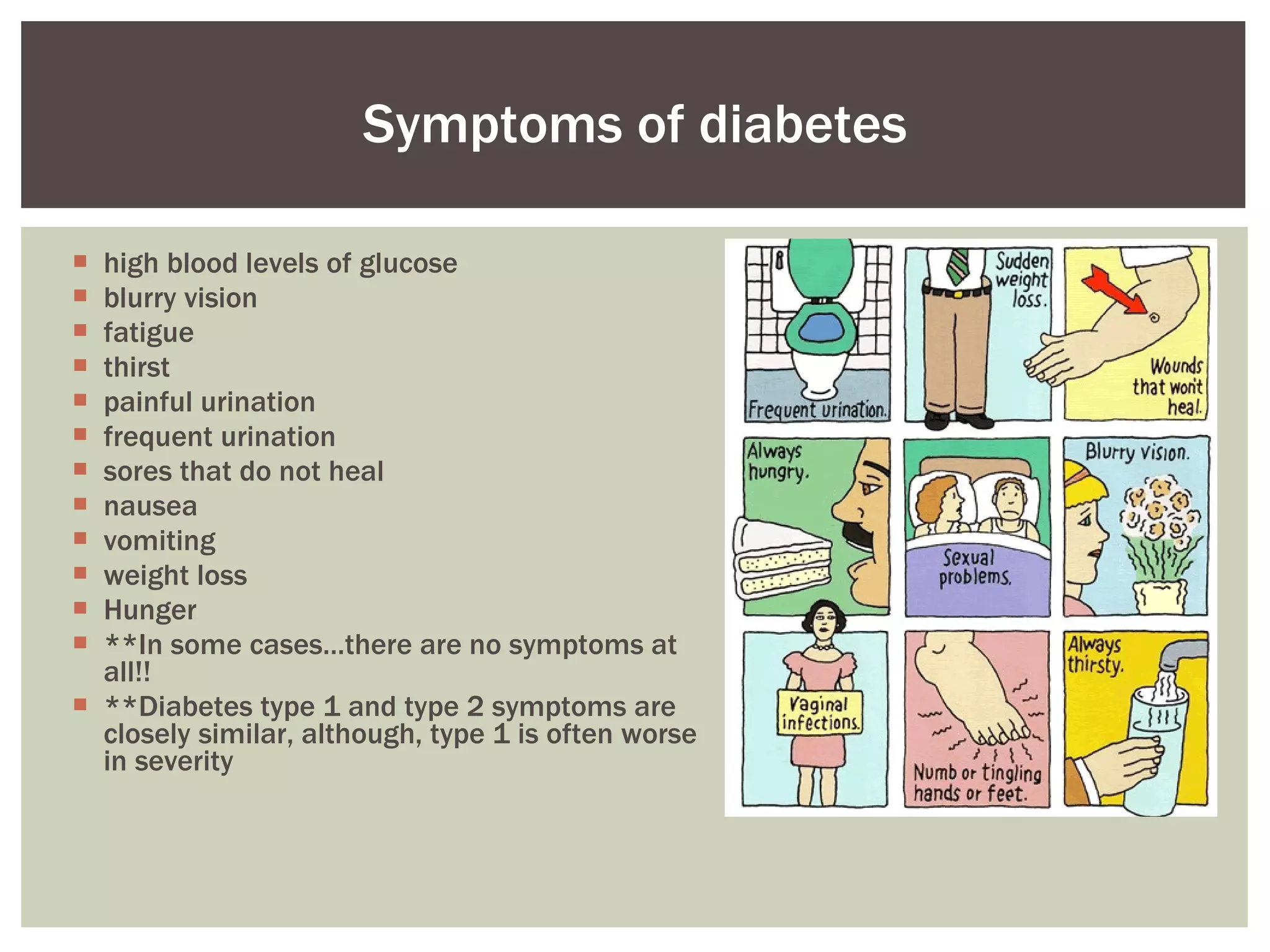
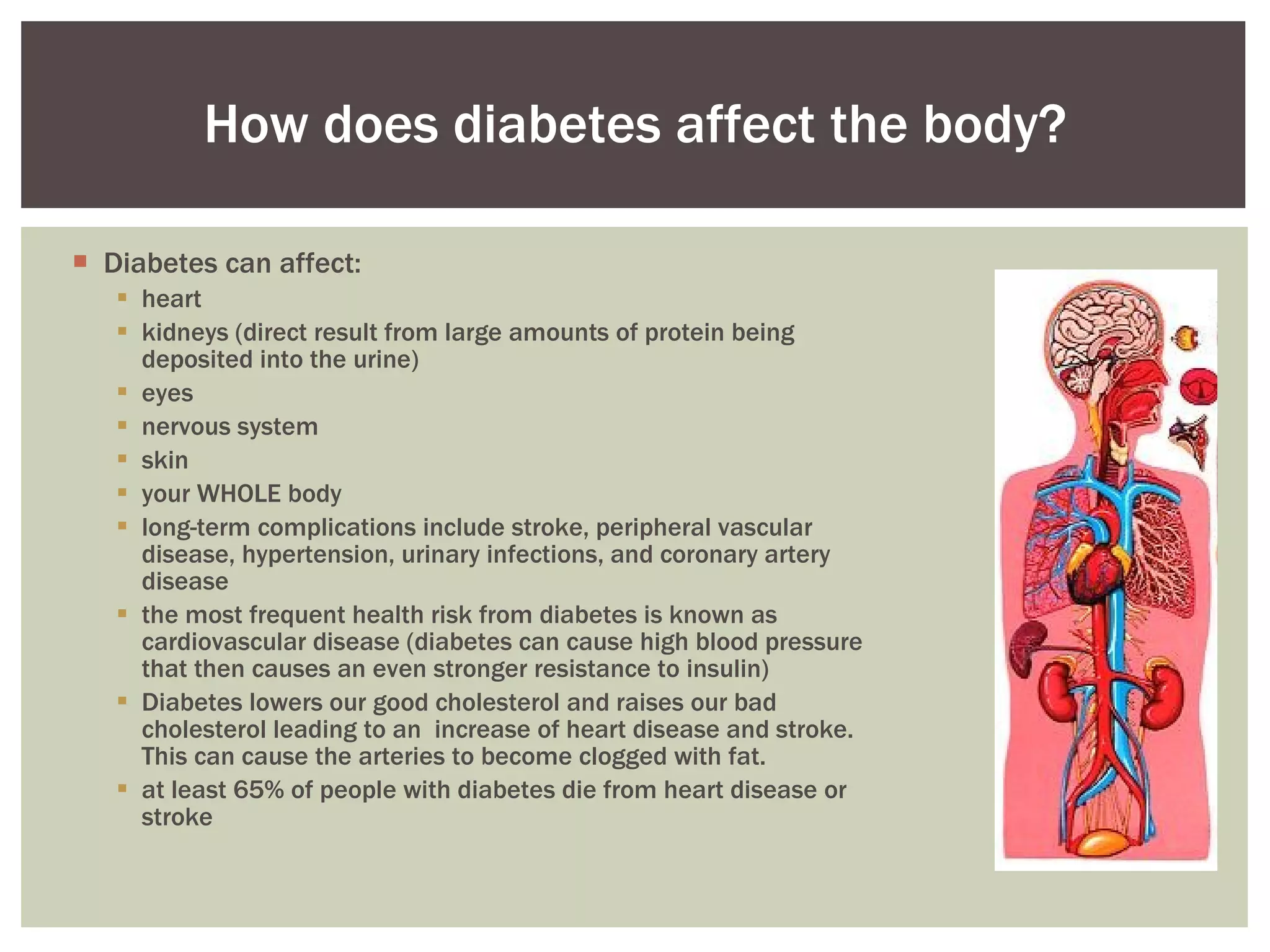
There are four main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, and pre-diabetes. Type 1 is usually diagnosed in childhood and requires daily insulin injections. Type 2 is the most common type and is often linked to obesity. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy, and pre-diabetes means blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 1 or 2. Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, thirst, hunger, and fatigue. Testing involves fasting plasma glucose tests and oral glucose tolerance tests. Managing diabetes involves diet, exercise, medication and monitoring blood sugar levels. Long-term complications can affect the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves and skin if diabetes is