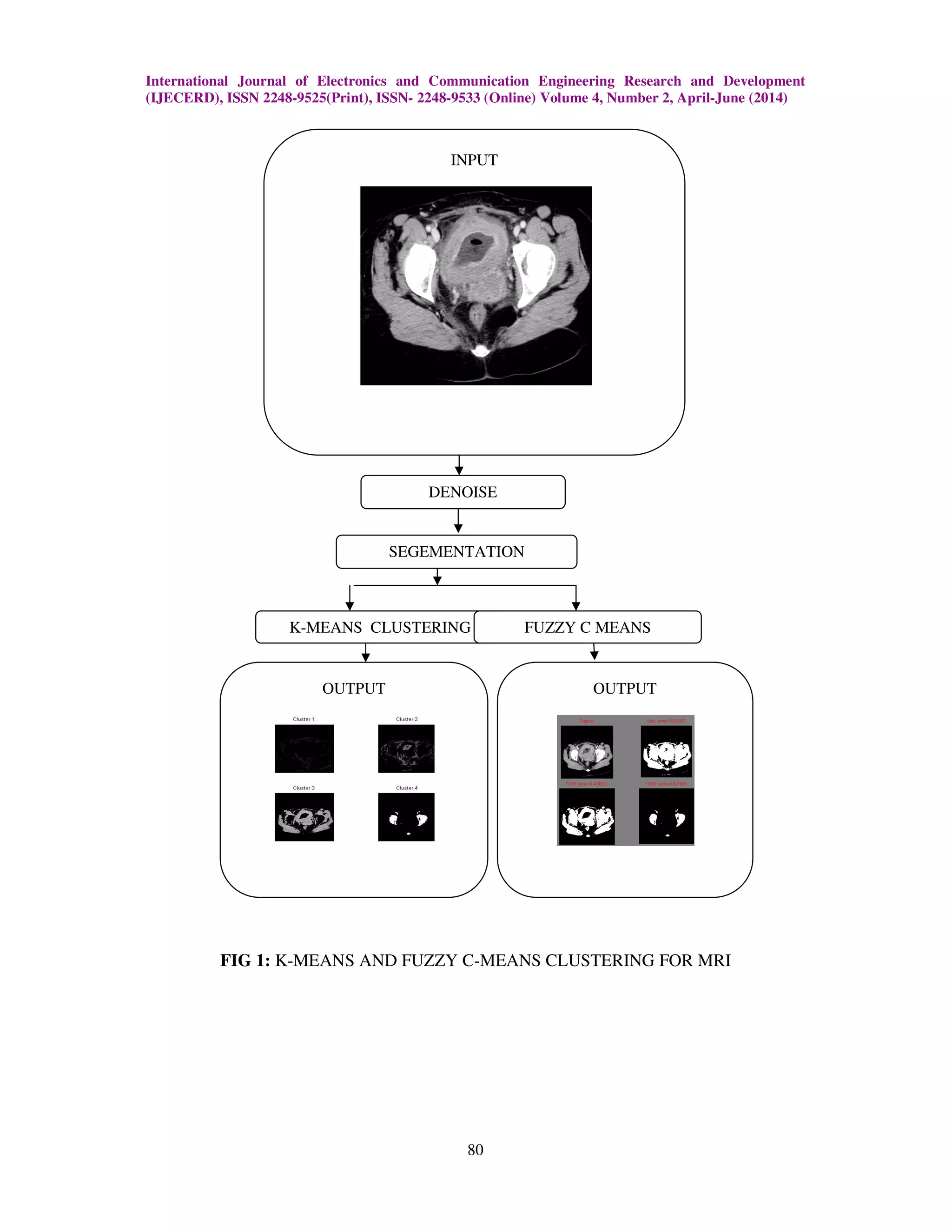
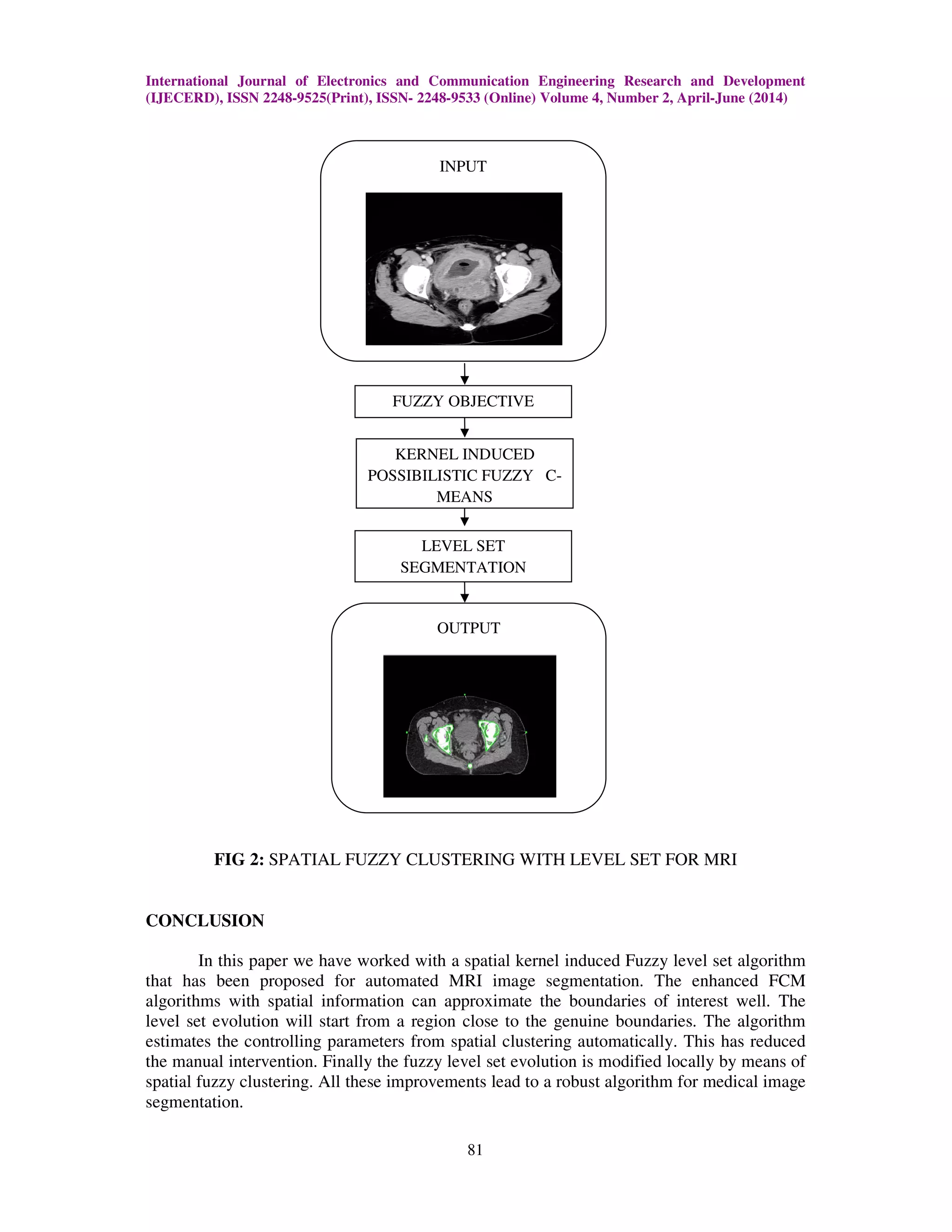
The document presents a new fuzzy level set algorithm for the segmentation of human bladder cancer cells using medical imaging techniques, including MRI. This algorithm enhances standard methods like k-means and fuzzy c-means by incorporating spatial information and adapting to reduce noise and artifacts, improving the accuracy of segmentation. The study concludes that the proposed kernel induced possibilistic fuzzy c-means method offers better robustness and computational simplicity for medical image analysis.

![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Research and Development
(IJECERD), ISSN 2248-9525(Print), ISSN- 2248-9533 (Online) Volume 4, Number 2, April-June (2014)
74
2. EXISTING METHOD (K-MEANS AND FUZZY C MEANS METHODS)
Morphological processing is constructed with operations on sets of pixels. Binary
morphology uses only set membership and is indifferent to the value, such as gray level or
color, of a pixel. Morphological image processing relies on the ordering of pixels in an image
and many times is applied to binary and gray scale images. Through processes such as
erosion, dilation, opening and closing, binary images can be modified to the user's
specifications. Binary images are images whose pixels have only two possible intensity
values. They are normally displayed as black and white. Numerically, the two values are
often 0 for black, and either 1 or 255 for white. The rest (usually black) is referred to as the
background color. However, depending on the image which is to be threshold, this polarity
might be inverted, and in which case the object is displayed with 0 and the background is
with a non-zero value. Some morphological operators assume a certain polarity of the binary
input image so that if we process an image with inverse polarity the operator will have the
opposite effect. For example, if we apply a closing operator to a black text on white
background, the text will be opened.
Steps for k-means:
1. Give the no of cluster value as k.
2. Randomly choose the k cluster centers
3. Calculate mean or center of the cluster
4. Calculate the distance b/w each pixel to each cluster center
5. If the distance is near to the center then move to that cluster.
6. Otherwise move to next cluster.
7. Re-estimate the center.
8. Repeat the process until the center doesn't move
Steps for Fuzzy C-means:
I. Initialize U=[uij] matrix, U(0)
II. At k-step: calculate the centers vectors C(k)=[cj] with U(k)
a. ܥ ൌ
∑ ௨ೕ
ಿ
సభ .௫
∑ ௨ೕ
ಿ
సభ
III. ܷ݁ݐܽ݀ݑሺሻ
, ܷሺାଵሻ
a. ݑ௩ ൌ
ଵ
∑ ቆ
ቛೣషೕቛ
ฮೣషೖฮ
ቇ
మ
షభ
ೖసభ
IV. If || U (k+1) – U (k)||< ε then STOP; otherwise return to step II.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/detectionofhuman-170209053408/75/DETECTION-OF-HUMAN-BLADDER-CANCER-CELLS-USING-IMAGE-PROCESSING-2-2048.jpg)





![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Research and Development
(IJECERD), ISSN 2248-9525(Print), ISSN- 2248-9533 (Online) Volume 4, Number 2, April-June (2014)
82
REFERENCES
[1] Chun-Ping Jen, Ching-Te Huang, "Diagnosis of Human Bladder Cancer Cells at
Different Stages Using Multispectral Imaging Microscopy" IEEE JOURNAL OF
SELECTED TOPICS IN QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 20, NO. 3,
[2] Ismail Ben Ayed,Polarimetric "Image Segmentation via Maximum-Likelihood
Approximation and Efficient Multiphase Level-Sets" IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON
PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 28, NO. 9,
SEPTEMBER 2006
[3] Christos Sakellarios1, Spiros Kostopoulos2, "Segmentation and Classification of
Histopathology Images for Abetting Diagnosis in Urinary Bladder Cancer" 4th
International Conference on Experiments/Process/System
Modeling/Simulation/Optimization 4th IC-EpsMsO Athens, 6-9 July, 2011
[4] Wenhui Li, Jinlong Zhu inJournal" A Medical Image Segmentation Based on
Improved Fuzzy Clustering and Level Set" of Information & Computational
Science 10:17 (2013) 5599–5606
[5] Ms. M. Parisa Beham Assistant Professor, Department of ECE Vickram College of
Engineering Madurai, TamilNadu, India "MORPHOLOGICAL IMAGE
PROCESSING APPROACH ON THE DETECTION OF TUMOR AND
CANCER CELLS"
[6] Feng SHI†1, Jie YANG1, " Automatic segmentation of bladder in CT images*"
Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A
[7] Manali Patil Samata Prabhu "Brain Tumor Identification Using K-Means
Clustering" International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology-
Volume4Issue3- 2013
[8] Wenhui Li, Jinlong Zhu "A Medical Image Segmentation Based on Improved
Fuzzy Clustering and Level Set" in Journal of Information & Computational
Science, china
[9] Pascal Martin, Philippe Re´ fre´ gier," Influence of the Noise Model on Level Set
Active Contour Segmentation" in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN
ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 26, NO. 6, JUNE 2004
[10] Dzung L. Pham "Adaptive Fuzzy Segmentation of Magnetic Resonance Images",
in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 18, NO. 9,
SEPTEMBER 1999](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/detectionofhuman-170209053408/75/DETECTION-OF-HUMAN-BLADDER-CANCER-CELLS-USING-IMAGE-PROCESSING-10-2048.jpg)