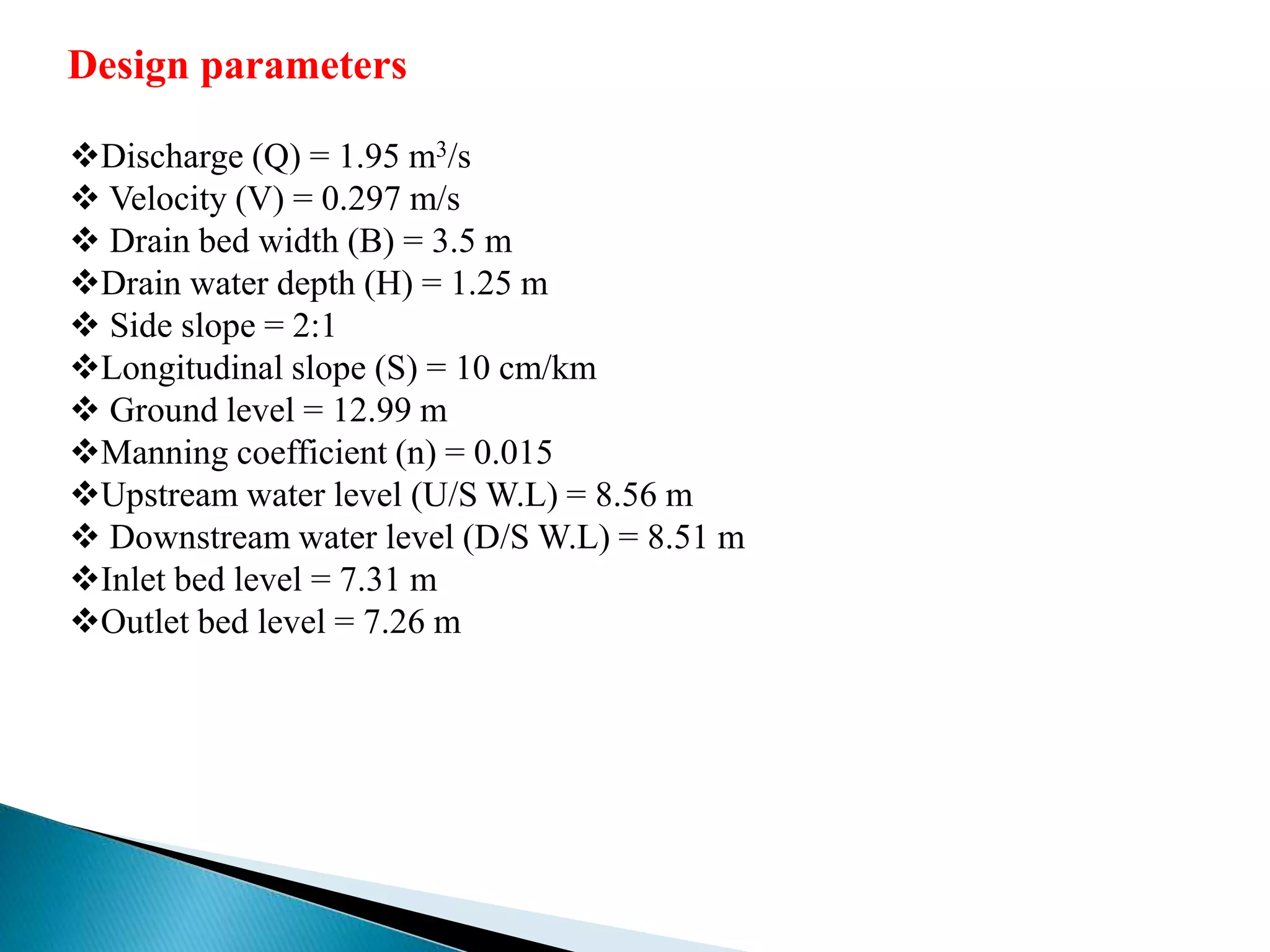
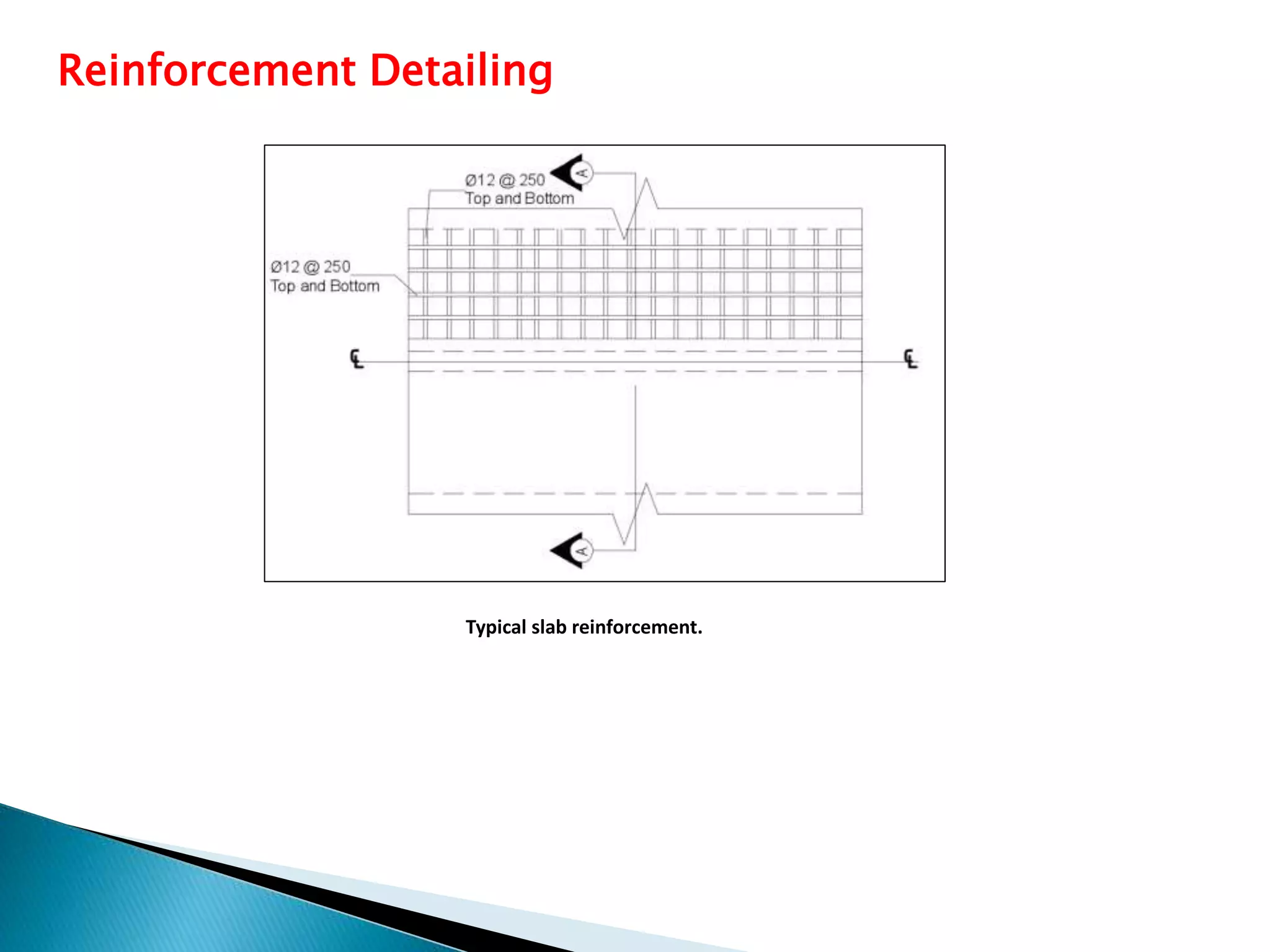
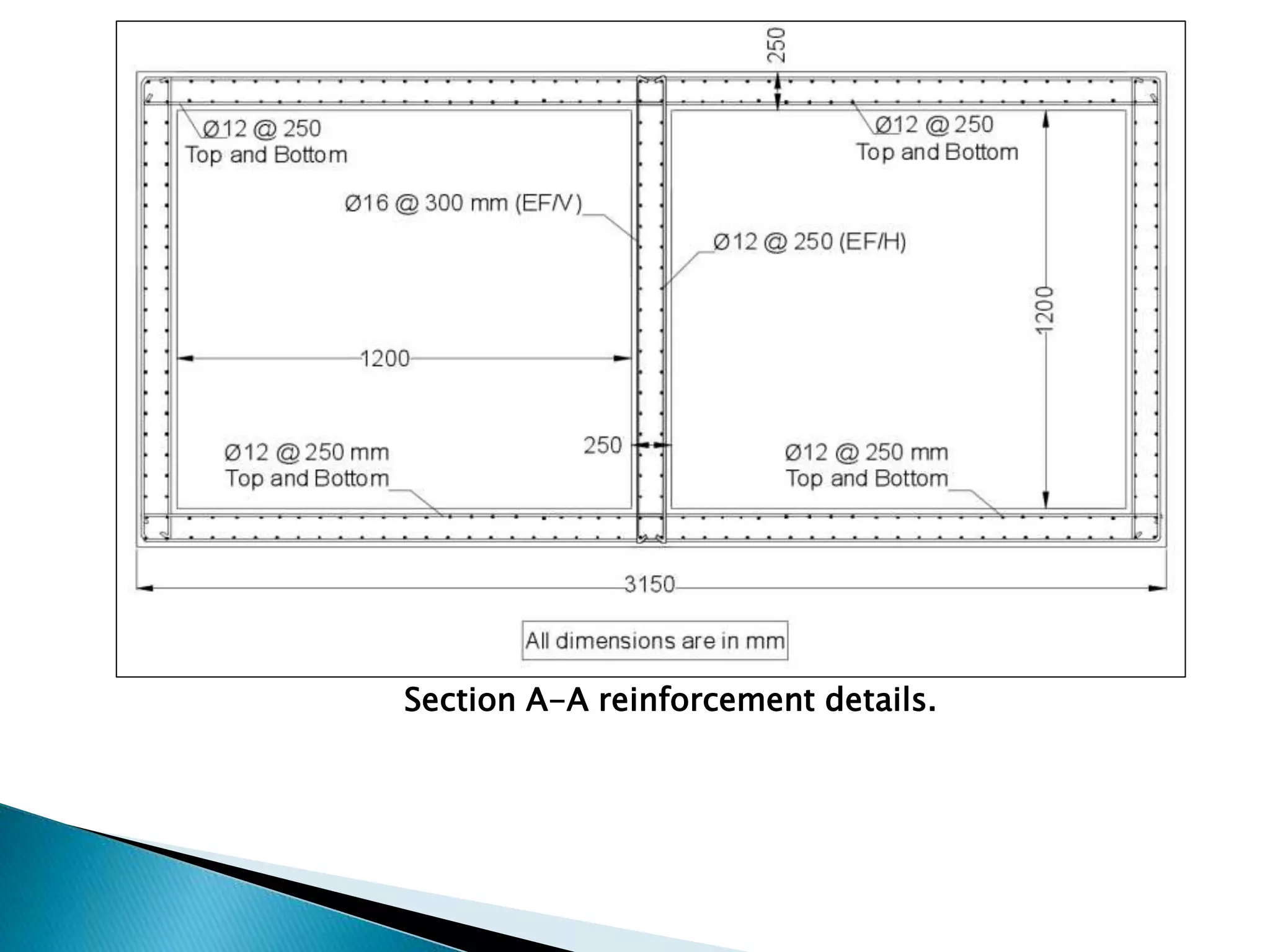
This document presents a summary of a presentation on analyzing and designing an RCC box culvert using ETABS. The presentation covers the objectives of determining loads, structurally designing the culvert, designing reinforcement, and analyzing the design in ETABS. It describes the culvert's design parameters from its hydraulic design and dimensions. It also details the typical reinforcement in the slab and walls. The conclusion recommends reinforcement sizes and validates the hand calculations with ETABS analysis results.