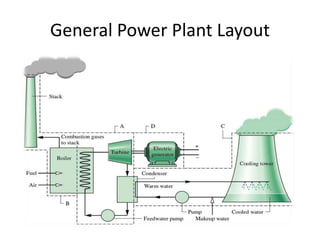
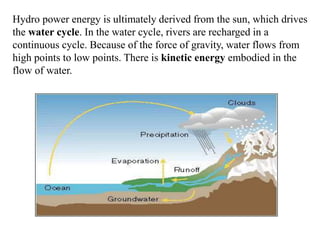
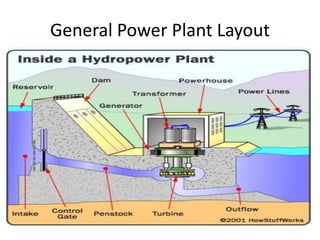
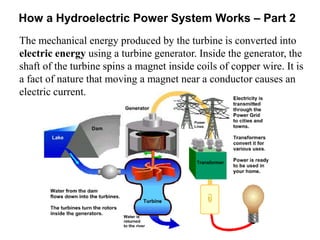
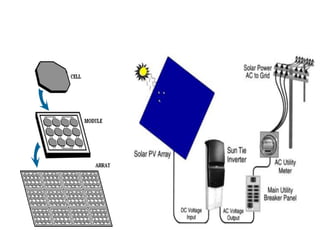
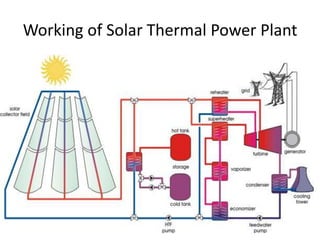
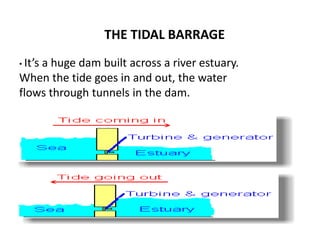
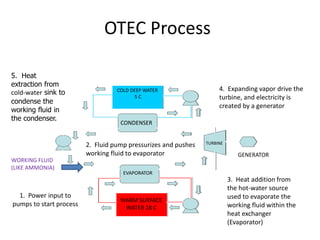
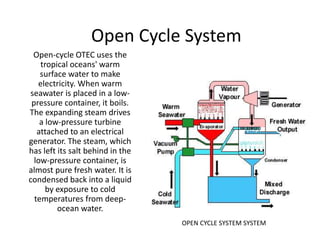
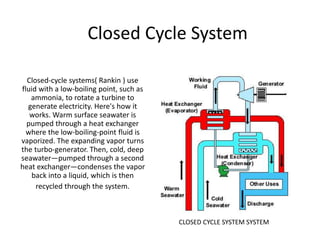
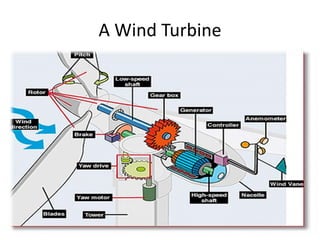
This document discusses different types of energy transformation technologies used in power plants, including thermal, hydro, solar, tidal, wind, and ocean thermal energy conversion. It provides details on the basic operations of thermal power plants, which convert heat from coal into steam to drive turbines and generators; hydroelectric plants, which use the kinetic energy of flowing water to drive turbines; solar photovoltaic and solar thermal plants, which convert sunlight into electricity; and wind farms, which use wind to drive turbines connected to generators. Diagrams illustrate the working principles of key components in these various energy transformation systems.