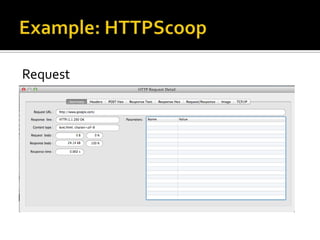
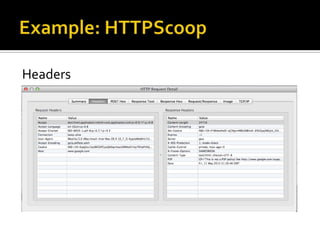
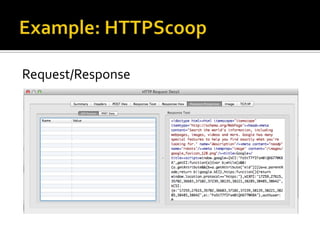
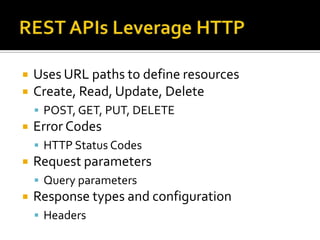
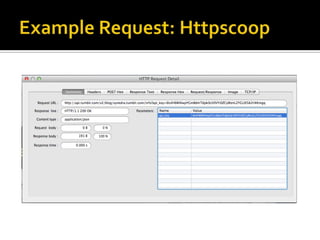
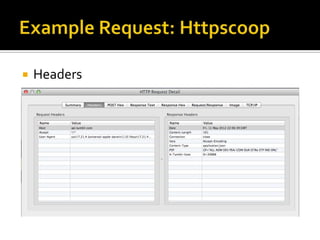
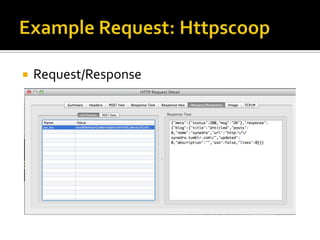
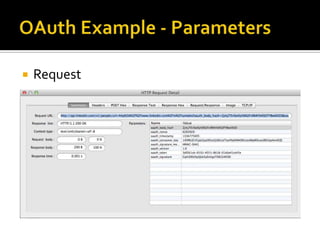
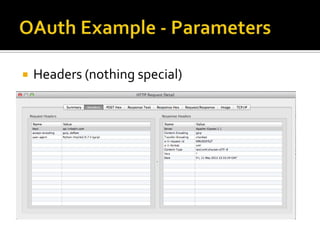
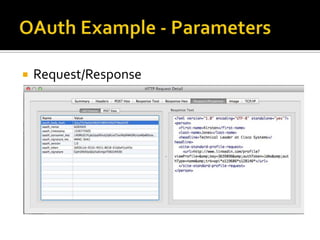
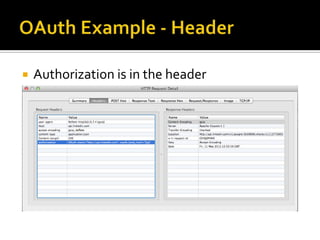
The document outlines the fundamentals of HTTP, REST web services, and OAuth authentication. It details how HTTP facilitates communication between web clients and servers via requests and responses, highlighting typical request headers and status codes. Additionally, it explains the OAuth process for securing API requests and managing user authentication and authorization.