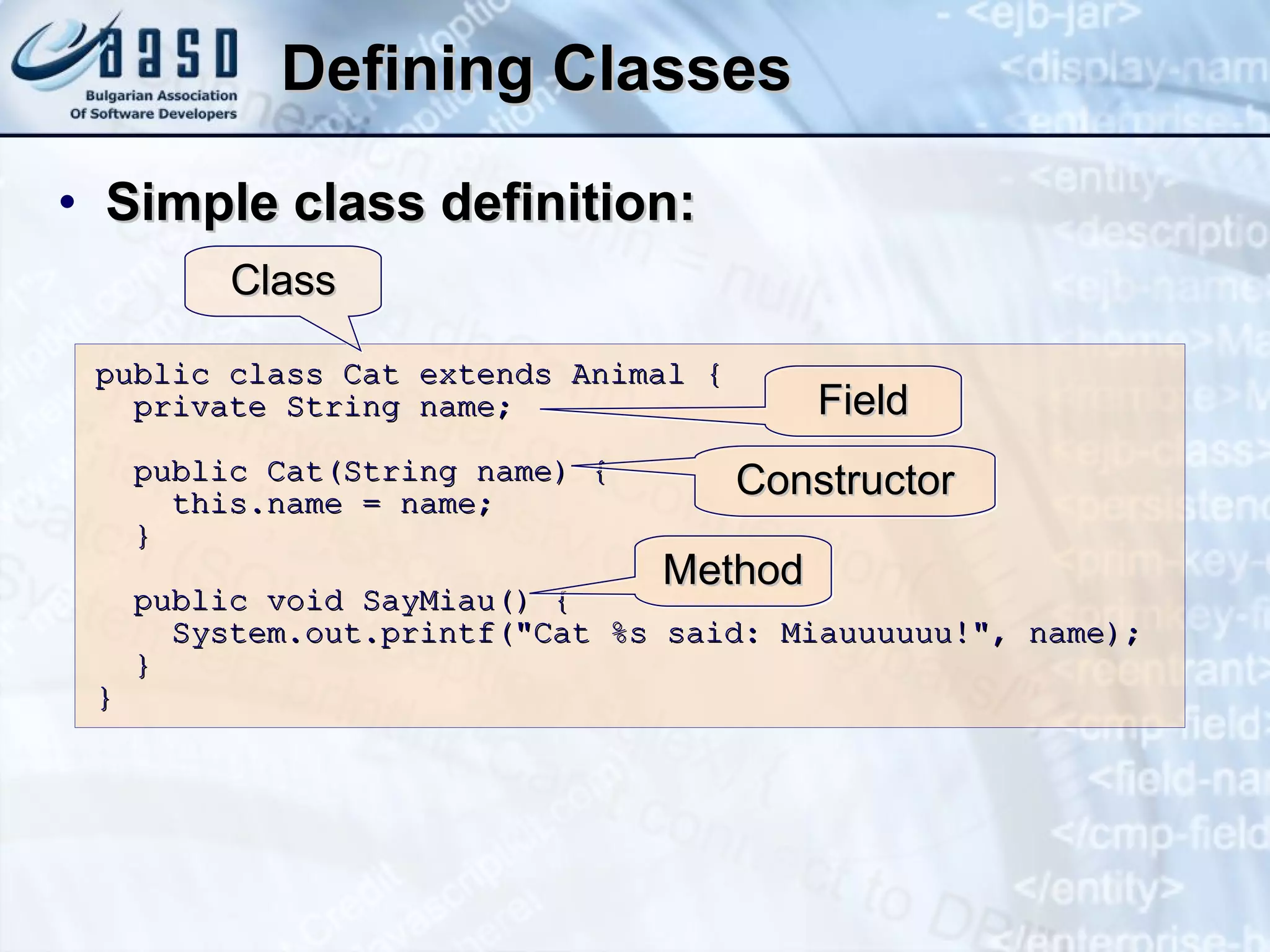
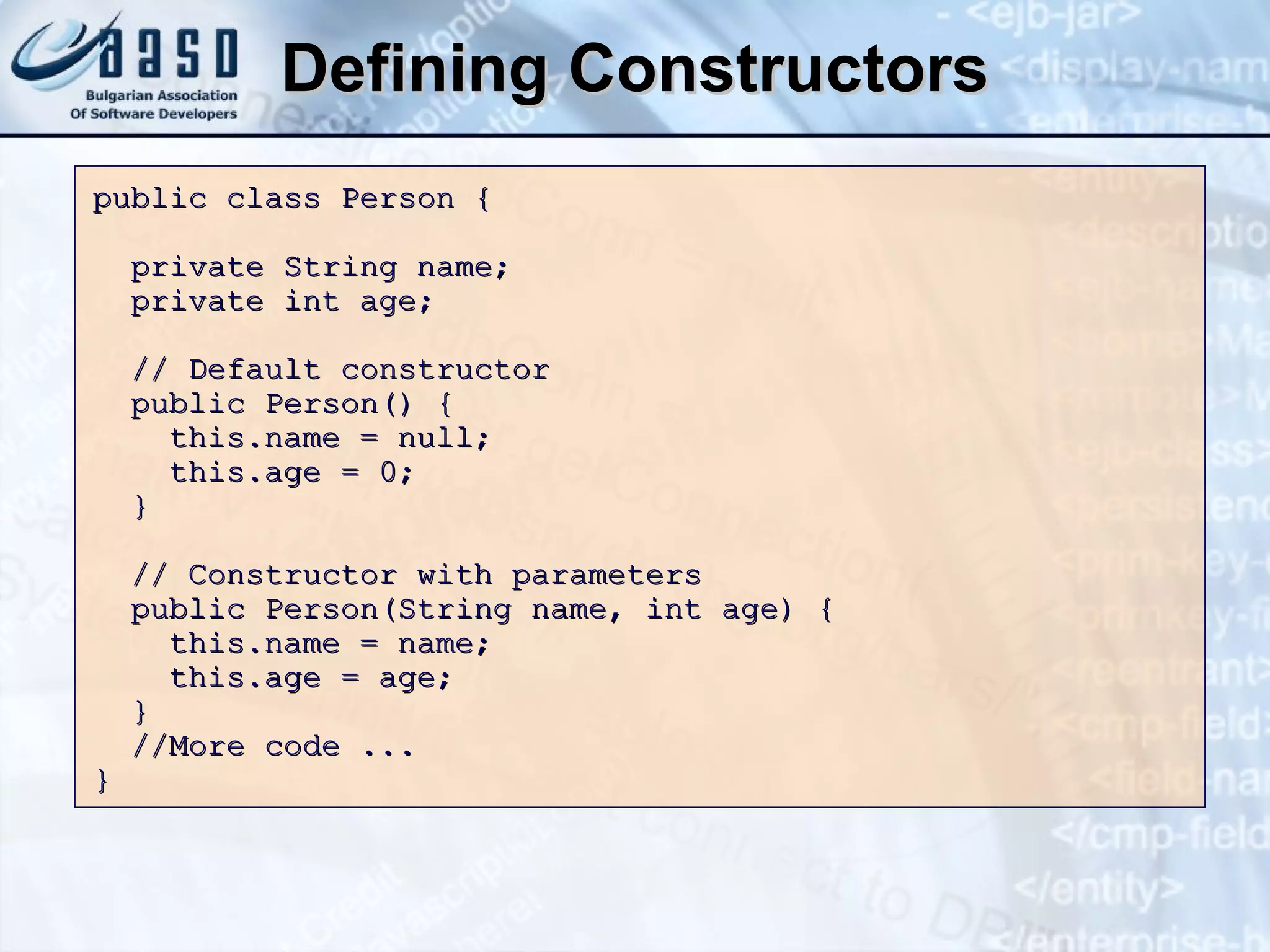
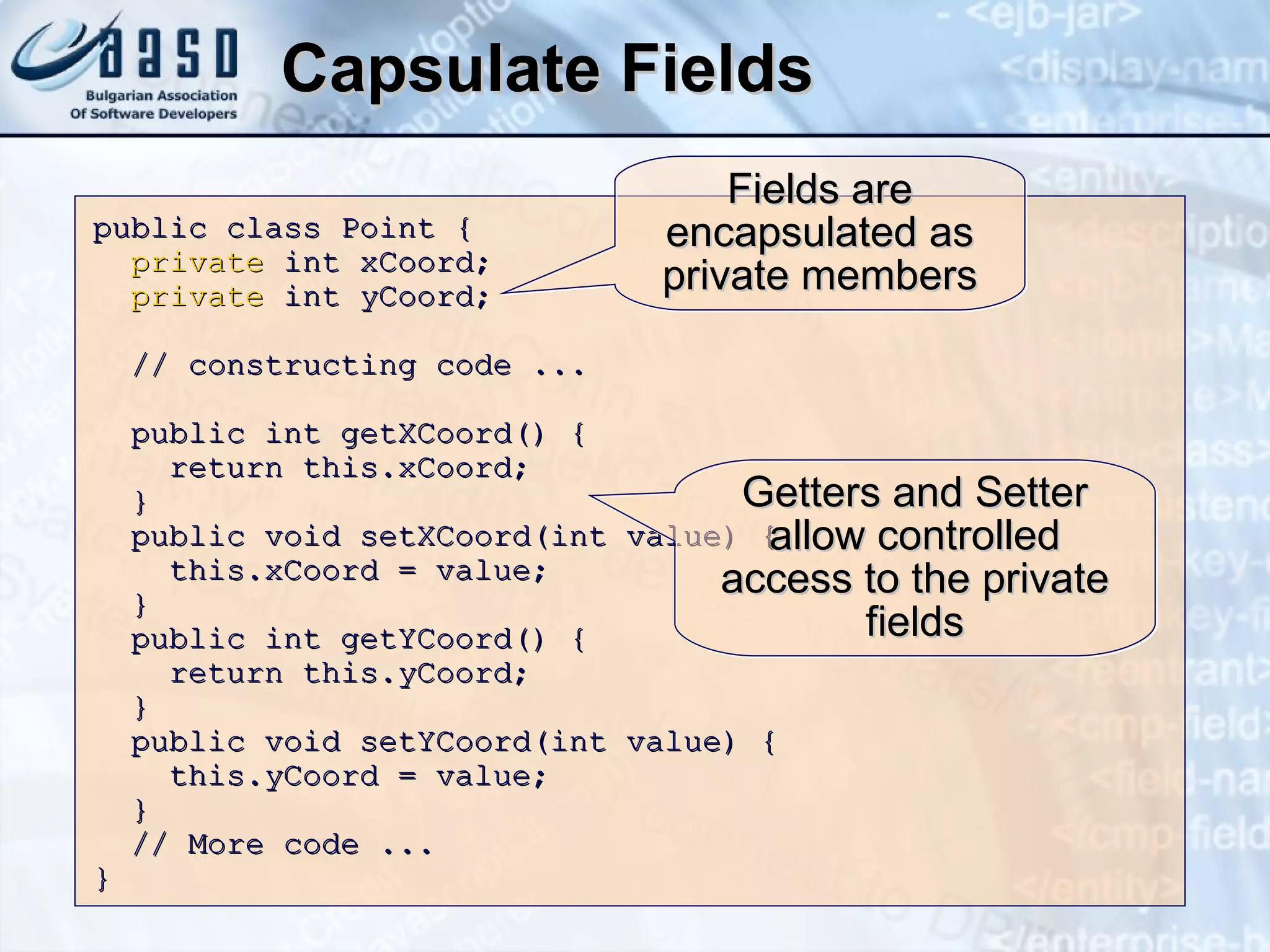
The document discusses defining classes and objects in Java. It covers defining simple classes, class elements like fields and methods, constructors, properties, static members, and using classes by creating instances and calling methods. Key points include classes define the structure of objects, constructors initialize object state, properties encapsulate fields, and static members are associated with a class not individual objects.








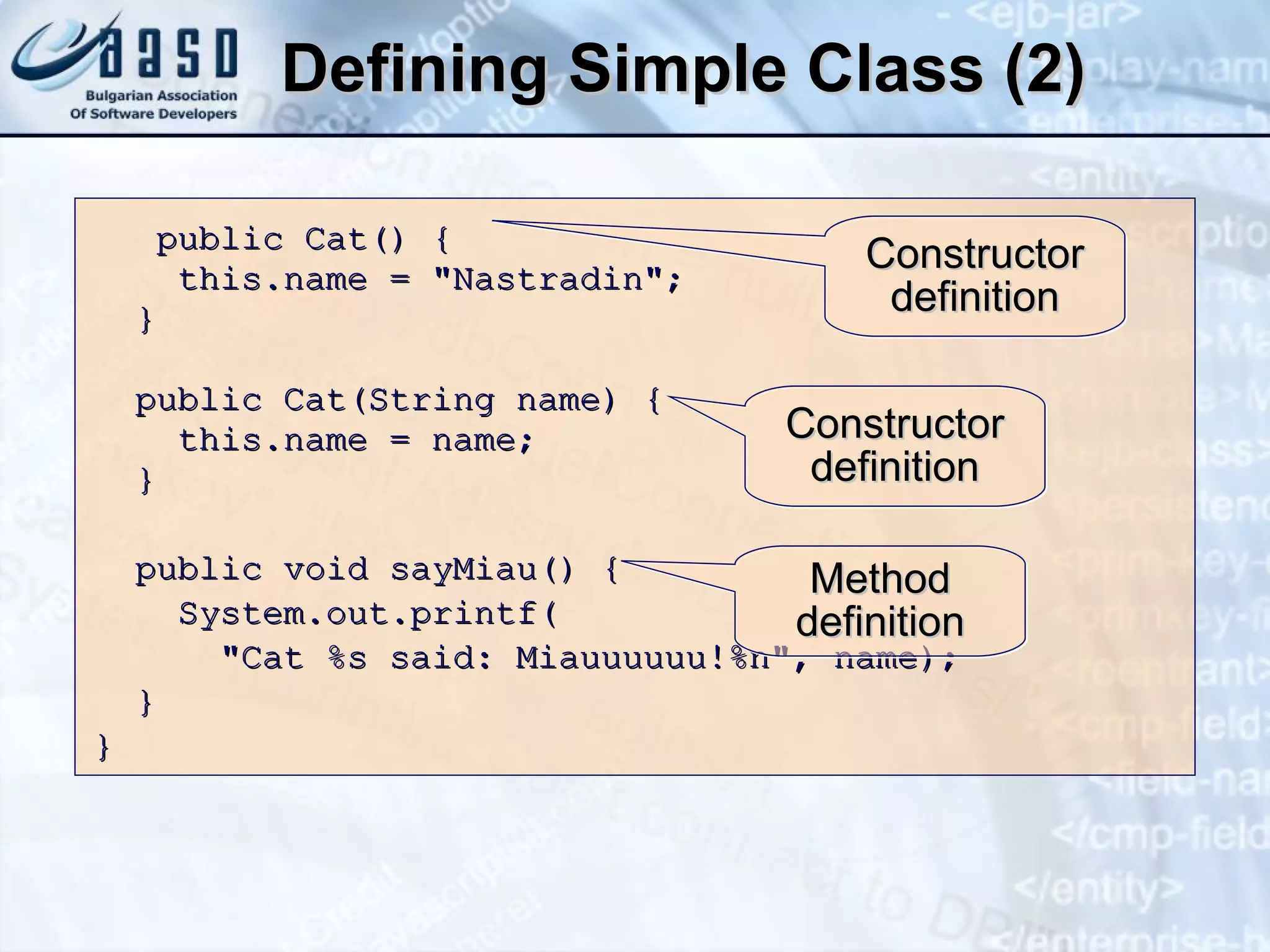





![Manipulating Class Instances public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Write first cat name: "); String firstCatName = input.nextLine(); // Assign cat name with a constructor Cat firstCat = new Cat(firstCatName); System.out.println("Write second cat name: "); Cat secondCat = new Cat(); // Assign cat name with a property secondCat.setName(input.nextLine()); // Create a cat with a default name Cat thirdCat = new Cat(); Sample task solution: // (The example continues on the next slide)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-101016130554-phpapp02/75/Defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-16-2048.jpg)
![Manipulating Class Instances (2) Cat[] cats = new Cat[] { firstCat, secondCat, thirdCat }; for(Cat cat : cats) { cat.SayMiau(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-101016130554-phpapp02/75/Defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-17-2048.jpg)


















![Static Members – Example public class Sequence { private static int currentValue = 0; private Sequence() { // Deny instantiation of this class } public static int nextValue() { currentValue++; return currentValue; } } public class TestSequence { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.printf("Sequence[1..3]: %d, %d, %d ", Sequence.nextValue(), Sequence.nextValue(), Sequence.nextValue()); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-101016130554-phpapp02/75/Defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-38-2048.jpg)

![Creating Static Methods public class Fraction { private int numerator; private int denominator; public Fraction(int num, int denom) { this.numerator = num; this.denominator = denom; } public static Fraction Parse( S tring val) { S tring[] parts = val. s plit( " / " ); int num = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]); int denom = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]); Fraction result = new Fraction(num, denom); return result; } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-101016130554-phpapp02/75/Defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-40-2048.jpg)
![Calling Static Methods Parsing custom type from string public static void main(String[] args) { String fractStr = "2/3"; try { fraction = Fraction.Parse (fractStr); System.out.println("fraction = " + fraction); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("Can not parse the fraction."); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-101016130554-phpapp02/75/Defining-classes-and-objects-1-0-41-2048.jpg)