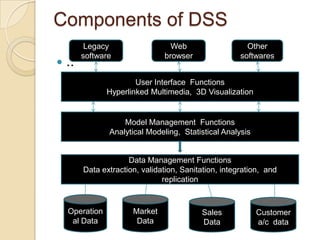
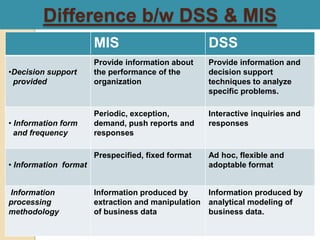
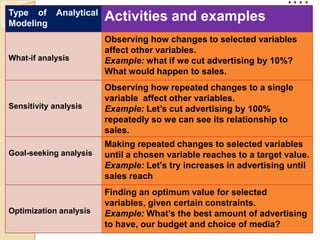
This document discusses decision support systems (DSS) and online analytical processing (OLAP). It defines DSS as interactive computer systems that help managers make decisions, using tools like analytical models, databases, and modeling processes. OLAP enables examining and manipulating large amounts of consolidated data from different perspectives. Both DSS and OLAP support analysis of operational data, markets, sales, and customers to help with decisions around pricing, forecasting, and risk.


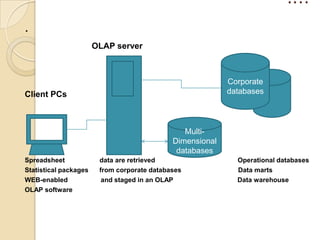
![Online Analytical Processing [OLAP]
OLAP enables managers to examine and
manipulate large amounts of detailed and
consolidated data from many perspectives.
OLAP involves analyzing complex
relationship among thousands or even
millions of data items stores in a data marts,
data warehouses and multidimensional
databases to discover patterns and trends
etc.
It provides fast answers to complex queries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionsupportsystem-121123112811-phpapp02/85/Decision-support-system-8-320.jpg)