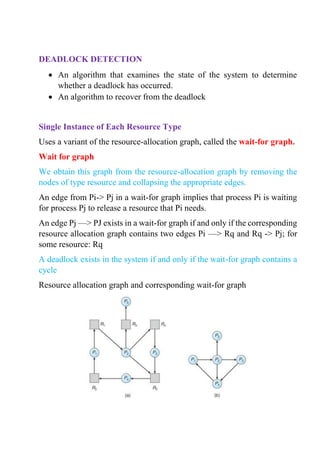
There are three main methods for dealing with deadlocks in an operating system: prevention, avoidance, and detection with recovery. Prevention ensures that the necessary conditions for deadlock cannot occur through restrictions on resource allocation. Avoidance uses additional information about future resource needs and requests to determine if allocating resources will lead to an unsafe state. Detection identifies when a deadlock has occurred, then recovery techniques like process termination or resource preemption are used to resolve it. No single approach is suitable for all resource types, so systems often combine methods by applying the optimal one to each resource class.


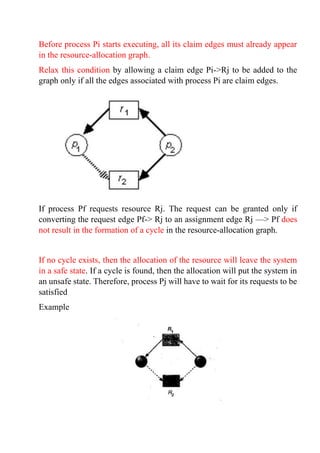
![BANKER'S ALGORITHM
The resource-allocation graph algorithm is not applicable to a resource
allocation system with multiple instances of each resource type
When a new process enters the system, it must declare the maximum
number of instances of each resource type that it may need.
This number may not exceed the total number of resources in the system.
When a user requests a set of resources the system-must determine whether
the allocation of the resources will leave the system in a safe state. If it will,
the resources are allocated; otherwise/the process must wait until some other
process releases enough resources
Let n be the number of processes in the system and m be the number of
resource types
Data structures
Available: A vector of length m indicates the number of available resources
of each type. If Available[j] = k, there are k instances of resource type Rj
available.
Max: An nx m matrix defines the maximum demand of each process. If
Max[i,j] - k, then P; may request at most k instances of resource type Rj.
Allocation: An n x m matrix defines the number of resources of each type
currently allocated to each process. If Allocation[i,j]= k, then process Pi- is
currently allocated k instances of resource type Rj.
Need: An n x m matrix indicates the remaining resource need of each
process. If Need[i,j] = k, then Pi may need k more instances of resource type
Rj to complete its task.
Note that Need[i,j] = Max[i,j] - Allocation[i,j].
SAFETY ALGORITHM
The algorithm for finding out whether or not a system is in a safe state can
be described as follows:
Steps of Algorithm:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-4-320.jpg)
![1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n respectively.
Initialize Work= Available and Finish[i] = false for i=1 to n
2. Find an index i such that both
a) Finish[i] == false
b) Needi<= Work
If no such i exists go to step 4.
3. Work= Work+ Allocationi
Finish[i]= true
Go to Step 2.
4. If Finish[i]== true for all i, then the system is in a safe state.
RESOURCE-REQUEST ALGORITHM
Let Request i be the request vector for process Pi. If Request[j] = k, then
process Pi, wants k instances of resource type Rj;. When a request for
resources is made by process Pi, the following actions are taken:
1. If Request i < Need i, go to step 2. Otherwise, raise an error condition,
since the process has exceeded its maximum claim.
2. If Requesti < Available, go to step 3. Otherwise, Pi, must wait, since the
resources are not available.
3. Have the system pretend to have allocated the requested resources to
process Pi by modifying the state as follows:
Available := Available – Request i
Allocation i := Allocation i + Request i
Need i= Need i — Request i
If the resulting resource-allocation state is safe, the transaction is completed
and process Pi is allocated its resources. However, if the new state is unsafe,
then Pi, must wait for Requesti and the old resource-allocation state is
restored](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-5-320.jpg)
![Example
Consider a system with five processes P0 through P5 and three resource
types A [10 instances], B [5 instances] and C [7 instances] time T0, the
following snapshot of the system has been taken:
Need = Max-allocation
System is in safe state <P1, P3, P4, P2, P0>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-6-320.jpg)

![Several Instances of a Resource Type
The wait-for graph scheme is not applicable to a resource-allocation system
with multiple instances of each resource type
DEADLOCK DETECTION ALGORITHM
Data structures used by deadlock detection algorithm
Available: A vector of length m indicates the number of available resources
of each type.
Allocation: An n x m matrix defines the number of resources of each type
currently allocated to each process
Request: An n x m matrix indicates the current request of each process. If
Request[i,j] = k, then process Pi is requesting k more instances of resource
type Rj.
ALGORITHM
1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n respectively. Initialize
Work= Available. For i=0, 1, …., n-1, if Requesti = 0, then Finish[i] = true;
otherwise, Finish[i]= false.
2. Find an index i such that both
a. Finish[i] = false.
b. Requesti < Work.
If no such i exists, go to step 4.
3. Work := Work + Allocation^
Finish[i] := true
go to step 2.
4.If Finish[i]== false for some i, 1<=i<n, then the system is in a deadlocked
state. Moreover, if Finish[i]==false the process Pi is deadlocked.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-9-320.jpg)
![Example
Five processes P1through P4 and three resource types A, B, C.
Resource type A has 7 instances, resource type B has 2 instances, and
resource type C has 6 instances
At time T0
The sequence <Po, P2,P3,P1,P4> will result in Finish[i] = true for all i.
Suppose now that process P2 makes one additional request for an instance
of type C
Modified Request Matrix
The system is now deadlocked consisting of the resources P1,P2,P3 and
P4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-10-320.jpg)














![Solution of Dining Philosophers Problem
A solution of the Dining Philosophers Problem is to use a semaphore to
represent a chopstick. A chopstick can be picked up by executing a wait
operation on the semaphore and released by executing a signal semaphore.
The structure of the chopstick is shown below
semaphore chopstick [5];
Initially the elements of the chopstick are initialized to 1 as the chopsticks
are on the table and not picked up by a philosopher.
The structure of a random philosopher i is given as follows −
do {
wait(chopstick[i] );
wait(chopstick[ (i+1) % 5] );
. .
. EATING THE RICE
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-25-320.jpg)
![signal( chopstick[i] );
signal( chopstick[ (i+1) % 5] );
.
. THINKING
.
} while(1);
In the above structure, first wait operation is performed on chopstick[i] and
chopstick[ (i+1) % 5]. This means that the philosopher i has picked up the
chopsticks on his sides. Then the eating function is performed.
After that, signal operation is performed on chopstick[i] and
chopstick[ (i+1) % 5]. This means that the philosopher i has eaten and put
down the chopsticks on his sides. Then the philosopher goes back to
thinking.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlockavoidance-os-220106143405/85/Deadlock-Avoidance-OS-26-320.jpg)


