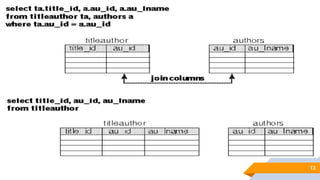
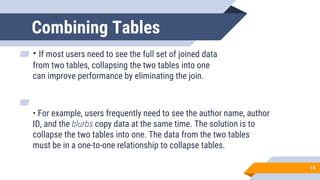
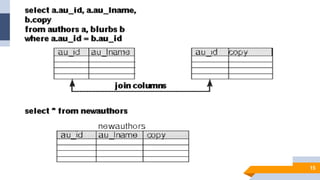
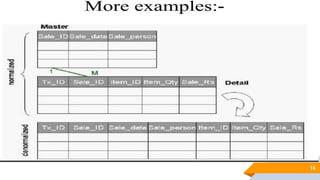
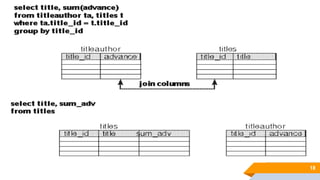
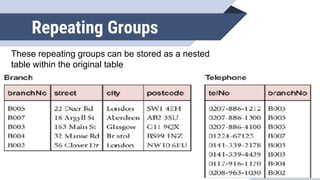
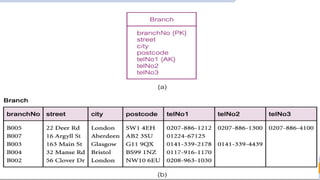
The document discusses de normalization, defined as the process of modifying a normalized database to allow controlled redundancy for improved performance. It outlines when to de normalize, methods for doing so, and highlights the advantages and disadvantages of this approach. While de normalization can enhance data retrieval speed and reduce complexity, it also carries risks such as increased storage requirements and potential integrity issues.