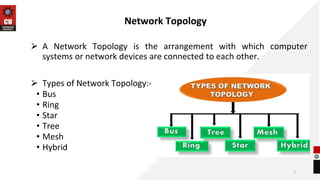
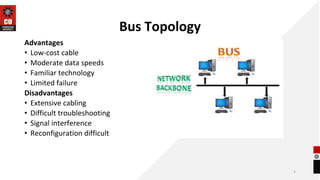
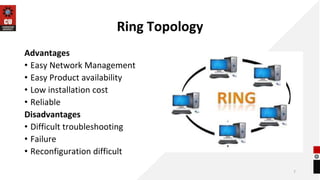
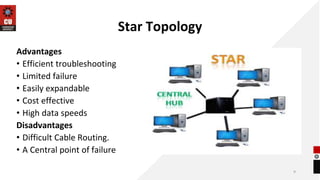
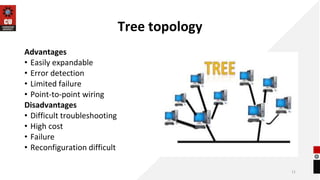
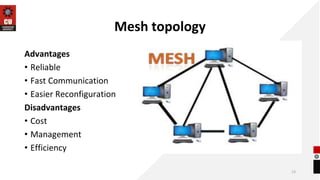
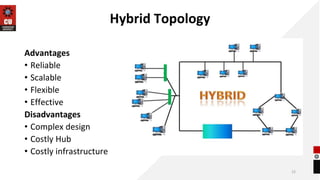
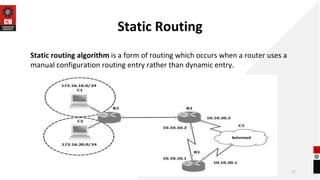
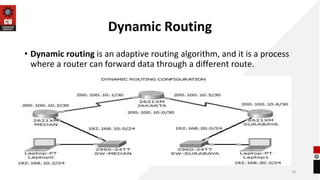
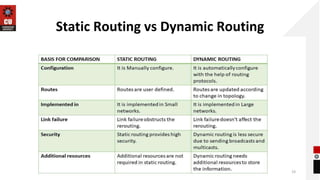
The document discusses network topologies and router configuration. It covers different network topologies like bus, ring, star, tree, mesh, and hybrid and describes their characteristics and advantages/disadvantages. It also discusses static and dynamic routing and how routers are configured for static and dynamic routing. The document aims to help students understand different network topologies and how to determine the appropriate one for different environments as well as the basics of router configuration.