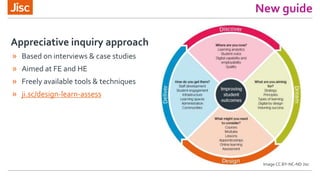
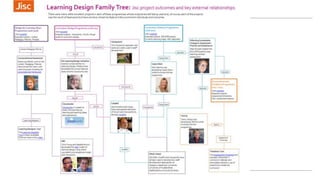
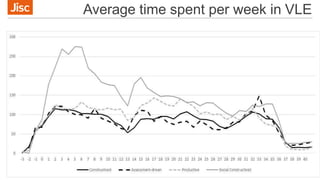
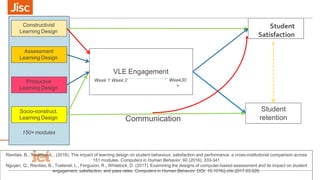
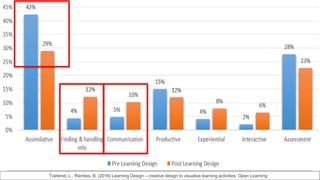
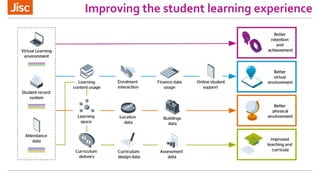
This document summarizes a workshop on using data to inform blended learning design. The workshop covered learning design principles and techniques, introduced a new guide on freely available tools and techniques, and discussed how institutions currently approach learning design and use data. Participants worked through examples of relating learning analytics data to evaluating and improving learning design. The workshop aimed to help participants apply data more purposefully to answer questions about students' experience and progress through a course.