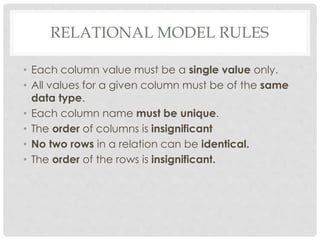
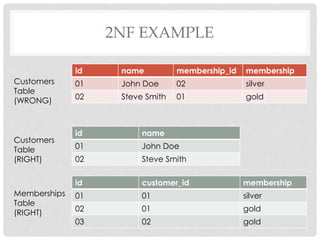
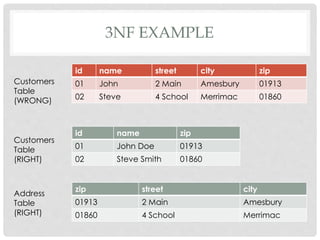
The document discusses database design principles when using MySQL. It covers relational model rules, functional dependencies, common design mistakes, and database normalization. Normalization is the process of organizing fields and tables to minimize redundancy and dependency. It involves dividing large tables and defining relationships between smaller tables. The objectives are to isolate data so that changes can propagate between related tables. Three forms of normalization are covered - first normal form eliminates repeating groups, second normal form removes partial dependencies, and third normal form removes non-key dependencies. Examples are provided to illustrate each normalization form.