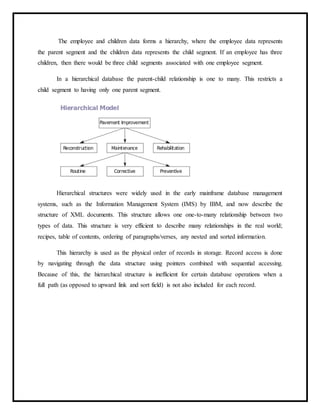
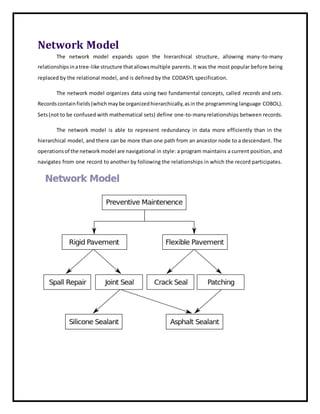
The document provides an overview of database models, describing how databases are organized for efficient data storage and retrieval. It explains various data models including hierarchical, network, relational, object-oriented, dimensional, and entity-relationship models, outlining their structures and relationships. Each model offers different methods for managing data and is suited for specific applications, illustrating the evolution and complexity of database management systems.