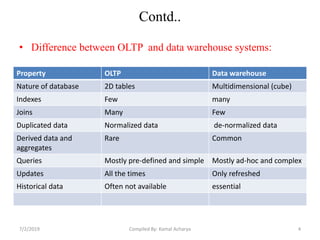
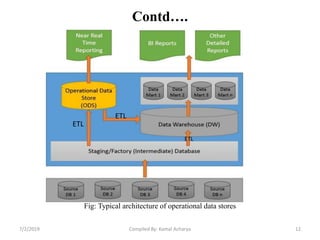
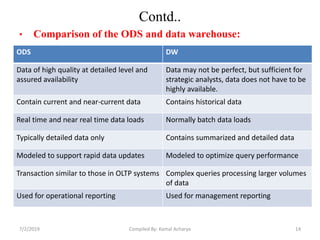
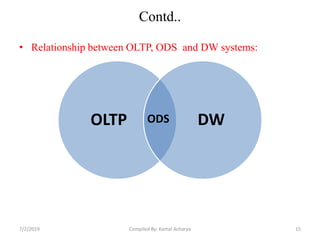
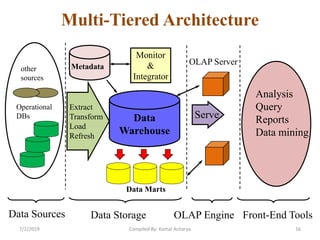
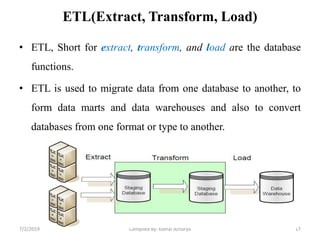
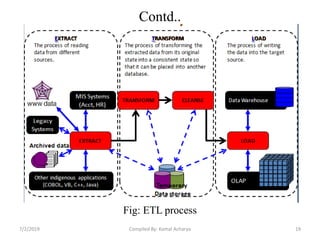
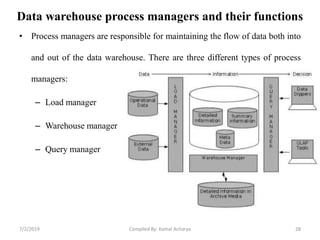
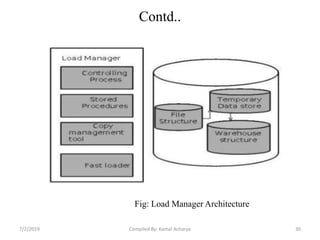
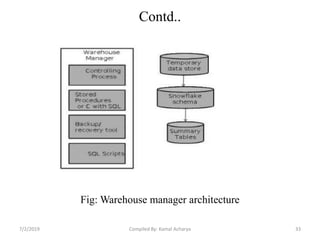
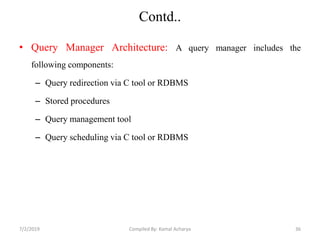
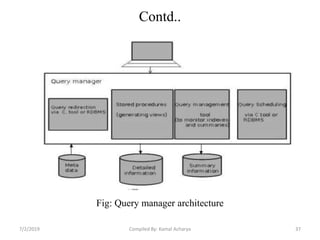
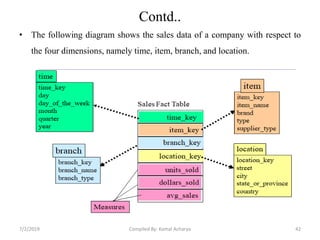
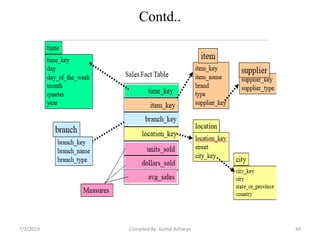
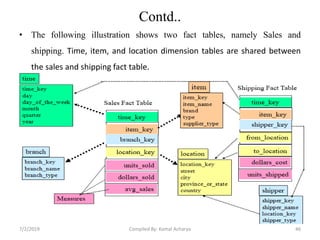
Data warehousing involves assembling and managing data from various sources to provide an integrated view of enterprise information. A data warehouse contains consolidated, historical data used to support management decision making. It differs from operational databases by containing aggregated, non-volatile data optimized for queries rather than updates. The extract, transform, load (ETL) process migrates data from source systems to the warehouse, transforming it as needed. Process managers oversee loading, maintaining, and querying the warehouse data.